Chemical Bonds and Compounds: Exploring Unity in Diversity
290 likes | 402 Vues
Explore how compounds form from atoms combining, represented by chemical formulas. Discover the similarities between how skydivers stay together and atoms bonding, shaping compound properties. See how ions interact to create ionic bonds and name resulting compounds. Unravel the mystery behind covalent bonding and its impact on molecular structure. Understand the essence of chemical bonds as the glue that holds elements together.

Chemical Bonds and Compounds: Exploring Unity in Diversity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 6Chemical Bonds and Compounds “Come Together” By John Lennon YouTube - John Lennon - Come Together (The Beatles Cover)
How do these skydivers stay together? How is this similar to the way atoms stay together?
Objectives: • Describe how compounds are made from combinations of atoms. • Explain how chemical formulas represent chemical compounds.
Section 6.1 • If we look at all the different things around us it is easy to see that everything is not an element. But we also know that there are just over 100 different elements and they make up millions of different substances. • How many letters in the alphabet? • How many words are made from those 26 letters? • Atoms are held together in compounds by chemical bonds.
Bonds determine the properties of a compound. • Many times the properties of compounds are often different from the properties that make them. • EXAMPLE + = CALCIUM CHLORIDE CALCIUM CHLORINE
CALCIUM ~ A GROUP 2 ALKALINE EARTH METAL (soft, silvery metallic solid) • CHLORINE ~ A HALOGEN is a greenish gas very poisonous to humans • These two come together to form a product we use to melt ice that forms on streets and sidewalks. • It was one of the powders in the “Baggie Blast” experiment we did a couple of weeks ago.
In every family the number of males to females varies. In my family there are 3 females to 2 males. Me, mom and my sister THE GIRLS. Dad and my brother THE BOYS. So there is a 3:2 ratio of females to males.
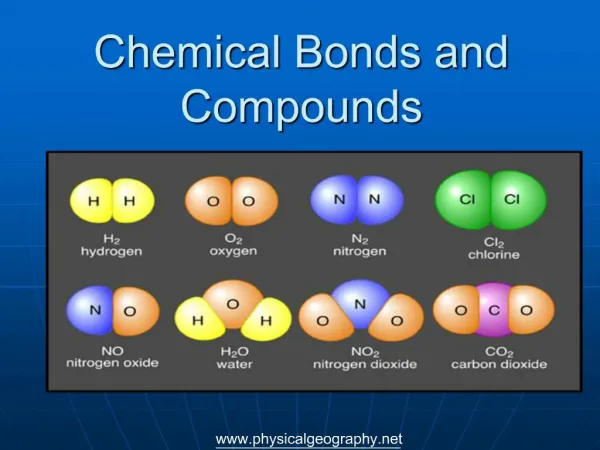
Atoms always combine in predictable numbers • For example NH3 is ammonia. The compound ammonia always has three hydrogen atoms for every nitrogen atom.
Chemical formulas • Chemical formulas use chemical symbols to represent the atoms of the elements and their ratios. C O 2
This chart shows the names, atoms, ratios and chemical formulas for several chemical compounds. Notice methane and propane are made from atoms of the same elements but in different ratios. Two totally different substances……… Propane in the tank on your grill and methane given off when cows BURP!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Same elements, different compounds Which one would you want to drink? or
Review • How many different atoms are in C12H22O11? 12 carbon atoms + 22 hydrogen atoms 11 oxygen atoms = 45 total atoms • How do properties of compounds compare with the elements that make them? • Most of the time VERY different
If a chemical formula has no subscripts, for example CO (carbon monoxide) What is the ratio of the atoms? 1 to 1
If CO2 is carbon dioxide then is H2O Dihydrogen monoxide? No silly teacher H2O is water!!!!!!!!!
Section 2objectives • Explain how electrons are involved in chemical bonding. • Describe what the different types of chemical bonds are. • Determine how chemical bonds affect structure.
What are some different ways workers connect materials? Hearst Bld NYC Look for it in a new movie Glue Nails screws
Chemical bonds between atoms involve electrons • Chemical bonds are the “glue” that holds atoms of elements together • Chemical bonds have an effect on the chemical and physical properties of compounds
Transfer Please!!!!!!!! • When a college student needs money to cover rent and other needs they call mom and dad and ask them to transfer money to their checking account. Mom or dad calls the bank and says they want to transfer money to little Johnny’s account.
A similar thing happens when the atom of a metal transfers an electron to the atom of a nonmetal.
Ionic bond: the force of attraction between positive and negative ions • Example: an atom from Group 1, like sodium (Na) forms a positive ion Na+ & meets an atom from Group 17 (a Halogen) chlorine (Cl) forms a negative ion Cl- the bond forms is ionic. NaCl is table salt. • Just like opposite ends of a magnet attract~~~~ these oppositely charged ions attract each other.
So how we name these monsters? • Name the positive metal element~ example sodium (Na) • Next take the name of the negative, nonmetal element, chlorine (Cl) and give it the ending –ide chloride • Now combine the two names making that monster’s name sodium chloride. We just call it salt!!!!
Let’s try some more! • What would lithium and iodine be called? • What about sodium and fluorine? • And calcium and chlorine? • Wow that is amazing YOU just learned to name ionic compounds!!!!!!!!!!!
Salts are formed from the positive ion of a metal and negative ion of a nonmetal. • Not all salts are the kind we put on our French fries. That is NaCl. • Calcium chloride CaCl2 is put on roads and sidewalks to melt snow and ice. • The metal ion in salts give off a characteristic flame color as you saw in the lady liberty fireworks site. • http://www.driveaway.com/lady_liberty/liberty_dl.htm
When 2 girls share the responsibilities of being head cheerleader what do we call them? • They are co-head cheerleaders. • When atoms share electrons in bonding we call this covalent bonding. • The electrons spend as much time around one atom as they do the other atom. They zip back and forth between atoms. • Some common substances held together by covalent bonds are: carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and several elements exist covalently bonded to themselves. H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, & I2.
Polar covalent bonds • A covalent bond in which the bonds are shared unequally. • Water is a perfect of example of a polar covalent bond. That is why water is a good solvent and we take a bath in it!! It has both positive and negative parts.
Review section 2 • What part of an atom is involved in bonding? The electron cloud (i.e. valence electrons) • Compare ionic and covalent bonds. See posters A polar covalent bond forms when? Two atoms share electrons unequally
Section 3 Substances’ properties depend on their bonds • Metals have unique bonds. They slide easily past each other giving metals their useful qualities (ie malleable, ductile, shiny and good conductors) • Ionic and covalent bonds give compounds certain properties (comparison demo of salt and PDC) Ductile??
copper graphite fragment diamond fragment Bonds can make elements look different.
Review What are the three forms of carbon? Diamond, graphite, and fullerene Metallic bonds make many metals good what? Good conductors of electricity