Pedigree Charts
240 likes | 788 Vues
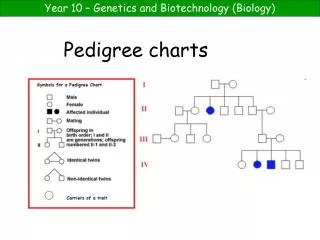
Pedigree Charts. The family tree of genetics. What is a Pedigree?. A pedigree is a chart of the genetic history of family over several generations. Scientists or a genetic counselor would find out about your family history and make this chart to analyze. Constructing a Pedigree. Male.

Pedigree Charts
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pedigree Charts The family tree of genetics
What is a Pedigree? • A pedigree is a chart of the genetic history of family over several generations. • Scientists or a genetic counselor would find out about your family history and make this chart to analyze.
Constructing a Pedigree • Male • Female
Connecting Pedigree Symbols • Married Couple/ couple with children • Siblings Examples of connected symbols:
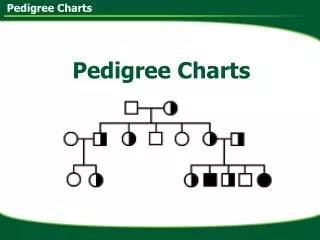
Example • What does a pedigree chart look like?
Example of Pedigree Charts • The Shaded means that person has that trait
Interpreting a Pedigree Chart • Determine whether the trait is dominant or recessive. (remember: the dominant traits shows if there is one or two, the recessive shows only if there are two) • If the trait is dominant, one of the parents must have the trait. • If the trait is recessive, neither parent has to have the trait because they can be heterozygous.
Heterozygous vs. Homozygous • Remember that an offspring gets one allele for a trait from each parent – that’s 2 alleles • If the alleles are the same, we say that offspring is homozygous – the same • If the alleles are different, we say the offspring is heterozygous – different
Hetero & Homo zygous display • An example: If the offspring has the dominant trait for tallness (T) from one parent and the recessive trait (t) from the other, then their genotype is Tt and they are heterozygous. (They are still tall) • Some pedigrees split their circles and squares into two and shade them according to whether the individual is heterozygous or homozygous.
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT INHERITANCE Approximately a 1:1 ratio of affected vs. unaffected progeny with one affected parent. Transmission can occur from affected father to affected son. Direct transmission from an affected parent to an affected child. (Affected children always have an affected parent.)
DOMINANT DISEASE Huntington’s Disease • Woody Guthrie • Arlo Guthrie • Children Lobster Foot Dominant allele -- you have the disease or you don’t
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE INHERITANCE Affected parents can have affected offspring. However, affected children typically do not have affected parents. Affected individuals can be either male or female.
RECESSIVE DISEASE • Albinism • Achondroplasia • Both parents can be carriers to have an affected child • 2 affected parents will usually produce an affected child
Example of Pedigree Charts • Dominant or Recessive? (Many or Few?)
Example of Pedigree Charts • Dominant or Recessive? (Many or Few?)
More affected males than females. Affected grand-father to grand-son thru carrier female. SEX-LINKED RECESSIVE TRAITS Females do not manifest the disorder.
Example of Pedigree Charts • Autosomal or Sex-Linked? (Males/Females)
Example of Pedigree Charts • Autosomal or Sex-Linked? (Males/Females)
Summary • Pedigrees are family trees that explain your genetic history. • Pedigrees are used to find out the probability of a child having a certain trait in a particular family.
Bent Pinky Dimples Hand Fold PTC Tasting Widow’s Peak Mid-digital hair Short Hallux (Big Toe) Finger Length Bent Little Finger Autosomal Dominant
Hitchhiker’s Thumb Attached Earlobe Unattached Earlobe Ear Wax Ear Diagram Tongue Roll Tongue Flip Tongue Fold
Examples sex-linked recessive traits: COLOR BLINDNESS