NUCLEAR MEDICINE
100 likes | 660 Vues
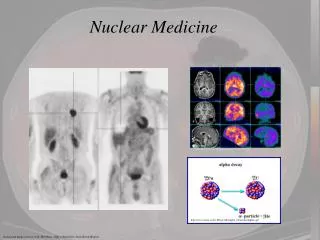
NUCLEAR MEDICINE. NUCLEAR MEDICINE. High Energy Photon Ionizing Radiation --Radiopharmaceutical Exposes Detector Projection Data Dynamic / Physiologic. Here we have an example of a nuclear medicine bone scan with anterior and posterior views.

NUCLEAR MEDICINE
E N D
Presentation Transcript
NUCLEAR MEDICINE • High Energy Photon • Ionizing Radiation --Radiopharmaceutical • Exposes Detector • Projection Data • Dynamic / Physiologic Here we have an example of a nuclear medicine bone scan with anterior and posterior views.
This branch of radiology uses radioisotopes for imaging. The radioisotopes produce gamma-rays that are emitted by the patient following intravenous injection of the isotope. The rays are detected by a gamma camera. Radioisotope investigation allows the assessment of function as well as structure. The commonest radioisotope used is technetium, which has a half-life of 6 h.
Common radioisotope investigations • Bone scan - Tc phosphonate to look for metastases • Lung ventilation - Tc DTPA aerosol, krypton gas • Lung perfusion - Tc micro-aggregate albumin to assess perfusion • ventilation/perfusion scans for investigation of pulmonary emboli • Cardiovascular - thallium scanning to look for cardiac perfusion abnormalities • Thyroid - iodine or technetium to assess thyroid function/nodules
With Nuclear Medicine a radioactive drug is administered, a pharmaceutical portion of the drug has been created to localize to a type of tissue. • The radioactive tag of the pharmaceutical serves to identify the site of accumulation. • The detector or gamma camera which is similar to a Geiger Counter measures the radiation distribution and maps it to a region.
NUCLEAR MEDICINE EXAMPLES • Bone • PET scan • Liver
RISK FACTORS • Use ionizing radiation that is known to damage cells. • Cancer risk