Pineapple Enzyme Lab: Impact on Gelatin Consistency
120 likes | 184 Vues
Explore how different pineapple types affect gelatin in this experiment testing bromelain's effect. Learn about anabolism and catabolism in gelatin.

Pineapple Enzyme Lab: Impact on Gelatin Consistency
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Background Information: Ask an expert. • Gelatin makes Jello a semi-solid. 1845 • Gelatin comes from bones and cartilage from pigs and cows • Enzyme Bromelain is in Pineapple • Vitamin C is a co-enzyme to Bromelain • Bromelain helps relieve pain in arthritis. • Bromelain breaks down mucus and helps those with arthritis and bronchus
Investigative Question: How do different types of pineapple affect gelatin? Hypothesis: If pineapple is put into gelatin, then ________ LABEL YOUR LAB BOOK!
Enzymes are Protein catalyst (starter) for chemical reactions cut (Catabolism) or add (Anabolism) substances in cells.
Anabolism: Catabolism in Jello • Anabolism: Starch (Carbohydrates) in the gelatin get thicker as it cools. • 0 + 0 + 0 = 000 • Catabolism: Bromelain (protein) in pineapple break the solution apart: (prevent it from getting thick. • 000 + Protein Enzyme = 0 + 0 + 0 +
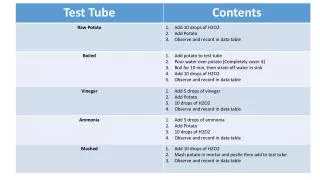
Procedure • Get 4 Dixie cups and label each with tape * fresh * canned * no pineapple 2. Put 2 pieces (about the same amount) of each type of pineapple different Cups. 3. Take the Dixie cup to the gelatin and pour enough to cover the pineapple 4. Only pour gelatin into Dixie Cup # 4.
Variables • Control Group: No pineapple, just gelation • (Check to see if there is something else making changes in the gelation) Manipulative Variables: fresh and frozen pineapple, other Responding Variable: What happens to the gelation Experimental Controls: Same pineapple, same temperature, same gelation, same ___ same____
5. Put the cups in a pan of ice with the ice to the Top level of the gelatin/pineapple. 6. Let the Dixie cups sit in ice for up to 10 minutes checking the control every 2 minutes by swirling or stirring the Dixie cups. 7. Record observations on a data table. 8. When finished, pour semi-solid mixtures into waste beaker - NOT DOWN THE DRAIN! 9. Clean lab thoroughly. 10. Observe other groups work. Record findings
Variables • Experimental (one tested to) Variable 1: • Responding (results) Variable: • Experimental Controls: (same/same)
Analysis Questions: • Describe the differences between Cups. • What was it like when you started and at the end? • Does the pineapple enzyme Bromelainbreakdown (catabolism) or build (anabolism) proteins? • After looking at the data, what is the best explanation for the results of experiment? • How could you increase validity. • How could you increase reliability?
Conclusion • Answer to the investigative question. • Data to support the answer to the investigative question. • Address any trends you see in the data. (What happened?) • Explain why the trend in data occurred.