Urinary System and its Functions
160 likes | 249 Vues
Learn about the urinary system - the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and their vital roles in maintaining water balance, electrolytes, pH, and more. Understand urine formation, filtration, and other key processes. Explore renal function tests and the importance of maintaining a healthy urinary system.

Urinary System and its Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Urinary System Dr. Manodeep Chakraborty
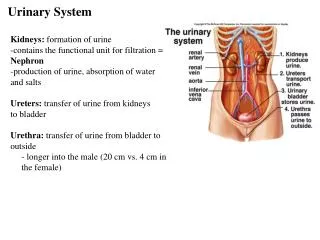
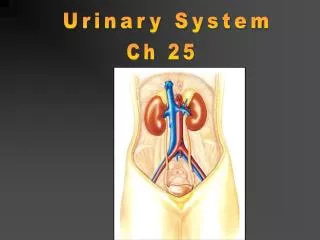
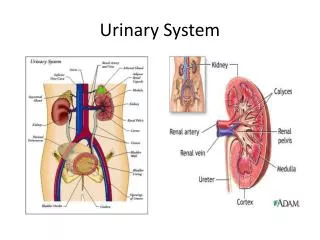
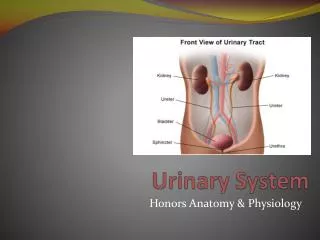
Urinary system is the main excretory system and consists of following structures • Kidneys (2) : Secretes urine • Ureters (2) : Convey the urine from the kidneys to urinary bladder • Urinary bladder : Where the urine collects and is temporarily stored • Urethra : Through which the urine is discharged from the urinay bladder to the exterior
Kidneys • Organs associated with the kidney • Right kidney • Left Kidney • Gross structures of the kidney • Microscopic structure of the kidney
Nephron • Glomerular capsule • Proximal Convoluted tubule • Henle’s loop • Distal convuluted tubule • Collecting tubules • Duct of bellini
Functions of Kidney • Formation of urine • Maintains water balance, urine output, osmotic pressure by ADH • Plays an important role in electrolyte balance • Maintains pH balance • Extra cellular fluid volume • Regulation of blood volume • Regulation of erythropoiesis • Regulation of blood pressure
Formation of Urine • Composition • H2O – 96 % • Urea – 2% • Uric acid • Creatinine • NH4+, Na+, K+, Cl-, Po4-, So4-, oxalates – 2% • Hippuric acid • Citrate, ketobodies
Include 3 process • Filtration • Selective reabsorption • Secretion
Acid Base Balance • Buffer system • Carbonic acid bicarbonate HCl + NaHCO3 NaCl + H2CO3 NaOH + H2CO3 NaHCO3 + H2O • Phosphate buffer NaOH + NaH2PO4 H2O + Na2HPO4 HCl + Na2HPO4 NaCl + NaH2PO4 • Haemoglobin-oxyhaemoglobin • Respiration CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ +CO3- • Kidney excretion
Micturition • Micturition is the physiological process of passing urine
Renal function tests • Glomerular function tests or clearance tests Insulin clearance test Creatinin clearance test Urea Clearance test • Tubular function tests Urea Concentration Urine acidification • Analysis of blood / serum Estimation of blood urea, serum creatinine, protein & electrolyte
Urine examination Volume, pH, Specific gravity, Osmolality, Presence of certain abnormal constituents ( Proteins, blood, ketone bodies, glucose) • Clearance tests C = u x v p • Creatinine clearance test (145ml/minute) • Urea clearance test (75ml/minute) • Standard Urea clearance Cs = u x √v P