Exploring the Evolution of Chordates: A Journey Through Phylogeny
470 likes | 580 Vues
Dive into the intricate evolutionary history of chordates, from Xenoturbellida to Vertebrates, highlighting key characteristics and milestones in their development. Discover the diverse forms, structures, and adaptations that have shaped these fascinating creatures.

Exploring the Evolution of Chordates: A Journey Through Phylogeny
E N D
Presentation Transcript
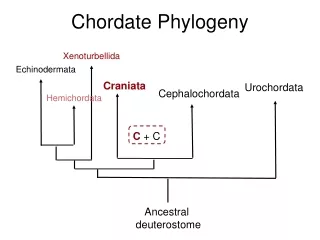
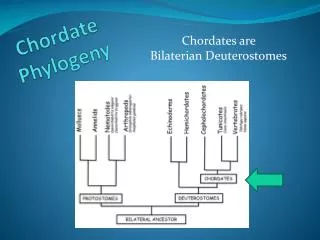
Chordate Phylogeny Xenoturbellida Echinodermata Craniata Urochordata Cephalochordata Hemichordata C + C Ancestral deuterostome
Chordate Phylogeny Myxiniformes - Hagfish (eeeeww!)
Chordate Phylogeny 40 extant species benthic marine scavengers predators
Chordate Phylogeny • Myxiniformes • tubular • notochord persists • cranial capsules = axial skeleton • no vertebrae (“honorary vertebrates”) • no bone • agnathous • pharyngeal “basket” • = visceral skeleton • median fins… • no lateral fins; no appendicular skeleton
Chordate Phylogeny • Myxiniformes • brain and sense organs poorly developed • eyes lack lenses and extrinsic musculature • optic tectum of midbrain poorly developed • lack lateral line system (no neuromasts) • lack electrosensitivity • single semicircular canal • cerebellum poorly developed • single median nostril • circulatory system has sinuses in addition to vessels • osmoconforming
Chordate Phylogeny Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Vertebrates Finally!! Craniates Ancestral craniate
Chordate Phylogeny Petromyzontiformes Lampreys about 40 extant species anadromous scavengers or ectoparasites buccal cavity tongue “teeth”
Chordate Phylogeny • Petromyzontiformes • tubular • notochord persists • agnathous • axial skeleton = cranial capsules and “arcualia” • no bone • pharyngeal “basket” • = visceral skeleton • median fins better developed than in hagfish • no lateral fins; no appendicular skeleton
Chordate Phylogeny • Petromyzontiformes • brain and sense organs better developed • eyes have lenses and extrinsic musculature • optic tectum of midbrain well developed • have lateral line system on head • scattered neuromasts over rest of body • have electrosensitivity • two semicircular canals (proprioception) • cerebellum better developed • single median nostril • circulatory system has only discrete vessels • osmoregulating
“cyclostomata” AKA “agnatha” Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Vertebrates Finally!! Ancestral craniate
Chordate Phylogeny Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes “ostracoderms” Vertebrates Finally!! “unresolved” extinct… Ancestral craniate
Chordate Phylogeny ostracoderm pics
Chordate Phylogeny • Ostracoderms • primarily Silurian and Devonian…(C/O) • agnathous • covered with bony plates • CaMgPO4 (hydroxyapatite) • anterior plates, posterior “tesserae” • perichondral bone • endochondral bone • well developed lateral eyes • two semicircular canals • lateral line system • median fins • without or with paired lateral fins
Chordate Phylogeny Myxiniformes Petromyzontiformes Heterostracans “ostracoderms” Vertebrates Finally!! Ancestral craniate
Chordate Phylogeny dorsoventrally flattened Heterostracans tesserae hypocercal tail shields perichondral bone “aspidin” fin spines late Cambrian fragments good fossils mid-Ordovician no bony endoskeleton AKA “pteraspida”
Chordate Phylogeny Myxiniformes Anaspids Petromyzontiformes Heterostracans “ostracoderms” Vertebrates Finally!! Ancestral craniate
Chordate Phylogeny • Anaspids • relatively elongate, fusiform • hypocercal tail • tesserae, or without plates • ventrolateral “fin folds” • sister group of lampreys?
Chordate Phylogeny lateral view tesserae, no plates hypocercal tail median fin ventral view ventrolateral “fin folds”
Chordate Phylogeny Myxiniformes Osteostracans Anaspids Petromyzontiformes Heterostracans “ostracoderms” Vertebrates Finally!! Ancestral craniate
Chordate Phylogeny osteostracans head shield tesserae heterocercal tail pectoral fin most derived group; Silurian and Devonian dorsoventrally flattened axial skeleton of cellular bone? extensive lateral line system
Chordate Phylogeny heavily ossified endocranium brain shape and cranial nerve pattern similar to gnathostomes sister group of gnathostomes
Chordate Phylogeny Gnathostomes Myxiniformes Osteostracans Anaspids Petromyzontiformes Heterostracans ??? “ostracoderms” Vertebrates Finally!! Ancestral craniate
Chordate Phylogeny otic capsule optic capsule nasal capsule P notochord A
Chordate Phylogeny otic capsule optic capsule nasal capsule P notochord A The visceral skeleton (the branchial arches) consist of metameric sets of cartinaginous rods or bars
Chordate Phylogeny a typical branchial arch frontal view lateral view pharyngobranchial epibranchial ceratobranchial hypobranchial basibranchial pharyngeal gill slits
Chordate Phylogeny otic capsule + optic capsule + nasal capsule = chondrocranium P A notochord
notochord Chordate Phylogeny chondrocranium and visceral skeleton…
Chordate Phylogeny notochord
Chordate Phylogeny notochord
Ancestral condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Pharyngobranchial of first branchial arch forms… Derived condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Trabecular cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Chordate Phylogeny
Ancestral condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Pharyngobranchial of first branchial arch forms… Pharyngobranchial of second branchial arch forms… Derived condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Trabecular cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Parachordal cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Chordate Phylogeny
Chordate Phylogeny opc nc otc pcc tc notochord
Chordate Phylogeny notochord
Ancestral condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Pharyngobranchial of first branchial arch forms… Pharyngobranchial of second branchial arch forms… Epibranchial of first branchial arch forms… Derived condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Trabecular cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Parachordal cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Palatoquadrate cartilage which forms upper jaw Chordate Phylogeny
Ancestral condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Pharyngobranchial of first branchial arch forms… Pharyngobranchial of second branchial arch forms… Epibranchial of first branchial arch forms… Ceratobranchial of first branchial arch forms… Derived condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Trabecular cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Parachordal cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Palatoquadrate cartilage which forms upper jaw Mandibular (Meckel’s) cartilage which forms lower jaw Chordate Phylogeny
Chordate Phylogeny notochord Some elements of the primitive visceral skeleton were incorporated into the developing “chondrocranium” and the developing jaws…
Chordate Phylogeny notochord Elements of the primitive visceral skeleton were incorporated into the developing chondrocranium, the developing jaws, and the jaw supports
Ancestral condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Pharyngobranchial of first branchial arch forms… Pharyngobranchial of second branchial arch forms… Epibranchial of first branchial arch forms… Ceratobranchial of first branchial arch forms… Epibranchial of second branchial arch forms… Ceratobranchial of second branchial arch forms… First pharyngeal pouch forms.. Derived condition Nasal, optic, and otic capsules form core of chondrocranium Trabecular cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Parachordal cartilage of the floor of the developing braincase Palatoquadrate cartilage which forms upper jaw Mandibular (Meckel’s) cartilage which forms lower jaw Upper hyoid arch Lower hyoid arch Spiracle Chordate Phylogeny
notochord Chordate Phylogeny
Chordate Phylogeny opc nc otc no pcc tc h s pq h m The derived condition