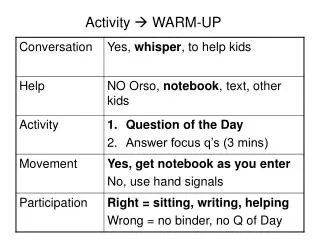
Warm up Activity:
150 likes | 173 Vues
Warm up Activity:. As you walk in, take your IP address. DO NOT share it with your classmates. For the next 5 minutes, your goal is to complete an accurate list of IP addresses and names for all students in the room.

Warm up Activity:
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Warm up Activity: As you walk in, take your IP address. DO NOT share it with your classmates. For the next 5 minutes, your goal is to complete an accurate list of IP addresses and names for all students in the room. You may only talk to one person at a time, but you may exchange as much information with that person as you want.
Domain Name System How the Internet Works: DNS
Were you frustrated? • IP addresses change all the time, so why do we not have to type in a different web address (www.google.com) every time they change? • Google and other websites IP address will not change that often. Only if they change providers. • Your phone will change IP addresses as you move around – Cell phone Cellular connected to ‘cells’ of towers which relay your signal. • How does a computer remember where to go? • How would a mail carrier know where to goif your address changed all the time?
Activity review: We created individual lists, which is highly inefficient The internet has a centralized list, which is much less frustrating
Review: IP addresses, Protocols A Protocol is a ‘rule’ or agreement. The term comes from diplomacy. Two representatives from countries meeting each other would not want to offend the other, so a shared form of etiquette and format is set ahead of time. Computers use a similar experience. Computers are guarded, yet willing to communicate with each other based upon set rules (just like a diplomat). IP stands for Internet Protocol. What do you think are some ‘rules’ or etiquette customs, computers might share?
What is a domain name? • Domain – Think “home” (Dominion, Territory, ‘region w/ specificfeature’) • When we type a web address: • www. (World Wide Web) “Hey! Take me to the internet!” [unnecessary now] • Salisbury The Domain name – specific to its nature; “home” • .edu The top level domain name (also specific to its nature think Education) • However a computer can’t really ‘read’ a domain name (computers work better w/ numbers; we work better w/ words, so we compromise!) • The domain name must be “resolved” (think – two countries agree on a resolution) Thus the computer changes the web address to a number ex: 205.181.112.101
Let’s find the IP addresses of various sites Use the worksheet to find the addresses of listed sites. Also, find the sites of 5 other of your favorite sites Observations?
DNS continued Domain Name Systems
Review • DNS – Domain Name System: the service which translates a URL to an IP • URL Uniform Resources Locator [website address] • IP Internet Protocol [ex: 10.42.132.144 the address of where the device lives on the internet] • Each device [computer] requests the IP of the website from the DNS system.
DNS - issues DNS is the large-scale system that translates human-readable web addresses into their numeric IP addresses so that computers can communicate. • This system however was not designed to be secure and that has resulted in some major security incidents over time.
Let’s find our IP address • If you have access to the Command Prompt (the C:/ prompt) you can type in CMD in the windows search bar to access it. • In the prompt, type ipconfig and you will see your computer’s IP address • If not: go to pingtool.org Type in a website wcboe.org code.org whatever you’d like Look up country, #of hops to get there and IP address
Video Code.org – DNS (Begin at 4:12)
DNS Attacks Research DNS attacks – Online and using Moodle links • Group 1: look up GOVERNMENT DNS attacks • Group 2: look up Attacks on commercial sites (companies) • Group 3: look up Denial of Service attacks
What is DNS • Why does the Internet use IP addresses? • Why don’t we need to know IP addresses? • Why do we need a Domain Name System? • Why don’t we all maintain our own DNS? • Is there one big DNS for the entire Internet? • How do you think all these DNS servers are maintained?