Erosion and Deposition: A Comprehensive Guide
270 likes | 413 Vues
Explore erosion processes by water, glaciers, wind, and living things, as well as mass movements. Learn about factors influencing erosion and ways to prevent it.

Erosion and Deposition: A Comprehensive Guide
E N D
Presentation Transcript
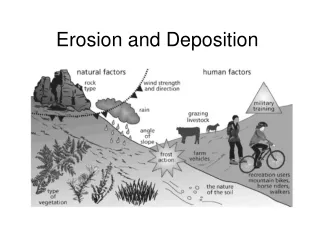
Two Important Definitions • Erosion: the removal of weathered rock and soil from its original location • Deposition: the dropping of eroded material in a different location (when you make a deposit at the bank; you are leaving money; here rock is deposited in a new place)
Gravity • The power behind most erosional agents • Rock is pulled downslope by the force of gravity
4 Types of Erosion • Erosion by Water • Erosion by Glacier • Erosion by Wind • Erosion by Living Things
1a. Erosion by Water • Rill Erosion : when a narrow stream cuts a small channel into the land (think narrow stream) • Gully Erosion: stream of water has gone beyond Rill Erosion and now the stream of water is deep and wide (think wider stream)
1b. Erosion by Water- Rivers and Streams • Each year streams carry billions of metric tons of sediments and weathered material to the coastal areas • Over time, the build up of sediment produces deltas (example: Colorado River Delta-right; Mississippi River Delta - left)
1c. Erosion by Water- Waves • Sand on an ocean shoreline is repeatedly picked up, moved, and deposited • Constant movement of water is a continuous erosional process • Deposits can lead to sand bars and barrier islands (example: Outer Banks of N.Carolina)
2. Glacial Erosion • Currently cover 10% of the Earth’s surface • Once covered 30% • Scraping and gouging the earth as they move huge rock and piles of debris over great distances • Glacial movements scratch and grind surfaces and deposit material over long distances
3. Wind Erosion • Moves fine, dry particles a great distance • Most common in areas without vegetation holding the soil into places • Can be prevented with a wind barrier (stand of trees or other vegetation planted perpendicular to the direction of the wind)
4. Erosion by Living Things Examples of Erosion by living things: • Excavating land • Planting a garden • Developing land • Building a highway All of these can lead to erosion
Mass Movement • Downslope moving of soil and weathered rock resulting from the force of gravity • ALL mass movements occur on slopes
Factors that Influence Mass Movement • Material’s weight • Materials resistance to sliding or flowing • Trigger (like at earthquake) • Water
Classification of Mass Movement • Creep: slow, steady downflow of loose weathered material a) slowly creep can cause once vertical utility poles and fences to tilt
2) Flows: slow movements of soil a) mudflows: swiftly moving mixtures of mud and water
Mudflow • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n1cCs-S5EKc
3) Slides: top layers of soil are thin and move downslope rapidly a) Landslides b) Slumps (landslide on a curved surface) c) Avalanche (snow melts in sun, refreezes at night and the fallen snow moves downslope)
Avalanche • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=99j17GL3qlE
4) Rockfalls: rocks are loosened by physical weathering, • they then break loose and fall downslope a) less likely in humid climates where a layer of soil and vegetation cover the rock
Rock fall • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZVYGJYnJTi0
People • Humans can minimize the destruction caused by mass movement by not building near the base of unstable slopes • >25o slopes are at the greatest risk of a catastrophic mass movement