Understanding Matrices: Basics of Structure, Addition, and Scalar Multiplication
90 likes | 257 Vues
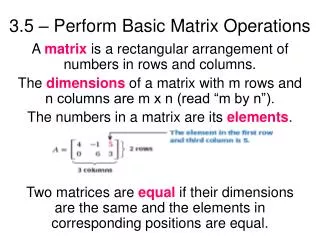
A matrix is a rectangular arrangement of numbers organized in rows and columns. The order of a matrix refers to its dimensions, indicating the number of rows and columns. To add two matrices, they must share the same order, allowing for the summation of their corresponding entries. In matrix algebra, a real number is termed a scalar. When multiplying a matrix by a scalar, each entry in the matrix is multiplied by the scalar value. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for further studies in linear algebra and its applications.

Understanding Matrices: Basics of Structure, Addition, and Scalar Multiplication
E N D
Presentation Transcript
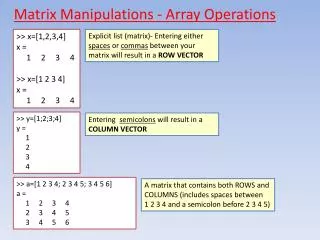
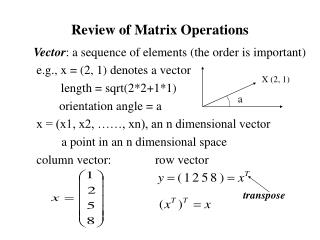
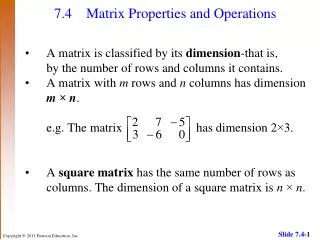
2. MATRIX: A rectangular arrangement of numbers in rows and columns.
The ORDER of a matrix is the number of the rows and columns.
The ENTRIES are the numbers in the matrix.
4. To add two matrices, they must have the same order. To add, you simply add corresponding entries.
8. In matrix algebra, a real number is often called a SCALAR. To multiply a matrix by a scalar, you multiply each entry in the matrix by that scalar.