Electric Circuit
231 likes | 670 Vues
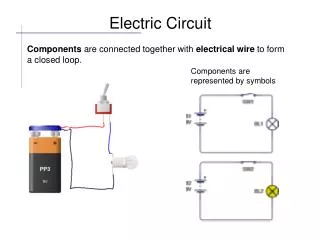
Electric Circuit. Components are connected together with electrical wire to form a closed loop. Components are represented by symbols. Electric Circuit. Electrical wire used to connect components is a conductor . A conductor allows electric current to flow through it easily.

Electric Circuit
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Electric Circuit Components are connected together with electrical wire to form a closed loop. Components are represented by symbols
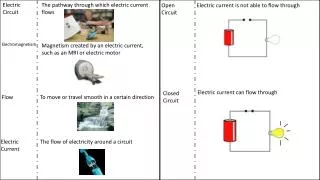
Electric Circuit • Electrical wire used to connect components is a conductor. • A conductor allows electric current to flow through it easily. • Good conductors include: copper, gold, silver, tin • Copper wire is generally used as it is most cost effective. • All electrical wires have a plastic cover. • Plastic is an insulator. • An insulator does not allow current to flow through it. • Avoids electric shock. • Insulators include: plastic, glass, wood
Electric Circuit Electric Current is the flow of electrons around a circuit. Electrons have a negative charge
Electric Circuit • Electric current is measured with an Ammeter • The ammeter is placed into the circuit (in series) • Unit of measurement is the Ampere or ‘amp’ • Represented by the letter I . I=3A
Electric Circuit • Voltage is measured using a Voltmeter. • The voltmeter is placed across a component (in parallel) • Unit of measurement is the Volt. • Represented by letter V.
Electric Circuit • Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current. • All components have resistance. • Electrical wire has resistance. • Unit of measurement is the Ohm (Ω) • Represented by the letter R
V I R Ohm’s Law Voltage , Current & Resistance are calculated using Ohm’s Law
Series Circuit • Components are connected one after the other • There is only one path for current to flow around • The current at all points in a series circuit is equal
Series Circuit • The voltage is shared between the components in a series circuit. • Components of equal resistance : voltage is shared equally
Series Circuit • The voltage is shared between the components in a series circuit. • Components of unequal resistance : voltage is shared proportionally
Parallel Circuit • Components are connected side by side • There is more than one path for current to flow around
Parallel Circuit The voltage across each path is always the same as the applied voltage • When component resistance in each path is the same
Parallel Circuit The voltage across each path is always the same as the applied voltage • When component resistance in each path is different
Parallel Circuit The voltage across each path is always the same as the applied voltage • When there is more than one component in a path
Parallel Circuit • The current is divided between the paths proportionally (Ohm’s Law)