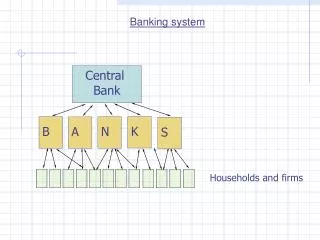
BANKING SYSTEM AND I.T.
420 likes | 769 Vues
BANKING SYSTEM AND I.T. III BANKING OPERATIONS AND SERVICES. Report by Jeaneth Michelle L. Balaba I.T. and Financial Capital Market Applications Graduate School of Business De La Salle University-Dasmariñas 11 March 2006. EVOLUTION OF MONEY. Some Forms of Money

BANKING SYSTEM AND I.T.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BANKING SYSTEM AND I.T. III BANKING OPERATIONS AND SERVICES Report by Jeaneth Michelle L. Balaba I.T. and Financial Capital Market Applications Graduate School of Business De La Salle University-Dasmariñas 11 March 2006
EVOLUTION OF MONEY Some Forms of Money Amber, beads, cowries, drums, eggs, feathers, gongs, hoes, ivory, jade, kettles, leather, mats, nails, oxen, pigs, quartz, rice, salt, thimbles, umiacs, vodka, wampum, yarns, and zappozats (decorated axes). Gold and precious metals Currency Gold standard Fiat money Credit money Electronic money (also known as digital money, electronic currency, digital currency or internet money) EFTS/direct deposit e-gold/Goldmoney/Pecunix//eeeCurrency Paypal/e-bullion
Hawala • From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Hawala (also known as hundi) is an informal value transfer system used primarily in the Middle East, Africa and Asia. • Its origins are not entirely clear, but it is believed to have been used first in the financing of long-distance trade in the early medieval period on trading routes such as the Silk Road, the Eastern Mediterranean and the Indian Ocean. Hawala is mentioned in texts of Islamic jurisprudence as early as the 8th century. In South Asia, it appears to have developed into a fully-fledged money market instrument, which was only gradually replaced by the instruments of the formal banking system in the first half of the 20th century. Today hawala is probably used mostly for migrant workers' remittances to their countries of origin. • In the most basic variant of the hawala system, money is transferred via a network of hawala brokers, or hawaladars. A customer approaches a hawala broker in one city and gives a sum of money to be transferred to a recipient in another, usually foreign, city. The hawala broker calls another hawala broker in the recipient's city, gives disposition instructions of the funds (usually minus a small commission), and promises to settle the debt at a later date. • The unique feature of the system is that no promissory instruments are exchanged between the hawala brokers; the transaction takes place entirely on the honor system. As the system does not depend on the legal enforceability of claims, it can operate even in a defunct legal and juridical environment. No records are produced of individual transactions; only a running tally of the amount owed one broker by the other is kept. Settlements of debts between hawala brokers can take a variety of forms, and need not take the form of direct cash transactions. • In addition to commissions, hawala brokers often earn their profits through bypassing official exchange rates. Generally the funds enter the system in the source country's currency and leave the system in the recipient country's currency. As settlements often take place without any foreign exchange transactions, they can be made at (black) market rates rather than official rates.
Official reported gold reserves • As 22 September 2005, the largest gold holdings in tonnes as reported by the World Gold Council[1]. The United States holding of gold is worth approximately $162.7 billion as of February 3rd 2006. • 1 United States 8,133.5 • 2 Germany 3,427.8 • 3 IMF 3,217.3 • 4 France 2,892.6 • 5 Italy 2,451.8 • 6 Switzerland 1,290.1 • 7 Japan 765.2 • 8 Netherlands 722.4 • 9 ECB 719.9 • 10 China, Mainland 600.0 • 11 Spain 493.3 • 12 Taiwan 423.3 • 13 Portugal 407.5 • 14 Russia 386.6 • 15 India 357.7 • 16 Venezuela 357.4 • 17 United Kingdom 311.3 • 18 Austria 307.5 • 19 Lebanon 286.8 • 20 Belgium 227.7 • 21 Philippines 187.9 • 22 BIS 185.3 23 Algeria 173.6 24 Sweden 155.4 25 Libya 143.8 26 Saudi Arabia 143.0 27 Singapore 127.4 28 South Africa 123.9 29 Turkey 116.1 30 Greece 107.9 31 Romania 104.9 32 Poland 102.9 33 Indonesia 96.5 34 Thailand 84.0 35 Australia 79.7 36 Kuwait 79.0 37 Egypt 75.6 38 Denmark 66.5 39 Pakistan 65.3 40 Kazakhstan 58.6
FUNCTIONS OF MONEY Specific functions (mostly micro-economic) • Unit of account (abstract) • Common measure of value (abstract) • Medium of exchange (concrete) • Means of payment (concrete) • Standard for deferred payments (abstract) • Store of value (concrete) General functions (mostly macro-economic and abstract) • Liquid asset • Framework of the market allocative system (prices) • A causative factor in the economy • Controller of the economy Money is anything that is widely used for making payments and accounting for debts and credits.
BASIC BANKING SERVICES DEPOSITS Checking (Current Account) Savings LOANS Consumer loans Business Loans Trade finance CHECK ENCASHMENT (Clearing) WIRE TRANSFERS/CASHIER’S CHECKS CREDIT CARDS/DEBIT CARDS/ATM CARDS SAFE DEPOSIT BOXES OTHER SERVICES: PAYMENT
RETAIL BANKING Deals directly with individuals and small businesses INVESTMENT BANKING Relates to activities in the financial market “Underwriting”
RETAIL BANKING • Commercial bank, is the term used for a normal bank to distinguish it from an investment bank. Since the two no longer have to be under separate ownership, some use the term "commercial bank" to refer to a bank or a division of a bank that mostly deals with corporations or large businesses. • Community development bank are regulated banks that provide financial services and credit to underserved markets or populations. • Postal savings banks are savings banks associated with national postal systems. Japan and Germany are examples of countries with prominent postal savings banks. • Private banks manage the assets of high net worth individuals. • Offshore banks are banks located in jurisdictions with low taxation and regulation, such as Switzerland or the Channel Islands. Many offshore banks are essentially private banks. • Savings banks traditionally accepted savings deposits and issued mortgages. Today, some countries have broadened the permitted activities of savings banks.
INVESTMENT BANKING • Investment banks "underwrite" (guarantee the sale of) stock and bond issues and advise on mergers. Examples of investment banks are Goldman Sachs of the USA or Nomura Group of Japan. • Merchant banks were traditionally banks which engaged in trade financing. The modern definition, however, refers to banks which provides capital to firms in the form of shares rather than loans. Unlike Venture capital firms, they tend not to invest in new companies.
UNIVERSAL BANKS Universal banks, more commonly known as a financial services company, engage in several of these activities. For example, Citigroup, a very large American bank, is involved in commercial and retail lending; it owns a merchant bank (Citicorp Merchant Bank Limited) and an investment bank (Salomon Smith Barney); it operates a private bank (Citigroup Private Bank); finally, its subsidiaries in tax-havens offer offshore banking services to customers in other countries. Almost all large financial institutions are diversified and engage in multiple activities. In Europe and Asia, big banks are very diversified groups that, among other services, distribute also insurance, whence the bancassurance term.
BANCASSURANCE • Bancassurance is the term used to describe the sale of insurance products in a bank. • The word is a combination of "banc" and "assurance" signifying that both banking and insurance is provided by the same corporate entity. • The usage of the word picked up as banks and insurance companies merged and banks sought to provide insurance, especially in markets that have been liberalised recently. It is a controversial idea, and many feel it gives banks too great a control over the financial industry. • In some countries, bancassurance is still largely prohibited, but it was recently legalized in countries such as the United States, when the Glass-Steagall Act was repealed after the passage of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act.
BancassuranceThe word "Bancassurance" came from the combination of the French word Banque (i.e., Bank) and Assurance (i.e., Insurance). In reality, it means that banks sell insurance policies and it is the system widely adopted in Europe, USA and Japan. Korea started this system from Sept 2003. By adding this system to the existing Banking services, banks can provide wider ranges of products and service in addition to the current products such as deposits, loans, and investments. Insurance companies, on the other hand, provide better products through bigger channels. HSBC has also started to provide very competitive life and non-life products from prominent policy providers such as AIG, ING, Samsung, Dongyang. The following is the list of the products we are providing currently.
Wealth management for High Net Worth and Ultra High Net Worth customers has been pioneered by Lombard International and the function is known as Privatbancassurance.
Companies Mentioned • ABN AMRO Holding N.V. (15) • American Express Company (9) • ASF (5) • Banca Monte deiPaschidi Siena S.p.A. (6) • Banco Sabadell (5) • Banco Santander Central Hispano S.A. (8) • Barclays PLC (17) • BNP Paribas Group (18) • Citibank, N.A. (18) • Credit Agricole, S.A. (28) • Credit Lyonnais (15) • Deutsche Bank AG (12) • Dresdner Bank AG (15) • Financial Institutions, Inc. (12) • Fortis (23) • HBOS plc (12) • HSBC Holdings plc (10) • ING Groep N.V. (15) • La Poste (14) • Lloyds TSB Group plc (14) • asterCard Incorporated (5) • Northern Rock plc (5) • SociétéGénérale (10) • niCreditS.p.A. (6) • Visa International (9)
ISLAMIC BANKING Islamic banks adhere to the concepts of Islamic law. Islamic banking revolves around several well established concepts which are based on Islamic canons. Since the concept of Interest is forbidden in Islam, all banking activities must avoid interest. Instead of interest, the Bank earns profit (mark-up) and fees on financing facilities that it extends to the customers. Also, deposit makers earn a share of the Bank’s profit as opposed to a predetermined interest.
TRANSACTION BANKING ANZ can provide your business with a transaction banking solution that is customised to suit your specific requirements. Our strong foundation and breadth of experience can help shape your business now and as it grows. By identifying and understanding your current and future needs, ANZ can provide a range of customised accounts, payables solutions, receivables solutions, electronic banking solutions, merchant facilities, commercial cards and liquidity management options and International requirements. These services can be integrated to assist you to: • better manage your working capital flows • reduce exposure to risk • eliminate idle balances • minimise exposure to transaction taxes and fees • manage fluctuations in your business cycle • provide improved services for your staff and customers' convenience • reduce your costs
Transaction BankingServices - Corporate Banking Payments Receivables Branch banking services Bankcards Standing orders and cash pooling services Time deposits Cheques
PAYMENT SERVICES Payroll accounts Group transfers Postal vouchers Foreign currency transactions
RECEIVABLES Group collection Request-for-debit Postal cheques SpeedCollect Buyer Identification Foreign currency receivables
Branch banking services • Citibank offers a wide range of teller services transactions in its growing branch network. • Teller services • Cash deposits in Forint and foreign currency Cash withdrawals in • Cash withrowals in forint and foreign currency • Forint and foreign currency Cash-bag deposits in bag and cash counting • Travelers chequecks sales and purchase
Bankcard PayLink Visa Electron Card • This card can be required for employees, who make purchases or withdraw money on behalf of the company. This card is an ideal tool for corporate purchases, it reduces the physical cash requirements of the daily transactions. Features and benefits: • Free of charge purchases. • Accepted at over 16,500 merchants in Hungary, and many more abroad. • Cash withdrawal from automated teller machines (ATMs) with Visa Electron logo all over the world. In Hungary it means more than 2300 ATMs. • PIN number ensures security. • Daily limits can be set in accordance with the users' requirements. • Based on your request our bank issues an unlimited number of PayLink Visa Electron cards for your employees. We open a card account linked to your main account for card transaction settlement only. • The daily available limit of the transactions made by all of the card holders equals to the balance of your • card account. Once a day Citibank automatically transfers funds from the main account to the card account to ensure that the balance on the card account is brought to the level defined by you. The sum of the cards' limit may exceed the limit of the card account, however, the card holders cannot spend more than the daily opening balance of the card account.
Standing orders and cash pooling services • By using standing orders you can give an instruction to Citibank to regularly (e.g. daily, weekly, monthly, etc) transfer fixed or variable amounts to a destination account. The bank fulfils these instructions automatically in line with the initial former requirements. • The following standing orders are offered by Citibank: • Regular transfers of fixed, pre-determined amounts • Target balance pooling services • Standing orders can be submitted in any foreign currency, and its frequency can be daily, weekly, monthly or annual yearly. • Liquidity management - Pooling services • Upon your requests pooling services can be set up with reverse, so the sweeps made at the end of the day are reversed at the beginning of the next day whilst the advantages of pooling can be still used. • In order to optimize your company's liquidity management these structures have to reflect the companys specific needs and organic framework. To set an optimal (either multi-layered or international) pooling structure our Bank is kindly available for you. • Further information • Standing orders of fixed amounts • Target balance pooling • Minimum target balance pooling (balance increased to a target value) • Maximum target balance pooling (balance reduction to a target value) • Cash pooling to a target balance Interest reallocation
Cheques • Travellers Cheques • Citibank offers AmEx Travellers Cheques in USD and Euro (EUR) to its corporate clients. The cheques can be purchased in different types of denominations in any of the Citibank branches. Travellers Cheques are more safer than cash because we can replace your lost cheques in a short time. • The unused Travellers Cheques are repurchased by the bank. • Foreign Currency Cheque Issuance • Citibank issues cheques in about 20 foreign currencies only for its corporate clients. The instruction for cheque issuance should be submitted to the bank duly signed, upon which the bank issues and sends the cheques to the beneficiary or to the client. The beneficiary can get the value of the cheque collected with the help of its own account holding bank. • Foreign Currency Cheque Collection • Citibank accepts cheques from its corporate clients in about 20 foreign currencies. The cheques to be collected should be mailed or submitted in person to Citibank accompanied by a chequeck collection instruction. After checking the formal requirements we forward them to the issuing bank for collection. The collection of the USD, Euro and British Pound cheques is the fastest, the fund is collected approximately in 3-5 days. Regarding other foreign currencies the collection period is longer. Upon receipt of the funds the amounts will be credited to your account with Citibank Zrt. immediately without delay, however, the funds are blocked until the 10th day of the recourse period, after which funds become available then from the 11th day the fund is available.
Treasury Services • If you want a risk-free form of investment, or if you have substantial currency sourcing requirements, in pesos, dollars, or euros, Metrobank has the tools and the organization to help you. • Purchase & Sale of Government Securities • Metrobank is an accredited dealer of Government Securities such as Treasury Bills, Treasury Notes, and Treasury Bonds. • Purchase & Sale of USD Government Securities • Metrobank is an accredited dealer of USD Government Securities. • Foreign Exchange Trading • We know that every cent counts. The Bank commits to providing you the best conversion rates at all times for USD/PhP or for major third currencies. Whatever the size, we aim to meet your requirements. • Currency Forwards • Currency Forwards allow you to lock-in the cost of your future foreign exchange requirements thus, taking away the uncertainty of fluctuating exchange rate. • Commercial Buy Sell Swap • The Commercial Buy Sell Swap provides you an alternative means of generating Peso funding while preserving your USD assets.
TREASURY OPERATIONS THE FOREX MARKET HEDGING Protecting companies against movements in the exchange rate CONTRACT Eliminate exchange risk FORWARD EXCHANGE CONTRACT Spot rate Forward rate
A forward exchange contract is a binding contract in which there is an agreement to buy or sell: a certain amount of foreign currency JPY at a specified future date December 21 at an exchange rate determined today 1.50
TYPES OF FORWARD CONTRACT FIXED FORWARD CONTRACT Used for transactions to be settled on specific dates OPTION FORWARD CONTRACT Used for transactions which can be settled at any time between 2 dates Bid rate = Offer rate
TRUST OPERATIONS • A trust institution: a legal entity that can hold and manage assets for one or more beneficiaries over time • Grantor is the creator of the trust • Trustee is the manager of the trust • Beneficiaries receive the benefits of the trust • Business trusts historically were formed among firms in the same industry to avoid competition and gain monopoly power • The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 in US and other legislation struck down such anti-competitive behavior • Today holding companies (ownership of affiliated firms) and consortiums (association or partnership of financial institutions but no cross ownership) have replaced trusts as a common form of business organisation • Trust institutions now handle employee benefit programmes, personal trusts and estates, and corporate trusts • Real estate investment trusts (REITs) is a trust that purchases real estate and offers shares of ownership to investors • Trust companies can be within or outside a bank for purposes of estate planning to distribute assets of an individual after death and reduce taxes for beneficiaries: US federal estate tax rates range from 37% to 55%!
ISSUES • Ripple monetary system • From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia • Ripple is an open-source software project for developing a peer-to-peer distributed social network service with a monetary honor system based on trust that already exists between people in real-world social networks. • National monetary systems rely on trust in large financial institutions as banks. Ripple cuts the banks right out of the picture by allowing anyone to act as a bank and grant credit within the Ripple system to anyone they know. The system keeps track of the source of all IOUs (I owe you's), so that debts that are not repaid are automatically borne by the issuer. • Each participant indicates which other participants he or she trusts, by offering to accept their IOUs up to a certain amount, like a line of credit. To make a payment to someone who trusts you, you simply adjust your IOU balance with them to indicate that that you owe them the amount of the payment. So the whole system acts as a distributed mutual bank.
Hawala after September 11 attacks • After the September 11 Attacks, the American government suspected that hawala brokers may have helped terrorist organizations to transfer money to fund their activities. The 9/11 Commission Report has since confirmed that the bulk of the funds used to finance the assault on the twin towers were not sent through the hawala system, but rather by inter-bank wire transfer to the SunTrust Bank in Florida, where two of the conspirators had opened a personal account. However as a result of intense pressure from the US authorities, widespread efforts are currently being made to introduce systematic anti-money laundering initiatives on a global scale, the better to curb the activities of the financiers of terrorism and those engaged in laundering the profits of drug smuggling. Whether these initiatives will have the desired effect of curbing such activities has yet to be seen; although a number of hawala networks have been closed down, and a number of hawaladars have been successfully prosecuted for money laundering, there is little sign that these "successes" have brought the authorities any closer to identifying and arresting a significant number of terrorists or drug smugglers. • In November, 2001, the Bush administration froze the assets of Al Barakat, a Somali remittance hawala company used primarily by the large Somali Diaspora. Many of its agents in several countries were initially arrested, though later freed after no concrete evidence against them were found. Many of them still have their assets frozen. • Hawala have been made illegal in some states of the US and other countries as they are seen to be a form of money laundering and terrorist funding.