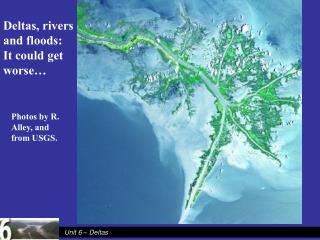
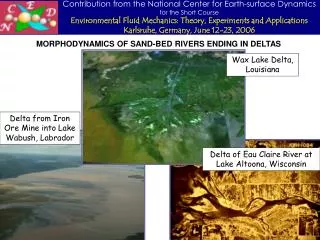
Deltas
940 likes | 3.15k Vues
Deltas. What is a Delta?. Deltas are landforms of deposition They are formed in the lower course of a river. They are named after the third letter of the Greek alphabet ( Δ ). How can you recognise a Delta?. River enters a lake or sea, velocity and capacity to carry a load is reduced.

Deltas
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is a Delta? • Deltas are landforms of deposition • They are formed in the lower course of a river. • They are named after the third letter of the Greek alphabet ( Δ )
How can you recognise a Delta? • River enters a lake or sea, velocity and capacity to carry a load is reduced. • What happens when a river is unable to carry a load? • Deposition
Where do Deltas form? • Deltas form where tides and currents are unable to remove all of the deposited sediment. • How is material or sediment transported? • Suspension • Solution • Bedload
When rivers flow into a shallow sea, friction causes it to deposit. • Forms an Island or a Braid in the centre of the estuary and mudflats along the banks of the river. • The channel is now divided and further deposition divides the channel further into smaller channels called distributaries.
What is in a Delta? • Top Alluvial Soil • Middle Sand Layers • Bottom Fine silt and clay
Types of Deltas Arcuate Delta Estuarine Delta Bird’s Foot Delta Lacustrine Delta
Arcuate Delta Triangular Shape Composed of coarse porous sand and gravel. River Nile, Egypt River Po, Italy
Estuarine Delta • River deposits alluvium along the banks of an estuary. • River Rhine, Germany • Hudson River, New York
Bird Foot Delta • Rivers carry huge amounts of fine, impermeable material such as clay or mud. • River deposits material and divides into distributaries. • The delta extends into the sea like toes to form a birds foot shape. • Mississippi Delta, USA
The Mississippi Delta Jetties have been built and dredging occurs to allow large vessels to navigate the delta channel Note the large amounts of sediment that surrounds the delta A bird’s foot delta located in Louisiana adjacent to the Gulf of Mexico
Lacustrine Delta • Rivers deposit stratified or sorted sediments as they flow into a lake. • Upper Lake, Glendalough • Lake Genava
Nile Delta Well developed distributaries Smooth delta front A mixed or intermediate delta influenced by both river and wave forces
People and the Mississippi Sediment deposited by distributaries Note the large sediment plumes The Mississippi River carries 200 million tons of sediment annually to the Gulf of Mexico.
The Danube Delta This delta attracts many tourists who enjoy watching the delta’s birds and other inhabitants The Danube is the second longest river in Europe The Danube Delta is the second largest in Europe (4300 square kilometers) and is home to one of the biggest reed beds in the world, vast stretches of other wetland types, and much wildlife.
Estuarine Delta deposits sediment on the side/bank of the estuary
Braiding When a river’s velocity falls rapidly, capacity for carrying a heavy load are reduced, and the channel may become choked with material, causing the river to braid i.e. the channel splits up into several smaller channels which flow around fresh ‘islands’ of deposited material before rejoining and further dividing.