Warm – up question;
470 likes | 492 Vues
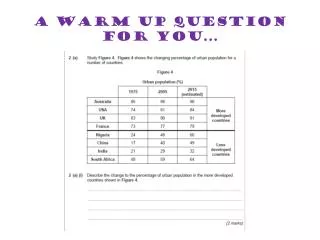
Learn about key features of Mercury and Venus, study for the test, and understand historical astronomers' models of the universe. Homework due on Friday. Aim to write an essay summarizing the inner and outer planets.

Warm – up question;
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Warm – up question; Write about three characteristics on Venus Exit Question. Write two facts about Neptune
The Triad ends on 10/24/2014 • That is 23 days from now • Do you know your current grade • If it is not the grade you want, what are you doing to change that grade. • Have you talk to your teachers yet
Objective:I will be able to write an identification of the basic characteristics of Mercury and Venus Homework: Study for chapter 29 test and get notebook ready, all due on Friday 10/3. Turn in essay if you have not already
Geocentric Retrograde motion Epicycles Heliocentric Ellipse Terrestrial planets Jovian planets Focus Astronomical unit Orbit period inertia Chapter 29 Vocabulary define and give one fact
Asteroids Asteroid Belt Trojan Asteroids Earth-grazers Comets Coma Oort Cloud Long period Comets Short period comets Meteor Fireball Meteor shower Meteorite Stony meteorites Iron meteorites Stony-iron meteorites Chapter 29 Vocabulary define and give one fact
Ptolemy Who is he? Greek astronomer lived in 200 AD? Was in Egypt look into the Geocentric universe. What did he do? Discovered that planets had a retrograde motion and introduced the epicycle to preserve the geocentric model Diagram his ideas Who first promoted this idea and when? Aristotle in 384 – 322 BC Compare models of the universe developed by Ptolemy and Copernicus (Page 591)
Copernicus Who is he? Polish astronomer lived in the 1500’s looking into the epicycles of the Geocentric model. What did he do? Determined that epicycles very flawed and that it was easier to explain retrograde motion with the sun at the center of the universe and orbit speeds getting slower as you get farther away from the sun. What was different? Geo is a earth center model verses heliocentric with the sun in the middle. Retrograde in a geo in explained with epicycle orbits, in a heliocentric it is explained with different orbit speeds Diagram his ideas Compare models of the universe developed by Ptolemy and Copernicus (Page 591)
Kepler Who was he? German mathematician and astronomer, lived in the late 1500’s to early 1600’s What did he do? Was hired by another astronomer to calculate the orbits of the planets from his observations. Discovered that a heliocentric model fit his calculations best Summarize Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion (Pages 591 - 593)
Name the first law Here Law of ellipses What does this law explain? It explains the orbit shape of the planets. What effect did it have? It gave planets a perihelion (closest) and an aphelion (farthest) in their orbits and introduced the idea of an average distance or astronomical unit Summarize Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion (Pages 591 - 593)
Second law Law of equal areas What does this law explain? This describes the speed a planet will travel at different points in its orbit What effect did it have? This helps show why planets move faster or slower in their orbit, if the orbit is stable and most importantly that it is always covering the same amount area in each part of it’s orbit Summarize Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion (Pages 591 - 593)
Third law Orbital Period What does this law explain? The relationship between average distance (AU) and the Orbit period What effect did it have? It provides a way to check the time it takes a planet to orbit the sun. K*r3=p2 Summarize Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion (Pages 591 - 593)
Newton What did he look at? Kepler told as how and Newton told us why planets moved in the orbits, his explanation showed us both motion in space and on earth. What did he name it? He named the explanation Inertia and the force gravity How did he explain it? An object in motion will continue in a straight line until an outside force acts on it. He compared it to rolling a ball along a surface. Summarize Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion (Pages 591 - 593)
Essay on the inner and outer planets (must be at least 5 paragraphs) • Type of planet (terrestrial or Jovian) • Tell me something about the Atmosphere • How long is the Day and year • Volcanism and terrane • Temperatures (day and night) • Magnetic field and gravity • Planet core
Terrestrial Planets The four inner planets of our solar system (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars). Formed close to the sun and materials with low boiling points were driven off. Mostly solid rock with a metal core, do not have rings, have impact craters. Identify the basic Characteristics of Mercury and Venus (Pages 594 - 596)
Mercury Closest to the sun, takes 88 days to orbit. It takes 59 days rotation, no moons. The sun obscures our view most of the time. In 74 and 79 Mariner 10 visited Mercury, revealed a heavily cratered surface ,planet has changed little since it’s formation. It may have been volcanic, evidence of lava flows and crustal contraction. Thin atmosphere due to distance from the sun and low gravity. At night (-173C) and day (427C) temperature change. A weak magnetic field indicates that it’s core may still be molten. Identify the basic Characteristics of Mercury and Venus (Pages 594 - 596)
Identify the basic Characteristics of Mercury and Venus (Pages 594 - 596) • Venus • Second from the sun. Orbits the sun in 225 days & rotates in 243 days, has no moons. • The planets rotation is backwards, the sun will rise in the west. • Venus is close to the earth in size, mass and density. • Its has a dense atmosphere, average temperature of 464C and atmospheric pressure 90 times that of earth. • Venus may have started off with oceans, but as the sun heated up and volcanic activity they boiled away. • The carbon dioxide built up in the atmosphere to 96%. • Because of the lack of water, clouds are made of sulfuric acid. • In the 70’s the Soviet Union sent several probes to the surface that lasted long enough to send images back of a rocky plain, some mountains and valleys. • Surface rock mainly basalt and granite. • In 1990 and 1992 Magellan orbited Venus and produced images of the surface mostly lava field, mountains and volcanoes.
Earth Third from the sun, completes a rotation in 23 hours 56 minutes and orbits in 365.24 days. The fifth largest planet, has one moon. Life exist on this planet, warm enough for liquid water and cool enough to keep it from escaping the atmosphere. Liquid water allowed carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to combine with this water and prevented it from building up in the atmosphere. This allows solar heat to escape the planet, keeping it cool enough for life to develop. Plants and cyanobacteria add to the oxygen levels in the atmosphere. Identify the basic Characteristics of Earth and Mars (Pages 596 - 597)
Mars Fourth from the sun, orbits in 687 days and rotation is 24 hours 37 minutes. Has season like earth because it is tilted on its axis much like earth, has two moons. Has been geologically active, Olympus Mons is 3 times higher then Mount Everest and a base the size of Nebraska. Deep canyons, Valles Marineris is as long as the United States – 4,500 km, formed from along a huge fault zone. The atmospheric pressure and temperature is too low to form liquid water. However several space probes have found evidence of flooding. What is left is trapped as ice at the polar ice caps. Summer at the equator is 20C and winter at the poles is -130C Identify the basic Characteristics of Earth and Mars (Pages 596 - 597)
Jovian Planets The four planets farthest from the sun are called the outer planets. They are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune They are called gas giants and are the largest planets in the solar system. They are also called Jovian because they are similar to Jupiter. The gas giants are larger, but less dense then the inner planets, they have thick atmospheres made mostly of hydrogen and helium. have a core of rock, metal and water. Identify the basic Characteristics of Jupiter and Saturn (Pages 598 - 600)
Identify the basic Characteristics of Jupiter and Saturn (Pages 598 - 600) • Jupiter, fifth planet from the sun. • twice the mass of all the other seven planets combined. • Takes 12 years to orbit and rotates in 9 hours and 50 minutes. • interior temperature is 30,000C and has a liquid metal core. • The planet is 92% hydrogen and helium, like the sun. • The different colors bands are due to water, methane, and ammonia moving around the planet. • The atmosphere temperature is between -160C and 20C. • The most recognized feature is the Great red spot.
Saturn Sixth from the sun, 1 billion Kilometers from the sun Second largest in the solar system Average temperature is -176 Has 151 moons and has a complex ring system Rotation period of 10 hours and 30 minutes Orbit period is 29.5 years Least dense planet in the solar system Identify the basic Characteristics of Jupiter and Saturn (Pages 598 - 600)
Uranus Seventh from the sun Third largest in the solar system Average temperature is -214 Has 20 moons and has 11 rings Rotation period of 17 hours and 14 minutes, rotating like a ball on it’s side Orbit period is 83.8 years Discovered in 1781 Greenish color indicates methane in the atmosphere. Identify the basic Characteristics of Uranus and Neptune (Pages 601 - 604)
Neptune Eighth from the sun, similar in size to Uranus Average temperature is -225 Has 8 moons and has 4 rings Rotation period of 16 hours and 07 minutes Orbit period is 163.7 years Discovered in mid-1800’s by Johann Galle Existence was predicted before it was discovered by John Couch Adams and Urbain Leverrier It has the solar systems strongest winds exceeding 1000 km/hr Identify the basic Characteristics of Uranus and Neptune (Pages 601 - 604)
Pluto Ninth from the sun Average temperature is -236 Has 1 moon that always faces the same side Rotation period of 6.4 days Orbit period is 248.6 years Discovered in 1930 by Clyde Tombaugh Accidental discovery, was looking for a planet x, Pluto is to small to cause wobble It distance from the sun varies from 4.4 billion km to 7.4 billion km Identify the basic Characteristics of Pluto (Pages 604 - 605)
Asteroids Largest of the small bodies in our solar system Most are between Mars and Jupiter, in the asteroid belt All the material in the belt would not be as massive as our moon The asteroid belt exist because gravity from Jupiter may have prevented a planet from forming Describe one physical characteristic of asteroids and comets
Three types of asteroids based on there composition Carbon materials make asteroids with a dark appearance Iron and Nickel asteroids have a metallic appearance Silicate look like the surface of the planet earth Describe one physical characteristic of asteroids and comets
Trojan asteroids travel in the same orbit as Jupiter, just ahead and just behind Earth grazers travel in orbits that cross the our orbit on there way around the Sun Describe one physical characteristic of asteroids and comets
Comets Made from rock, dust, methane, ammonia and ice The core or nucleus is between 1km and 100km diameter The coma is a dust cloud that forms around the comet as it approaches the sun The tail is formed from the dust being pushed back by the solar winds Some have a long period orbit Some have a short period, less then 100 years. Halley’s comet comes by every 76 years, it last passed in 1986. Describe one physical characteristic of asteroids and comets
Meteoroids are found in space Sometimes some will survive the entry into our atmosphere to become a meteorite Meteorites are found on the surface of planets Most are less then 1kg Meteors cross our atmosphere most will burn up as a shooting star Most are between 1mm and 1 cm in diameter Some will vaporize quickly in a flash of light called a fireball, a loud sound may follow If a large number enter our atmosphere at one time it is called a meteor shower About 1 million kg fall every day Compare and contrast meteoroids, meteorites, and meteors