DISPLACEMENT
120 likes | 263 Vues
N4. N5. ELECTRICITY & CHEMISTRY. CHEMISTRY. CHEMISTRY. DISPLACEMENT. N4. N5. ELECTRICITY & CHEMISTRY. CHEMISTRY. CHEMISTRY. DISPLACEMENT. After completing this topic you should be able to : .

DISPLACEMENT
E N D
Presentation Transcript
N4 N5 ELECTRICITY& CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY DISPLACEMENT
N4 N5 ELECTRICITY& CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY DISPLACEMENT After completing this topic you should be able to : • State a displacement reaction occurs when a metal is added to a solution containing ions of a metal lower in the electrochemical series. • State the reaction of metals with acids can establish the position of hydrogen in the electrochemical series. • Use the Electrochemical Series to make a prediction about a displacement reaction. • Identify the reactants, which undergo oxidation and reduction during a displacement reaction. N5 • Combine oxidation and reduction reactions to give a redox reaction. N5
DISPLACEMENT METALS AND SOLUTIONS AIM: To find out what happens when a metal is placed in a solution containing a metal ion. Using a dimple tray, small pieces of Mg, Zn and Cu were placed into solutions containing different metal ions. If a reaction takes place the surface of the metal changes colour. Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) Mg2+(aq) Mg Zn Cu
METALS AND SOLUTIONS RESULTS SOLUTION METAL Mg METAL ION FORMULA Zn Cu • = reaction • = no reaction MgSO4 (aq) Mg2+ (aq) ZnSO4 (aq) Zn2+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) CuSO4(aq) Ag+(aq) AgNO3(aq) Magnesium (Mg) reacted with most of the metal ion solutions. Copper (Cu) only reacted with the solution containing the silver ion (Ag+).
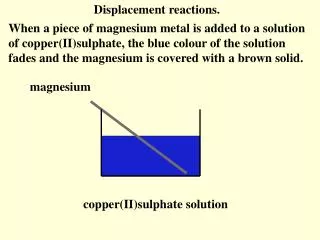
DISPLACEMENT Magnesiumreacted with every solution EXCEPT magnesium sulfate. The magnesium was pushing the metals in the solutions out and taking their place. When magnesium was placed in copper(II)sulfatesolution, copper metal was pushed out by the magnesium and magnesium sulfatesolution formed. Mg2+ Cu2+ SO42- Magnesium has displaced the copper(II) ion from the copper(II) sulfate solution to form copper metal. Cu Mg magnesium copper(II)sulfate + magnesiumsulfate + copper CuSO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) Cu(s) Mg(s) + +
DICTIONARY - DISPLACEMENT REACTION When a metalpushes another metal out of a solution and takes its place in the solution, we call this a DISPLACEMENT REACTION. ELECTROCHEMICAL SERIES RULE 2 A metal will displace another metal which is LOWER DOWN the ELECTROCHEMICAL SERIES from its solution. ELECTROCHEMICAL SERIES The electrochemical series can be used to predict when a displacement reaction will take place. Magnesium is above zinc, copper and silver and therefore was able to DISPLACE these metals from their solutions.
ACIDS AND METALS All acids contain the hydrogen ion [H+(aq)]. When a metal reacts with an acid the hydrogen ions in the acid are displaced out of the acid as hydrogen gas [H2(g)]. All metals above hydrogen on the ELECTROCHEMICAL SERIES can displace hydrogen ions [H+(aq)]from an acid as hydrogen gas [H2(g)]. This means metals above hydrogen react with acids. When magnesium is placed in sulphuric acid the magnesium displaces the hydrogen ionsas hydrogen gas molecules. H2 Magnesiumsulphate also forms. H+ H+ SO42- Mg Mg2+ magnesium sulphuric acid + magnesiumsulphate + hydrogen H2SO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) H2(g) Mg(s) + +
N5 DISPLACEMENT& REDOX CHEMISTRY A DISPLACEMENTREACTION is also a REDOXREACTION as electrons are transferred from one reactant to another. Zincdisplaces copper from copper(II) sulfateto produce a solution of zincsulfate. The zinc atoms each lose 2 electrons to form zinc ions. + Zn(s) Zn2+(aq) 2 e- e- e- Zn2+ Zn Cu2+ The zinc atoms are OXIDISED. SO42- Cu The copper(II) ions in the solution each gain 2 electrons from thezinc atomsto form copper atoms. Cu(s) The copper(II) ions are REDUCED. 2 e- Cu2+(aq) +
In all DISPLACEMENTREACTIONS the metalthatis added to a solution containing metal ions (or hydrogen ions in an acid) undergoes OXIDATION. The metal ions in solution (or hydrogen ions in an acid) undergo REDUCTION. + Mg(s) Mg2+(aq) 2 e- H2 The magnesium atoms are OXIDISED. e- e- H+ H+ SO42- Mg2+ H2(g) 2 e- 2 H+(aq) + Mg The hydrogen ions (H+) are REDUCED.
N5 REDOX EQUATIONS CHEMISTRY AREDOXEQUATION can be written by combining the equations for the oxidation and reduction reactions. EXAMPLE: Zincdisplacing copper from copper(II) sulfateto produce a solution of zincsulfate. Combining the oxidation and reduction reactions to give the redox reaction, results in the 2 electrons (2e-)cancelling, as they will appear on opposite sides of each reaction. + Zn(s) OXIDATION Zn2+(aq) 2 e- Cu(s) 2 e- Cu2+(aq) REDUCTION + Zn2+(aq) Zn(s) Cu2+(aq) Cu(s) + + REDOX Znisoxidised. Cu2+isreduced.
When combining oxidation and reduction reactions the number of electrons lost by the oxidation reaction must be the SAME as the number of electronsgained by the reduction reaction. EXAMPLE: Aluminiumdisplacing nickel from nickel(II)nitrateto produce a solution of aluminiumsulfate. The oxidation reaction is multiplied by 2, and the reduction reaction is multiplied by 3. This ensures both reactions have 6 electrons. + Al(s) OXIDATION Al3+(aq) 3 e- Ni(s) 2 e- Ni2+(aq) REDUCTION + + 2 Al(s) 2Al3+(aq) 6 e- 3Ni(s) 6 e- 3Ni2+(aq) + 2 3 2 Al3+(aq) 2 Al(s) 3 Ni2+(aq) 3 Ni(s) + REDOX + Complete the WRITING REDOX EQUATIONS examples on page 5 of the Metal Chemistry and Electricity & Chemistry Examples Booklet. Alisoxidised. Ni2+isreduced.