Understanding Stress, Deformation, and Energy in Physics
60 likes | 197 Vues
This article delves into key concepts in physics related to stress, deformation, and energy, highlighting the relationships between various forces and types of stress. Learn about stress units, the reversible nature of elastic deformation, and the distinctions between shear and tensile stress. We also explore simple harmonic motion (SHM), focusing on the maximum potential and kinetic energies and their conditions. This comprehensive overview is essential for students and enthusiasts seeking to grasp fundamental physics principles.

Understanding Stress, Deformation, and Energy in Physics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
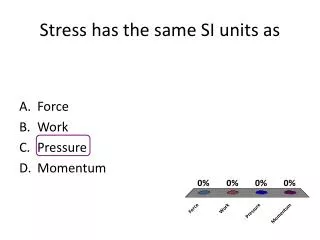
Stress has the same SI units as • Force • Work • Pressure • Momentum
Which type of deformation is reversible? • compressive • elastic • plastic
The forces used to measure shear stress and tensile stress are perpendicular to each other. • True • False
Total energy in simple harmonic motion is a maximum • At equilibrium position • At max displacement • At max velocity • None of the above • Any of the above
Kinetic energy in SHM is a maximum • when passing through the equilibrium position • when distance from equilibrium is maximized • neither of the above
Elastic potential energy in SHM is a maximum • when passing through the equilibrium position • when distance from equilibrium is maximized • neither of the above