Climate Factors and Weather Patterns
170 likes | 219 Vues
Explore the factors influencing climate and weather patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and geographic elements. Learn about latitude, altitude, bodies of water, and ocean currents. Delve into microclimates and how they shape local weather conditions.

Climate Factors and Weather Patterns
E N D
Presentation Transcript
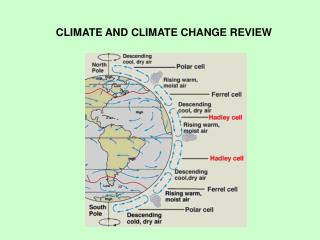
Chapter 4: Climate and Climate Change Section 1: What Causes Climate
Weather:condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time (short term) Climate:average conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds and clouds in an area (long term)
What Causes Climate? • Temperature (cold or warm climate) • Precipitation (dry or humid climate)
Factors Affecting Temperature • Latitude • Altitude • Distance From Large Bodies of Water • Ocean Currents
Latitude • Latitude: The distance from the equator measured in degrees • Temperature Zones • Tropical Zones: warm climates • Temperate Zones: ranging temperatures • Polar Zones: cold climates
Altitude • Altitude: elevation above sea level • High land areas have cooler climates • Higher altitudes = cooler temperatures • Lower altitudes = warmer temperatures
Distance From Large Bodies of Water • Marine Climates: warmer winters and cooler summers • Continental Climates: colder winters and warmer summers
Ocean Currents • Oceans and lakes can affect temperatures/climate • Ocean Currents- streams of water within the ocean that move in regular patterns • 3 examples: Gulf Stream, North Atlantic Drift, California Current
Factors Affecting Precipitation • Prevailing Winds • Mountain Ranges
Prevailing Winds • movement of air masses caused by directional winds in a region • The amount of water vapor in an air mass influences how much rain or snow will fall • The amount of water vapor in the prevailing wind depends on where the wind comes from
Mountain Ranges • Air forced up the mountain cools, condenses, and creates clouds • Falls as precipitation on windward side • Leeward side of mountain has drier conditions
Similar to ______or ______breezes, but occurs over ________ area.___________ are type of seasonal winds.Monsoons: Sea or land breeze over a large region that changes _________ with the ___________.Thailand and part of India get most of the rain from the ________ monsoons.The __________ monsoons winds brings very little rain to same regions.
Microclimates • Microclimates: small region with specific climate conditions • Examples: parks, cities, areas near lakes or ponds, gardens, etc.