DO NOW
190 likes | 354 Vues
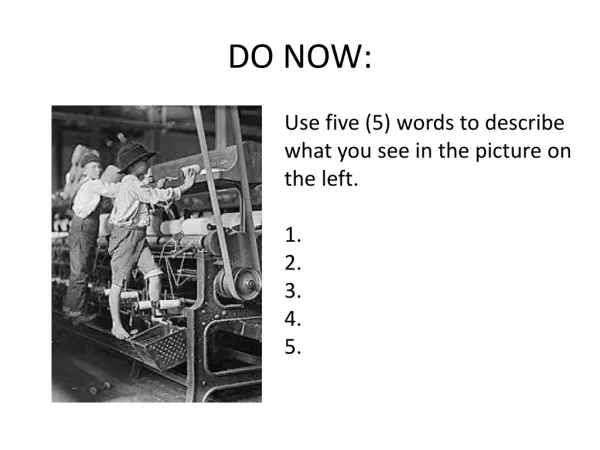
DO NOW. What phase of mitosis do chromosomes first become visible? What happens in the S phase? What role do the spindle fibers play? Draw anaphase. Meiosis.

DO NOW
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DO NOW • What phase of mitosis do chromosomes first become visible? • What happens in the S phase? • What role do the spindle fibers play? • Draw anaphase.
Meiosis occurs in diploid cells. The chromosomes duplicate once, and through two successive divisions, four haploid cells are produced, each with half the chromosome number of the parental cell.
Crossing-Over Section 11-4
Crossing-Over Section 11-4
Crossing-Over Section 11-4
Figure 11-15 Meiosis Section 11-4 Meiosis I
Figure 11-15 Meiosis Section 11-4 Meiosis I Meiosis I
Figure 11-15 Meiosis Section 11-4 Meiosis I Meiosis I
Figure 11-15 Meiosis Section 11-4 Meiosis I
Figure 11-15 Meiosis Section 11-4 Meiosis I
Figure 11-17 Meiosis II Section 11-4 Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Meiosis I results in two haploid (N) daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original. The chromosomes line up in a similar way to the metaphase stage of mitosis. The sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell. Meiosis II results in four haploid (N) daughter cells.
Figure 11-17 Meiosis II Section 11-4 Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Meiosis I results in two haploid (N) daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original. The chromosomes line up in a similar way to the metaphase stage of mitosis. The sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell. Meiosis II results in four haploid (N) daughter cells.
Figure 11-17 Meiosis II Section 11-4 Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Meiosis I results in two haploid (N) daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original. The chromosomes line up in a similar way to the metaphase stage of mitosis. The sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell. Meiosis II results in four haploid (N) daughter cells.
Figure 11-17 Meiosis II Section 11-4 Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Meiosis I results in two haploid (N) daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original. The chromosomes line up in a similar way to the metaphase stage of mitosis. The sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell. Meiosis II results in four haploid (N) daughter cells.
Figure 11-17 Meiosis II Section 11-4 Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Meiosis I results in two haploid (N) daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original. The chromosomes line up in a similar way to the metaphase stage of mitosis. The sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell. Meiosis II results in four haploid (N) daughter cells.
http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/meiosis/proi.htmlhttp://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/meiosis/proi.html