humidity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
humidity • Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is the gas phase of water and is invisible.Humidity indicates the likelihood of precipitation, dew, or fog. Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin.
Three main measurements of Humidity: • Absolute Humidity • Relative Humidity • Specific Humidity
Absolute Humidity • Absolute humidity is the mass of water vapor contained in a given volume of air. It ranges from zero to roughly 30 grams per cubic meter when the air is saturated at 30 °C. The absolute humidity changes as air pressure changes.
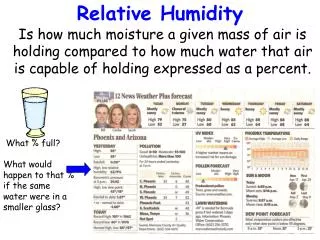
Relative Humidity • Relative humidity is a term used to describe the amount of water vapor in a mixture of air and water vapor. It is defined as the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor in the air-water mixture to . The relative humidity of air depends not only on temperature but also on pressure of the system of interest.
Specific Humidity • Specific humidity is the ratio of water vapor to dry air in a particular mass, and is sometimes referred to as humidity ratio. However, specific humidity is also defined as the ratio of water vapor to the total mass of the system in meteorology.
Dew point • The dew point temperature is the temperature at which the air can no longer "hold" all of the water vapor which is mixed with it, and some of the water vapor must condense into liquid water. • If the air temperature cools to the dew point, or if the dew point rises to equal the air temperature, then dew, fog, or clouds begin to form.
:At an air temperature of 50°C and a relative humidity of 70%, the absolute humidity is 58.1g/m3 and the dew point temperature is 43°C.