Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)
330 likes | 507 Vues
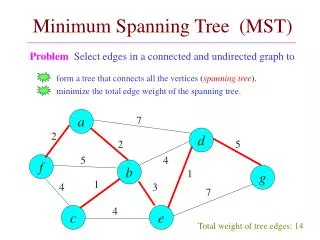
Minimum Spanning Tree (MST). Motivation. For an electrical circuit certain pins have to be grounded. Finding the arrangement of wires (connecting those pins) that uses the least amount of wire.

Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Motivation For an electrical circuit certain pins have to be grounded. Finding the arrangement of wires (connecting those pins) that uses the least amount of wire. Let a G(V,E) be a graph such that (u, v) E and a weight w(u,v) corresponding to wire needed to join u and v. We are looking for an acyclic subset T E that connects all vertices and whose total weight w(T) is minimized.
Motivation Since T is acyclic and connects all the vertices, it must form a tree. Since it spans the graph, it is called a spanning tree. MST or actually means Minimum Weight Spanning Tree.
Minimum Spanning Tree • Problem: given a connected, undirected, weighted graph: 6 4 5 9 14 2 10 15 3 8
6 4 5 9 14 2 10 15 3 8 Minimum Spanning Tree • Problem: given a connected, undirected, weighted graph, find a spanning tree using edges that minimize the total weight
Minimum Spanning Tree • Which edges form the minimum spanning tree (MST) of the following graph? A 6 4 5 9 H B C 14 2 10 15 G E D 3 8 F
Minimum Spanning Tree • Answer: A 6 4 5 9 H B C 14 2 10 15 G E D 3 8 F
Prim’s Algorithm MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 14 2 10 15 3 8 Run on example graph
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 14 2 10 15 3 8 Run on example graph
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 14 2 10 15 r 0 3 8 Pick a start vertex r
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 14 2 10 15 u 0 3 8 Black vertices have been removed from Q
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 14 2 10 15 u 0 3 8 3 Black arrows indicate parent pointers
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 14 14 2 10 15 u 0 3 8 3
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 14 14 2 10 15 0 3 8 3 u
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 14 14 2 10 15 0 8 3 8 3 u
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 10 14 2 10 15 0 8 3 8 3 u
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 10 14 2 10 15 0 8 3 8 3 u
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 10 2 14 2 10 15 0 8 3 8 3 u
Prim’s Algorithm 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 10 2 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3 u
Prim’s Algorithm u 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 10 2 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3
Prim’s Algorithm u 4 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 10 2 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3
Prim’s Algorithm u 4 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 5 2 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3
Prim’s Algorithm u 4 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 5 2 9 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3
Prim’s Algorithm u 4 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 5 2 9 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3
Prim’s Algorithm u 4 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 5 2 9 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3
Prim’s Algorithm u 4 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 5 2 9 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3
Prim’s Algorithm 4 6 4 9 5 MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); 5 2 9 u 14 2 10 15 0 8 15 3 8 3
Review: Prim’s Algorithm MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); What is the hidden cost in this code?
Review: Prim’s Algorithm MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; DecreaseKey(v, w(u,v));
Review: Prim’s Algorithm MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; DecreaseKey(v, w(u,v)); How often is ExtractMin() called? How often is DecreaseKey() called?
Review: Prim’s Algorithm MST-Prim(G, w, r) Q = V[G]; for each u Q key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; p[r] = NULL; while (Q not empty) u = ExtractMin(Q); for each v Adj[u] if (v Q and w(u,v) < key[v]) p[v] = u; key[v] = w(u,v); What will be the running time?A: Depends on queue binary heap: O(E lg V) Fibonacci heap: O(V lg V + E)