Chapter 13 Transformer Applications
211 likes | 977 Vues
Chapter 13 Transformer Applications. Chapter Objectives: Understand magnetically coupled circuits. Learn the concept of mutual inductance. Be able to determine energy in a coupled circuit. Learn how to analyze circuits involving linear and ideal transformers.

Chapter 13 Transformer Applications
E N D
Presentation Transcript
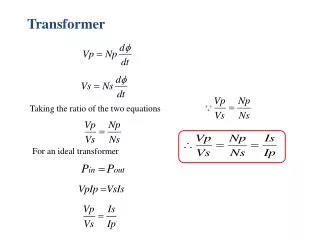
Chapter 13Transformer Applications Chapter Objectives: • Understand magnetically coupled circuits. • Learn the concept of mutual inductance. • Be able to determine energy in a coupled circuit. • Learn how to analyze circuits involving linear and ideal transformers. • Be familiar with ideal autotransformers. • Learn how to analyze circuits involving three-phase transformers. • Be able to use PSpice to analyze magnetically coupled circuits. • Apply what is learnt to transformer as an isolation device and power distribution Huseyin Bilgekul Eeng224 Circuit Theory II Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Eastern Mediterranean University
The linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) is a sensor that can reveal displacement using transformer effects. A constant low-level ac signal is applied to the primary. Voltage level induced in the secondary is based on core position, which is moved by some external force. Position of the core can be related to the secondary voltage. LVDT Transformer: LVDT transformer: (a) construction; (b) maximum displacement; (c) minimum displacement; (d) graph of induced voltage versus displacement.
Three phase transformer connections • A Y-Y three phase transformer connection. • A Δ-Δ three phase transformer connection.
Fluorescent Lamp (a) general appearance (b) internal view with ballast.
Fluorescent Lamp (a) Schematic of single-bulb fluorescent lamp; (b) starter; (c) internal view of ballast transformer.
Electrical Isolation A transformer providing AC isolation in a rectifier circuit. • Electrical ISOLATION exists between two devices when there is no physical connection between them. A transformer provides AC isolation in a rectifier circuit
DC Isolation • A transformer providing DC isolation between two amplifier stages
High Voltage Isolation • A transformer providing isolation between power lines and the voltmeter
Impedance Matching • A transformer used as a IMPEDANCE MATCHING device A transformer is used to match the load resistance to the source resistance to provide Maximum Power Transfer to the load. • A transformer matching the speaker to the amplifier. A transformer is used to match the loudspeaker to the output impedance of the amplifier.
Impedance Matching Impedance Matching for public address system
Power Distribution • A typical power distribution system