Notes on Assignment 3
100 likes | 123 Vues
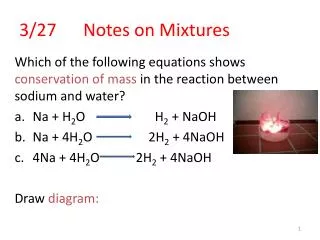
Notes on Assignment 3. Foundations of Artificial Intelligence. English to FOPC (Similar to Assignment 3 - Problem 2). Not all students take both History and Biology. ~ " x student( x ) => (takes( x , hist ) / takes( x , bio )). or alternatively.

Notes on Assignment 3
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Notes on Assignment 3 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
English to FOPC(Similar to Assignment 3 - Problem 2) Not all students take both History and Biology ~ "x student(x) => (takes(x, hist) /\ takes(x, bio)) or alternatively $x student(x) /\ ~(takes(x, hist) /\ takes(x, bio)) Only one student failed History $x student(x) /\ fails(x, hist) /\ ( "y student(y) /\ fails(y, hist) => x = y Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
Forward Chaining Proof – Example(Similar to Assingment 3 - Problem 1) KB1: (A \/B) => E KB2: ~D \/ C KB3: D /\ C => A KB4: D Give a derivation (proof) for the sentence E. 1. D KB4 2. C Step 1, KB2, using Resolution rule 3. D /\ C Step 1, Step 2, using AND-Introduction 4. A Step 3, KB3, using Modus Ponens 5. A \/ B Step 4, using OR-Introduction (introducing B) 6. E Step 5, KB1, using Modus Ponens Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
Similar to Assignment 3 - Problem 1(resolution-refutation) • Can we do this using resolution-refutation? • First need to convert everything into clause form • Next we need to negate the sentence to be proved and convert to clause form: KB1.1: ~A \/ E KB1.2: ~B \/ E KB2: ~D \/ C KB3: ~D \/ ~C \/ A KB4: D KB1: (A \/B) => E KB2: ~D \/ C KB3: D /\ C => A KB4: D E ~E Initial subgoal for resolution Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
X Similar to Assignment 3 - Problem 1(resolution-refutation) Subgoal Resolve with ~E KB1.1: ~A \/ E KB1.1: ~A \/ E KB1.2: ~B \/ E KB2: ~D \/ C KB3: ~D \/ ~C \/ A KB4: D ~A KB3: ~D \/ ~C \/ A ~D \/ ~C KB4:D KB2:~D \/ C ~C ~D KB4:D Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
Resolution Example (Assignment 3 - Problem 3) • John likes all kinds of food. • Apples are food. • Chicken is food. • Anything anyone eats and isn't killed by is food. • Bill eats peanuts and is still alive. • Anyone who is killed by anything is not alive. • Sue eats everything Bill eats. • "x food(x) => likes(john, x) • food(apple) • food(chicken) • "x"y eats(x, y) /\ ~killed-by(x, y) => food(y) • eats(bill, peanuts) /\ alive(bill) • "x"y killed-by(x, y) => ~alive(x) • "x eats(bill, x) => eats(sue, x) Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
Resolution Example(Assignment 2 - Problem 5) • "x food(x) => likes(john, x) • food(apple) • food(chicken) • "x"y eats(x, y) /\ ~killed-by(x, y) => food(y) • eats(bill, peanuts) /\ alive(bill) • "x"y killed-by(x, y) => ~alive(x) • "x eats(bill, x) => eats(sue, x) Clausal Form • 1. ~food(x) \/ likes(john, x) • 2. food(apple) • 3. food(chicken) • 4. ~eats(x, y) \/ killed-by(x, y) \/ food(y) • 5a. eats(bill, peanuts) • 5b. alive(bill) • 6. ~killed-by(x,y) \/ ~alive(x) • 7. ~eats(bill, x) \/ eats(sue, x) Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
Resolution Example(Assignment 2 - Problem 5) • 1. ~food(x) \/ likes(john, x) • 2. food(apple) • 3. food(chicken) • 4. ~eats(x, y) \/ killed-by(x, y) \/ food(y) • 5a. eats(bill, peanuts) • 5b. alive(bill) • 6. ~killed-by(x,y) \/ ~alive(x) • 7. ~eats(bill, x) \/ eats(sue, x) Prove that john likes peanuts: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
Resolution Example(Assignment 3 -Problem 3) 1. ~food(x) \/ likes(john, x) 2. food(apple) 3. food(chicken) 4. ~eats(x, y) \/ killed-by(x, y) \/ food(y) 5a. eats(bill, peanuts) 5b. alive(bill) 6. ~killed-by(x,y) \/ ~alive(x) 7. ~eats(bill, x) \/ eats(sue, x) What food does sue eat? ( i.e., $x food(x) /\ eats(sue, x)? ) $x food(x) /\ eats(sue, x) negate ~($x food(x) /\ eats(sue, x)) This can be resolved with candidate clauses 2, 3, and 4 Convert to clause form ~food(x) \/ ~eats(sue, x)) Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
English to FOPC(Similar to Assignment 3 - Problem 2) Not all students take both History and Biology ~ "x student(x) => (takes(x, hist) /\ takes(x, bio)) or alternatively $x student(x) /\ ~(takes(x, hist) /\ takes(x, bio)) Only one student failed History $x student(x) /\ fails(x, hist) /\ ( "y student(y) /\ fails(y, hist) => x = y Foundations of Artificial Intelligence