Acute Sinusitis
350 likes | 533 Vues
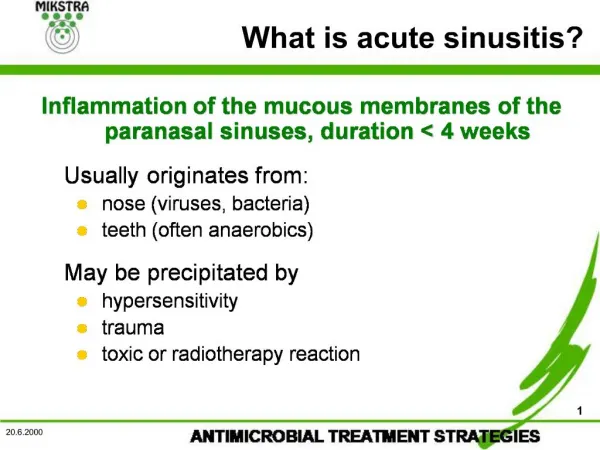
Acute Sinusitis. Definition. Acute bacterial infection of the mucosa of one or more paranasal sinuses, usually rhinogenic in origin and is characterized by acute facial pain/ head ache and purulent nasal discharge. Anatomical considerations:. Osteo-meatal complex. Types.

Acute Sinusitis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Definition Acute bacterial infection of the mucosa of one or more paranasal sinuses, usually rhinogenic in origin and is characterized by acute facial pain/ head ache and purulent nasal discharge.
Types Depending on the site Unilateral/ bilateral Pansinusitis Multisinusitis Maxillary/ frontal/ ethmoidal/ sphenoidal Depending on whether the sinus is draining or not Open type Closed type Depending on the pathology Suppurative Non-suppurative
Etiology Rhinogenic- Commonest (85%) Usually after viral rhinitis (Flu) Any form of rhinitis Dental (Maxillary) Root abscess, dental procedure, etc. Trauma RTA, Swimming and diving, FB, barotrauma, etc. Iatrogenic- nasal packing, septal surgery Hematogenous- Rare
Predisposing factors for Acute rhinosinusitis Mucosal odema of MM Any form of rhinitis: Viral, bacterial, Irritant, allergic, VMR, atrophic, etc. (environmental factors play role) Mechanical (anatomical) obstruction of nose/ MM DNS, spur, polyp, hypertrophic turbinate, any mass, FB, nasal packing, etc. Pathological mucous Thick mucous (mucoviscidosis, cystic fibrosis) Primary mucociliary dysfunction Others: Poor general health, immunodeficiency states, DM, nutritional deficiency, etc.
Bacteriology Str.Pneumoniae B-hemolytic streptococcus H.influenzae Stap. Aureus Klebsiella pneumoniae Others
Pathogenesis Obstruction to sinus ostium/ meatus Stasis of secretions (serous-mucinous): Non-suppurative Secondary bacterial invasion: Suppurative Severity and resolution depends on Open/ closed. May drain creating accessory opening. Organism virulence Host resistance Treatment received
Pathology Acute inflammatory changes: Hyperemia, odema, acute infl. infliterate. Increased activity of the mucous glands Severe suppuration Mucosal destruction Empyema Bony destruction Complications
Clinical features: SymptomsDepends on the sinus involved Constitutional symptoms: Fever, malaise, lethargy Headache/ facial pain: Dull ache, postural/diurnal. Max: Facial, forehead Frontal: Forehead, “Office headache” Ethmoid: Between the eyes, may > with eye movement Sphenoid: Vertex, occipetal Nasal discharge mucous/ mucopurulent/ purulent/ blood stained Anterior/ postnasal Nasal obstruction Cheek/ lid congestion, swelling
Clinical features: SignsDepends on the sinus involved Fever Tenderness Cheek swelling Lid odema: in ethmoid and frontal Inflamed nasal mucosa especially the meatus Discharge in MM/ SM as on anterior/posterior rhinoscopy Postural test Transillumination test Signs of complications
Investigations Clinical diagnosis Diagnostic nasal endoscopy (DNE) Radiological X-ray PNS Water’s view (Occipetomental) Caldwel view (Occipetofrontal) Lateral view Base skull view (Submento-vertical) CT scan: indicated in impending complications C/S: rarely done
Normal Sinuses Acute Maxillary Sinusitis
Treatment- Medical Antibiotics Nasal decongestants (Topical/systemic) Anti-inflammatory analgesics Medicated steam inhalation Mucolytics Hot fomentation
Surgical drainage If not responding to medical treatment Impending or manifest complications Depends on the sinus involved
Drainage procedures Acute maxillary: Antral washout/ endoscopic MMA Acute frontal: Frontal trefination/ endoscopic frontal recess clearance Acute ethmoiditis: External ethmoidectomy/ endoscopic ethmoidectomy Acute sphenoiditis: External sphenoethmoidectomy/ endoscopic sphenoidotomy
Complications Chronic sinusitis Acute sinusitis or acute exacerbations of chronic sinusitis may give rise to following complications: Orbital Intracranial Osteomyelitis Septic focus for other infections
Signs of impending/ manifest complications Spiking fever Lid odema, facial/orbital swelling Proptosis, reduced vision, reduced extraoccular movt. Severe headache and hyperirritable Projectile vomiting Meningeal signs Hypothermia Altered sensorium
Orbital complications Common in acute ethmoiditis or frontal sinusitis Direct spread/ ostitis/ thrombophlebitic Odema of the lids Subperiosteal abscess Orbitial cellulitis Orbital abscess Superior orbital fissure syndrome: Deep orbital pain, frontal headache, progressive paralysis of extraoccular movements Blindness
Intracranial Anterior cranial fossa and cavernous sinus closely related Meningitis Extradural abscess Subdural abscess Frontal lobe abscess Cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis, etc
LATERAL SINUS THROMBOSIS DELTA SIGN
Conclusion “Acute sinusitis especially in a child should be treated adequately to prevent consequent chronic sinusitis or other more severe complications which may be even fatal”.