The Human Respiratory System: Functions and Importance
340 likes | 685 Vues
Explore the purpose, gas exchange, and essential parts of the respiratory system, including the nose, mouth, lungs, and alveoli. Learn how breathing works and how diseases like bronchitis and lung cancer affect the respiratory system.

The Human Respiratory System: Functions and Importance
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Purpose • Gas Exchange • The lungs take in oxygen and let out Carbon Dioxide • Gas Exchange takes place between the lungs and capillaries
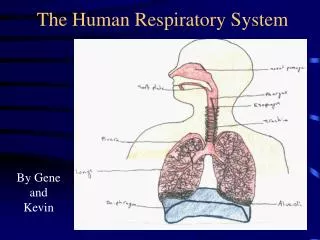
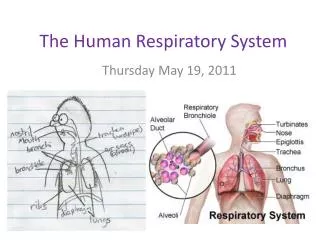
Important Parts • The Respiratory system consists • Nose (Mouth) • Pharynx • Larynx • Trachea • Bronchi • Lungs • (Bronchial tubes/Bronchioles) • (Alveoli)
Nose/Mouth Nose Mouth
Nose/Mouth • Air moves from the nose to mouth and throat • This is a passageway for both air and food • As the air is taken in it is warmed up before traveling through the rest of the system
Pharynx and Larynx Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx
Pharynx and Larynx • After the air is warmed its moves from the throat to the pharynx • The air than travels into the larynx
Larynx • The vocal cords are two highly elastic folds of tissue in the larynx • Muscles pull together • Air causes the cords to vibrate and sound comes out
Trachea Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Trachea
Trachea • A flap of tissue called the epiglottis covers the entrance to the trachea when you swallow • Held open by horseshoe shaped rings of cartilage. • The Trachea branches off into two large passageways called the bronchi • Each leads to a lung on each side of the chest
Bronchi Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Trachea R. Bronchus L. Bronchus
Bronchi • In each lung, the bronchi are divided into small tubes called bronchioles • (***If a piece of food accidentally gets past the epiglottis, it will most likely fall into the right bronchus.***) • The left one has a sharper bend due to the presence of the heart and major blood vessels directly underneath it.
Bronchial Tubes/Bronchioles Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Trachea R. Bronchus L. Bronchus Bronchioles
Alveoli • Alveoli are at the ends of the bronchioles and are tiny air sacs that bunch together like a bunch of grapes • Each alveoli are surrounded by a bunch of capillaries that is the place of gas exchange between the lungs and blood
Alveoli Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Trachea R. Bronchus L. Bronchus Bronchioles Alveoli
Lung Health • The hairs that line the nasal passageway trap large dust particles • Cells produce a think layer of mucus that traps inhaled particles • Cilia in the lungs sweep trapped particles and mucus away
Gas Exchange • Oxygen diffuses in the moisture on the inner surface of the alveoli and then diffuses across the capillaries into the blood • Carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses in the opposite direction • Air in has 21% oxygen, .04 % CO2 • Air out has 15% oxygen and 4% CO2
Breathing • Lungs have no muscles attached to them • A large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity is called the diaphragm controls the process
Diaphragm Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Trachea R. Bronchus L. Bronchus Bronchioles Alveoli Diaphragm
Breathing • When you inhale the diaphragm contracts and expands the volume of the chest cavity • This creates a vacuum and the lungs are forced to expand pulling in air • Breathing is controlled by the amount of CO2 in the blood, not O2
Diseases • Emphysema is caused by loss of elasticity of the lungs-hard to breathe • Bronchitis is the bronchi being swollen and clogged with mucus • Lung Cancer is particular deadly because it spreads to other locations
Other diseases • Pneumonia: alveoli become filled with fluid • Tuberculosis: bacterial infection of lungs that can cause a hole in the lungs
The Respiratory System Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Trachea R. Bronchus L. Bronchus Bronchioles Alveoli Diaphragm