Stability
410 likes | 711 Vues
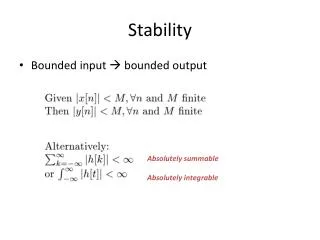
Stability. BIBO stability: Def: A system is BIBO-stable if any bounded input produces bounded output. otherwise it’s not BIBO-stable. Asymptotically Stable.

Stability
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Stability • BIBO stability: Def: A system is BIBO-stable if any bounded input produces bounded output. otherwise it’s not BIBO-stable.
Asymptotically Stable A system is asymptotically stable if for any arbitrary initial conditions, all variables in the system converge to 0 as t→∞ when input=0. All variables include y & its derivatives all state variables but y=Cx+Du=Cx if x→0 then y→0 only need to check x→0 0
If there is no pole/zero cancellation, BIBO-stable A.S. If system is C.C. & C.O. no pole/zero cancellation BIBO-stable A.S. Exact pole/zero cancellation only happens mathematically, not in real systems. From now on, assume no p/z cancellation BIBO stable A.S. all char. val<0 all eigenvalues<0 all poles<0
Thm: If a system is A.S. then it is BIBO-stable But BIBO-stable A.S. (mathematically)
A polynomial is said to be Hurwitz or stable if all of its roots are in O.L.H.P A system is stable if its char. polynomial is Hurwitz A nxn matrix is called Hurwitz or stable if its char. poly det(sI-A) is Hurwitz all eigenvalues<0
Routh-Hurwitz Method From now on, when we say stability we mean A.S. / M.S. or unstable. We assume no pole/zero cancellation, A.S. BIBO stable M.S./unstable not BIBO stable Since stability is determined by denominator, so just work with d(s)
Repeat the process until s0 row Stability criterion: • d(s) is A.S. iff 1st col have same sign • the # of sign changes in 1st col = # of roots in right half plane Note: if highest coeff in d(s) is 1, A.S. 1st col >0 If all roots of d(s) are <0, d(s) is Hurwitz
Example: ←has roots:3,2,-1
(1x3-2x5)/1=-7 (1x10-2x0)/1=10 (-7x5-1x10)/-7
Routh Criteria Regular case: (1) A.S. 1st col. all same sign (2)#sign changes in 1st col. =#roots with Re(.)>0 Special case 1: one whole row=0 Solution: 1) use prev. row to form aux. eq. A(s)=0 2) get 3) use coeff of in 0-row 4) continue
Example ←whole row=0
Useful case: parameter in d(s) How to use: 1) form table as usual 2) set 1st col. >0 3) solve for parameter range for A.S. 2’) set one in 1st col=0 3’) solve for parameter that leads to M.S. or leads to sustained oscillation
Example + s+3 s(s+2)(s+1) Kp
+ K(s+z) s+p 1 s(s2+2s+8) -