Understanding Niches and Competition: Insights from Darwin's Quote
130 likes | 240 Vues
Charles Darwin's insight into the struggle for existence underscores the critical concept of niches and competition within ecosystems. An organism's niche is its unique role, encompassing its interactions, habitat, and the environmental factors it depends on. Competition arises when different individuals or species vie for the same limited resources, highlighting the dynamics of coexistence. From competition for food among lions, hyenas, and cheetahs to mutual benefits in partnerships, understanding these interactions is essential to grasping ecological balance and biodiversity.

Understanding Niches and Competition: Insights from Darwin's Quote
E N D
Presentation Transcript
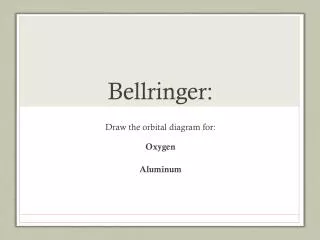
Bellringer “As more individuals are produced that can possibly survive, there must…be a struggle for existence, either one individual with another of the same species, or with the individuals of distinct species, or with the physical conditions of life.” - Charles Darwin How does this quote relate to niches and competition?
Section 2 How Species Interact with Each Other
I. An Organism’s Niche niche _____ the unique role of a species within an ecosystem A niche includes an organisms: physical home environmental factors species interactions
Habitat is different from niche Habitat is location Think of a niche as the organism’s job or function Niche example, Fruit Bat: Lives in trees and caves Pollinates flowers Spreads seeds Interacts with hawks and owls
II. Ways In Which Species Interact Competition ___________ relationship in which different individuals or populations attempt to use the same limited resource Can occur: Between species Within species Indirectly
Between species: Lions, Hyenas, and Cheetahs all compete for the same food on the African savannah’s Within species: Two different loblolly pines growing close to each other Think of this as more of a resource limitation
Indirect Competition: Two closely relates species sharing a habitat resulting in Niche restriction or Niche differentiation: Examples… Both mice and man will consume crops such as corn, however in this relationship these organisms will rarely interact
Two monkey species feed at different heights within a tree Two species of mice, one nocturnal and one diurnal, both feed on insects. They feed at different times
Predation, Parasitism, Mutualism, and Commensalism Predator/Prey – One organism eating another Example: snake (predator) eating a mouse (prey)
Parasitism – An organism that takes nourishment from an organism Two parts: Parasite – organism that feeds on another organism Host - organism that is providing nourishment to the parasite
Different from a predator b/c the parasite spends all or most of its life in or on the host
Mutualism – Two organisms living in harmony helping each other out A butterfly and a flower. How do they help each other?
Commensalism – One species benefits, the other is not harmed but doesn’t benefit Describe the relationship between the following organisms. How are each an example of commensalism?