What is Public Opinion?
380 likes | 711 Vues
What is Public Opinion?. Public Opinion. What the public thinks about a particular issue or set of issues at a particular time. Efforts to Influence and Measure Public Opinion. Early Efforts to Measure Public Opinion. 1824 - 1936 Crude postcard polling

What is Public Opinion?
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Public Opinion • What the public thinks about a particular issue or set of issues at a particular time.
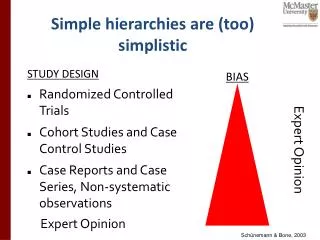
Early Efforts to Measure Public Opinion 1824 - 1936 • Crude postcard polling • Survey postcards would be mailed to potential voters • Straw Polls • Non-representative of the general population. • Relied on asking as many people as possible a given set of questions and paid no attention to having a random or scientific sample.
Recent Efforts to Measure Public Opinion • In 1936 George Gallup successfully predicted the winner of that year’s election. • In 1948 the Gallup Organization and many other pollsters incorrectly predicted that Thomas E. Dewey would defeat President Harry S. Truman. • In the 2000 election (Bush v. Gore) the Gallup Organization announced the election was too close to call.
The Family School and Peers The Mass Media Social Groups Impact of Events Political Ideology
The Family • Many children adopt their parents’ political ideology.
School and Peers • Schools instill a sense of patriotism and respect for the nation at an early age. • From age five onward, a child's peers effect their political ideology more and more.
The Mass Media • Television pundits and radio personalities help to influence public opinion. • Rush Limbaugh lead a successful voter raid on behalf of Hillary Clinton against Obama during the 2008 primaries in Texas and Ohio.
Social Groups • Religion • Race and Ethnicity • Gender • Age • Region
Impact of Events • Political events can greatly change public opinion • Resignation of Richard Nixon and the Watergate scandal created huge distrust between the public and politicians.
Political Ideology and Public Opinion About Government • Political Ideology – The coherent set of values and beliefs about the purpose and scope of government held by groups and individual.
Personal Benefits • More and more people are “voting with their pocket book.” • the elderly favor Social Security.Americans have trouble forming opinions on issues that don’t directly affect them. • Americans know very little about the rest of the world, so they don’t very often develop opinions about it.
Political Knowledge • Americans, in general, have a very poor understanding of history and politics, despite abundant access to information and education.
Cues from Leaders • Political leaders often greatly influence the political ideology of the public.
Traditional Public Opinion Polls • Determine the Content and Phrasing the Questions • Selecting the Sample • Contacting Respondents
Political Polls • Push Polls – telephone “polls” that spread negative or even false information about an opposing candidate. • Tracking Polls – allow presidential candidates to monitor short term campaign developments. • Exit Polls – used to help new outlets predict the outcome of elections.http://www.cnn.com/ELECTION/2008/results/polls/#val=USP00p1
Bush's campaign strategists, including Karl Rove, devised a push poll against John McCain. South Carolina voters were asked "Would you be more likely or less likely to vote for John McCain for president if you knew he had fathered an illegitimate black child?". They had no interest in the actual percentages in the poll, the goal was to suggest that [McCain had a black child]. This was particularly vicious since McCain was campaining with his adopted [dark skinned] Bangladeshi daughter
Some aspects of McCain's smear were hardly so subtle. Bob Jones University professor Richard Hand sent an e-mail to 'fellow South Carolinians' stating that McCain had 'chosen to sire children without marriage.' It didn't take long for mainstream media to carry the charge. CNN interviewed Hand and put him on the spot: 'Professor, you say that this man had children out of wedlock. He did not have children out of wedlock.' Hand replied, 'Wait a minute, that's a universal negative. Can you prove that there aren't any?'"
Shortcomings of Polling • Sampling Error – accuracy. • Limited Respondent Options – limited possible responses. • Lack of Information – Public may not be accurately informed or disaffected. • Intensity – polls don’t depict how strongly some one feels about an issue.
How Polling and Public Opinion Affect Politicians, Politics, and Policy
“All Government Rests On Public Opinion” • As a result public opinion inevitably influences the actions of politicians. • As a consequence of extensive polling, there is a “bandwagon” effect that results in people jumping behind a candidate, just because polls show that the public is in support of a candidate.
Support for legalization of marijuana reaches all time high. Marijuana