CE-Notes 71-72 Law Enforcement
170 likes | 266 Vues
CE-Notes 71-72 Law Enforcement. DO NOW: Week 13. MONDAY: What was the 1st social contract in the colonies? What English document first limited the power of the king and protected the rights of citizens? TUESDAY: What was the first law code called?

CE-Notes 71-72 Law Enforcement
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DO NOW: Week 13 MONDAY: • What was the 1st social contract in the colonies? • What English document first limited the power of the king and protected the rights of citizens? TUESDAY: • What was the first law code called? • What English document inspired our Bill of Rights? • What was America’s first Constitution? WEDNESDAY: • What type of law is based on precedent or previous court decisions? • What type of law is made by government agencies? • What type of law deals with treaties and trade agreements between nations?
Identify which type of lawCommon, criminal, civil, statutory, constitutional, administrative or international • OSHA requires all Construction workers to wear hardhats on a site. • Slavery is outlawed in the 13th Amendment • Paris Hilton sues the National Enquirer for libel (printing false statements about her). • A woman robs the local bank and steals a car to get away • The United States signs an agreement with North Korea not to produce any more nuclear weapons • The NC General Assembly passes a law that all school buses must stop at railroad tracks • North Carolina schools were found in violation of the precedent set in Brown v. Board of Education and told to integrate their schools in 1971
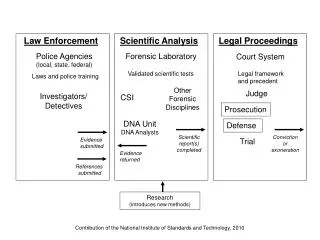
Law Enforcement • CE Notes 71-72
Objectives • SWBAT Identify the various procedures in the enactment, implementation, and enforcement of law • SWBAT compare responsibilities, jurisdictions, and methods of law enforcement agencies.
RAP 71 • Who is responsible for keeping order in the County? • Who is responsible for keeping order in the city? • What does jurisdiction mean?
Notes 71 • All Law enforcement agencies are under the Executive Branch of city, county, state or federal government. • Department of Justice (DOJ): Enforces Federal Law and oversees all federal law enforcement agencies except the CIA and Secret Service. • The Attorney General is the head of the DOJ & part of the President’s cabinet
Purpose of federal agencies: each has specialized skills which can help to enforce laws. • Ex: the DEA (drug enforcement administration) has agents specialized in preventing drug trafficking.
Notes 72 Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI): • Jurisdiction: Federal • Function: investigates all federal crimes in the US • Examples: crimes crossing state lines, investigating terrorist threats within the US
Notes 72: National Security • Central Intelligence Agency (CIA): • Jurisdiction: Federal • Function: responsible for the USA’s national security. Investigates international threats. • Ex: gets information on terrorists in other countries
Secret Service: • Jurisdiction: Federal • Function: Protects the Pres. & VP. Investigates $$ counterfeiting. • Ex: president’s security guards
Notes 72 • State Bureau of Investigation (SBI): • Jurisdiction: State • Function: Assists local law enforcement in large criminal investigations. • Ex: investigating a string of bank robberies across the state or computer crimes against children.
State Troopers: • Jurisdiction: State • Function: Enforce traffic laws on state highways. • Ex: monitor speed on roads like I-85, or Route 1
Notes 72 County Jurisdiction: • Sheriff: • Jurisdiction: County • Function: enforces laws in both the incorporated and unincorporated areas of the county. • Ex: Sheriff is responsible for courthouse security
City/Town Jurisdiction • Police: • Jurisdiction: City/Town • Function: enforces city & ordinances • Ex: make an arrest following robbery
Magistrate: In criminal cases determines if further action is warranted when a police officer or a citizen claims that a crime has been committed. • National Guard: reserve militaries in each state that are called to federal service. Can serve in the US or abroad.
PIT 71 LAW ENFORCEMENT THEATER!! • You will have 10 min to plan how to act out your enforcement scenarios. • Your act will last 30 seconds long • If the class correctly guesses which law enforcement agency will be called in to deal with your scenario you will be rewarded.