X-ray Image Segmentation using Active Shape Models
270 likes | 458 Vues
X-ray Image Segmentation using Active Shape Models. Mayuresh Kulkarni (KLKMAY001). Presentation Overview. Introduction Problem Description Basic Segmentation Techniques Active Shape Models (ASMs) Performance Evaluation of ASMs Conclusions. Introduction. Medical Imaging

X-ray Image Segmentation using Active Shape Models
E N D
Presentation Transcript
X-ray Image Segmentation using Active Shape Models MayureshKulkarni (KLKMAY001) Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Presentation Overview • Introduction • Problem Description • Basic Segmentation Techniques • Active Shape Models (ASMs) • Performance Evaluation of ASMs • Conclusions Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Introduction • Medical Imaging • Using Digital Imaging for applications in medicine • MRI scans, CT scans, digital X-rays etc. • In this thesis • Digital X-rays of the tibia • Image Segmentation Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
The Problem • The Big Picture • Detecting bone fractures automatically • X-ray Image segmentation • Feature Extraction • Pattern Recognition • The first step • X-ray image segmentation • Extracting the bone from the image Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Basic Segmentation Techniques • Image Segmentation methods • Edge detection: Sobel, Prewitt, Roberts, Canny • Texture Analysis: Range and Std filtering • Limitations of basic techniques • Detect all edges • Detects the skin and the bone edge • Difficult to separate the bone from the X-ray Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Filtering and Thresholding • Assumes that X-rays are ideal • The brightness is uniform • Bone boundary is brighter than the skin boundary • 2 Levels of thresholding • Multiplying mask with original image Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Filtering and Thresholding Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
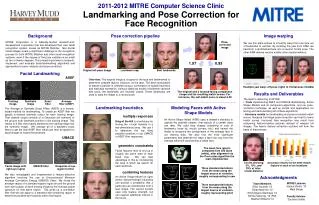
Active Shape Models • Training images are landmarked • Learning the shape from training images • Creating profile models at landmark points • Recording the shape • Searching the shape in the test image Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
ASM: Sub-models • Profile Model • Analyzes the landmark points • Stores the image behaviour around landmarks • Builds a profile model for each landmark • Shape Model • Defines the permissible shapes and landmarks • Introduces a constraint on the search shape • Calculates the mean shape Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Training Images Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
The Mean Shapes Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Creating profile Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Searching the shape Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Defining the Error • Hand annotating the X-ray images • Distance transform • Comparing the ASM output to hand annotated images • Visual Check • Does the ASM track the bone? • Is it effective? Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Performance Evaluation Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Performance Evaluation Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Performance Evaluation Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Performance Evaluation Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
Conclusions • Basic segmentation techniques • Work for certain images • Separate the bone • But are susceptible to noise • Active Shape Models • Extract the bone effectively • Perform well with different bone orientations Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
THANK YOU Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
References • M. Donnelley. Computer aided Long-bone Segmentation and Fracture Detection. PhD thesis, Flinders University of South Australia, January 2008. • C. Ying. Model-Based Approach for Extracting Femur Contours in X-ray Images. Master’s thesis, National University of Singapore, 2005. • T. F. Cootes and C. J. Taylor. Technical Report: Statistical Models of Appearance for Computer Vision. Technical report, The University of Manchester School of Medicine, 2004. • T. F. Cootes, C. J. Taylor, D. Cooper, and J. Graham. A Trainable Method of Parametric Shape Description. 2nd British Machine Vision Conference, pages 54–61, 1991. • S. E. Lim, Y. Xing, Y. Chen, W. K. Leow, T. S. Howe, and M. A. Png. Detection of Femur and Radius Fractures in X-Ray Images. 2nd International Conference on Advances in Medical Signal and Information, pages 249–256, 2004. • V. L. F. Lum, W. K. Leow, Y. Chen, T. S. Howe, and M. A. Png. Combining classifiers for bone fracture detection in X-ray Images. Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)
References 8. T. P. Tian, Y. Chen, W. K. Leow, W. Hsu, T. S. Howe, and M. A. Png. Computing neck- shaft angle of femur for x-ray fracture detection. International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, 2003. • T. T. Peng. Detection of Femur Fractures in X-ray images. PhD thesis, National University of Singapore, 2002. Mayuresh Kulkarni (BSc. Elec. Eng. UCT)