Chapter 14 Acids and Bases
190 likes | 495 Vues
Chapter 14 Acids and Bases. 14.8 Acid-Base Titration. Titration http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g8jdCWC10vQ&list=PL13E6D5AEF3861CE0&index=8&feature=plpp_video. Acid-Base Titration. Base (NaOH). Titration is a laboratory procedure used to determine the molarity of an acid

Chapter 14 Acids and Bases
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 14 Acids and Bases 14.8 Acid-Base Titration
Titration • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g8jdCWC10vQ&list=PL13E6D5AEF3861CE0&index=8&feature=plpp_video
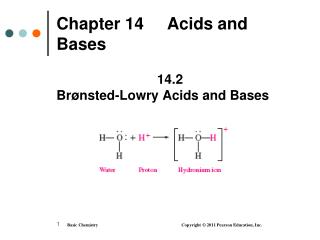
Acid-Base Titration Base (NaOH) Titration • is a laboratory procedure used to determine the molarity of an acid • uses a base such as NaOH to neutralize a measured volume of an acid Acid solution
Indicator An indicator • is added to the acid in the flask • changes the color of the solution when the acid is neutralized
End Point of Titration At the end point, • the indicator has a permanent color • the volume of the base used to reach the end point is measured • the molarity of the acid is calculated using the neutralization equation for the reaction
Example of Calculating Molarity What is the molarity of 10.0 mL of HCl solution if 18.5 mL of 0.225 M NaOH are required to neutralize the HCl? HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) STEP 1State the given and needed quantities and concentration. Given 18.5 mL of a 0.225 M NaOH solution 18.5 mL of NaOH = 0.0185 L of NaOH 10.0 mL of HCl = 0.0100 L of HCl Need molarity of HCl solution
Calculating Molarity (continued) STEP 2Write a plan to calculate molarity. L of NaOH moles of NaOH moles of HCl molarity of HCl STEP 3 State equalities and conversion factors including concentrations. 1 L of NaOH = 0.225 mol of NaOH 1 L NaOH and 0.225 mol NaOH 0.225 mol NaOH 1 L NaOH 1 mol of NaOH = 1 mol of HCl 1 mol HCl and 1 mol NaOH 1 mol NaOH 1 mol HCl
Calculating Molarity (continued) STEP 4 Set up problem to calculate needed quantity. 0.0185 L NaOH x 0.225 mol NaOH x 1 mol HCl 1 L NaOH 1 mol NaOH = 0.00416 mol of HCl Molarity of HCl = 0.00416 mol HCl = 0.416 M HCl 0.0100 L HCl
Learning Check Calculate the milliliters of 2.00 M H2SO4 needed to completely neutralize 0.0500 L of 1.00 M KOH. H2SO4(aq) + 2KOH(aq) K2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l) 1) 12.5 mL 2) 50.0 mL 3) 200. mL
Solution STEP 1State the given and needed quantities and concentration. Given 0.0500 L of a 1.00 M KOH solution 1 L of H2SO4 = 2.00 mol of H2SO4 1000 mL of H2SO4 = 1 L of H2SO4 Need milliliters of H2SO4 solution STEP 2Write a plan to calculate milliters. L of KOH moles of KOH moles of H2SO4 liters of H2SO4 mL of H2SO4
Solution (continued) STEP 3 State equalities and conversion factors including concentrations. 1 L of KOH = 1.00 mol of KOH 1 L KOH and 1.00 mol KOH 1.00 mol KOH 1 L KOH 2 mol of KOH = 1 mol of H2SO4 1 mol H2SO4 and 2 mol KOH 2 mol KOH 1 mol H2SO4 1 L of KOH = 1000 mL of KOH 1 L KOH and 1000 mL KOH 1000 mL KOH 1 L KOH
Solution (continued) STEP 3 (continued) 1 L of H2SO4 = 2.00 mol of H2SO4 1 L H2SO4 and 2.00 mol H2SO4 2.00 mol H2SO4 1 L H2SO4 STEP 4 Set up problem to calculate needed quantity. 0.0500 L KOH x 1.00 mol KOH x 1 mol H2SO4 1 L KOH 2 mol KOH x 1 L H2SO4 x 1000 mL H2SO4 = 12.5 mL of H2SO4 2.00 mol H2SO4 1 L H2SO4 (1)
Learning Check A 25.0 mL sample of phosphoric acid is neutralized by 42.6 mL of 1.45 M NaOH. What is the molarity of the phosphoric acid solution? 3NaOH(aq) + H3PO4 (aq) Na3PO4(aq) + 3H2O(l) 1) 0.62 M 2) 0.841 M 3) 0.185 M
Solution STEP 1State the given and needed quantities and concentration. Given 42.6 mL of a 1.45 M NaOH solution 25.0 mL of a H3PO4 solution Need molarity of H3PO4 solution STEP 2Write a plan to calculate molarity. mL of NaOH L of NaOH moles of NaOH moles of H3PO4 liters of H3PO4 molarity of H3PO4
Solution (continued) STEP 3 State equalities and conversion factors including concentrations. 1 L of NaOH = 1.45 mol of NaOH 1 L NaOH and 1.45 mol NaOH 1.45 mol NaOH 1 L NaOH 3 mol of NaOH = 1 mol of H3PO4 1 mol H3PO4 and 3 mol NaOH 3 mol NaOH 1 mol H3PO4 1 L of NaOH = 1000 mL of NaOH 1 L NaOH and 1000 mL NaOH 1000 mL NaOH 1 L NaOH
Solution (continued) STEP 3 (continued) 1 L of H3PO4 = 1000 mL of H3PO4 1 L H3PO4 and 1000 mL H3PO4 1000 mL H3PO4 1 L H3PO4 STEP 4 Set up problem to calculate needed quantity. 0.0426 L NaOH x 1.45 mol NaOH x 1 mol H3PO4 1 L NaOH3 mol NaOH = 0.0206 mol of H3PO4
25.0 mL H3PO4 x1L H3PO4 = 0.0250 L H3PO4 1000 mL H3PO4 0.0206 mol H3PO4 = 0.841 M (2) 0.0250 L H3PO4 Solution (continued) 18