Immune System
340 likes | 472 Vues
Immune System. Innate immunity is present before any exposure to pathogens and is effective from the time of birth It involves nonspecific responses to pathogens Innate immunity consists of external barriers plus internal cellular and chemical defenses

Immune System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
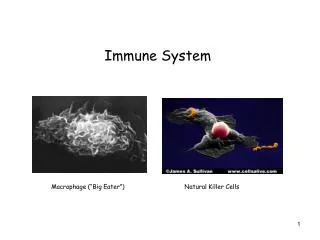
Innate immunity is present before any exposure to pathogens and is effective from the time of birth • It involves nonspecific responses to pathogens • Innate immunity consists of external barriers plus internal cellular and chemical defenses • Key internal defenses are macrophages and other phagocytic cells
Acquired immunity, or adaptive immunity, develops after exposure to agents such as microbes, toxins, or other foreign substances • It involves a very specific response to pathogens • Recognition is by white blood cells called lymphocytes • Some lymphocytes produce antibodies; others destroy infected cells, cancer cells, or foreign tissue
LE 43-2 ACQUIRED IMMUNITY Slower responses to specific microbes INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes External defenses Internal defenses Skin Phagocytic cells Humoral response (antibodies) Mucous membranes Antimicrobial proteins Secretions Inflammatory response Invading microbes (pathogens) Cell-mediated response (cytotoxic lymphocytes) Natural killer cells
Microbes Pseudopodia LE 43-4 MACROPHAGE Vacuole Lysosome containing enzymes
Natural Killer Cells • Natural killer (NK), also known as Cytotoxic T Cells, cells attack virus-infected body cells and cancer cells • They trigger apoptosis in the cells they attack
Cell-mediated immune response Humoral immune response First exposure to antigen LE 43-14_3 Antigens displayed by infected cells Antigens engulfed and displayed by dendritic cells Intact antigens Activate Activate Activate Secreted cytokines activate B cells Cytotoxic T cell Helper T cell Gives rise to Gives rise to Gives rise to Active and memory helper T cells Memory cytotoxic T cells Active cytotoxic T cells Plasma cells Memory B cells Defend against infected cells, cancer cells, and transplanted tissues Secrete antibodies that defend against pathogens and toxins in extracellular fluid