Digestion in the Mouth
80 likes | 232 Vues
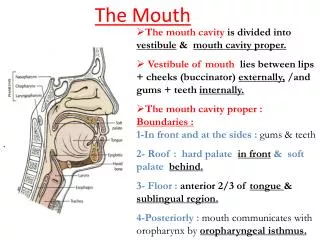
Digestion in the Mouth. Digestion of Molecules. Fats Broken down by lipolysis Broken down into fatty acids & glycerol Proteins Broken down into amino acids Carbohydrates Main source of energy Basic unit: saccaride

Digestion in the Mouth
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Digestion of Molecules • Fats • Broken down by lipolysis • Broken down into fatty acids & glycerol • Proteins • Broken down into amino acids • Carbohydrates • Main source of energy • Basic unit: saccaride • Polysaccarides are complex (large) molecules which become digested into disaccarides • Disaccarides eventually get broken down into monosaccarides
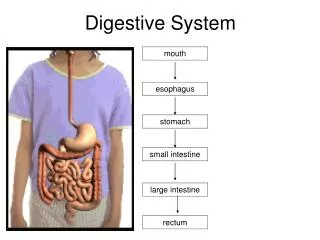
Two Types of Digestion • Mechanical (Physical) Digestion • Food is broken down into smaller pieces by chewing, grinding, etc. • Chemical Digestion • Food changes form by reacting with acids and enzymes in the digestive tract
Teeth • Necessary for initial breakdown of food • Very in size and shape • Two sets of teeth: • Primary (starting at ~age 6) • Permanent (6-13 years) • Most adults have 32 teeth: • 8 Incisors • 4 Canines • 8 Premolars • 12 Molars
Teeth Cont’d • Incisors • Front of mouth • Good for biting/cutting • Canines (eye teeth) • Beside incisors • Pointed shape • Good for tearing/shredding food • Premolars/Molars • Sides of mouth • Square shaped • Good for grinding/chewing http://www.yummybubby.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/wisdomteeth.jpg
Tongue Acts as a taste organ Mixes saliva with food Moves food to rear of mouth for swallowing Saliva contains amylase which breaks down carbohydrates http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/68/Fungal_tounge.jpg
Salivary Glands • 3 different ones • Produces saliva • Saliva • Needed to help moisten food • Contains enzymes • 99.5% water • 0.75-1.5 Liters of saliva produced daily • Enzymes • Chemicals that help speed up digestion
Swallowing Moves chewed up food into throat Chewed up food is called bolus Occurs by muscle movements in tongue and mouth