The Nervous System
170 likes | 234 Vues
Explore the intricate network of neurons in the nervous system, including the resting and action potentials, synapses, and neurotransmitters. Discover how electrical impulses are transmitted and coordinated, impacting movement and responses in the body. Test your knowledge with a quiz on nervous system functions and neuron components.

The Nervous System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
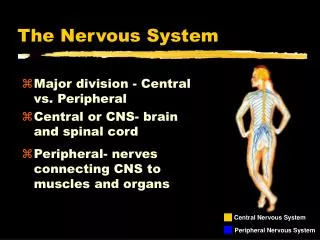
Nervous System • Network of connected cells, tissue, and organs • Controls thoughts, movement, life processes • Quick responses • Ex: Sunny day pupils shrinking
Neurons • AKA: Nerve Cells • Transfer electrical impulses to/from the brain • 3 Main Parts • Cell body: contains nucleus and organelles • Dendrites: branches that receive messages from neighboring cells • Axon: extension that carries messages away from the cell body
Resting Potential • Defined: Neuron at rest • Neuron Exterior: • Positive charge • Mainly Na+ outside the cell • Neuron Interior: • Negative charge (from various proteins) • K+ inside the cell
Action Potential • Defined: Electrical impulse is triggered • Front end of impulse • Channels open and allow Na+ to enter the cell • Negative impulse attracted towards positive Na+ • Back end of impulse • Channels open to allow K+ to exit the cell • Interior returns to normal • Impulse pulled along by the changing of electrical charges
Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ negative impulse K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+
Synapse • Defined: Gap between neurons • Problem: Impulse cannot cross the gap • Solution: Impulse converted into chemical molecules (neurotransmitters) • Steps: • Impulse reaches neuron’s end • Vesicle releases neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters attach to neighboring neuron • New impulse created
Impulse stimulates a vesicle, which contains neurotransmitters Vesicle exits the cell and dissolves impulse Start of another cell End of one cell
Neurotransmitters stimulate a new impulse Neurotransmitters cross the synapse and attach to receptors of a neighboring neuron impulse impulse Start of another cell End of one cell
Brain …. …. …. …. Feet
Motor neurons reach the muscles… and causes MOVEMENT!
Kobe Kuiz • What is the function of the nervous system? • List the 3 main parts and describe the purpose of the 3 main parts of a neuron. • Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. • What is a synapse and why is it a problem for neurons? • What are the roles of the following during an action potential? • NA+ • K+ • Neurotransmitters