Resequencing Genome
400 likes | 647 Vues
Resequencing Genome. Timothee Cezard EBI NGS workshop 16/10/2012. NGS Course – Data Flow. Rajesh Radhakrishnan Rasko Leinonen Arnaud Oisel Marc Rossello Vadim Zalunin. ENA/SRA submission and retrieval. Overview. Sequence archives. Karim Gharbi. Data compression. DNA

Resequencing Genome
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Resequencing Genome TimotheeCezard EBI NGS workshop 16/10/2012
NGS Course – Data Flow Rajesh Radhakrishnan RaskoLeinonen Arnaud Oisel Marc Rossello VadimZalunin ENA/SRA submission and retrieval Overview Sequence archives KarimGharbi Data compression DNA Sequencing RNA Sequencing Guy Cochrane Gene regulation Gene annotation Gene expression Resequencing & assembly Genome variation & disease RNA-Seq Ensembl gene build TimotheeCezard ChIP-seq analysis RNA-Seq Transcriptome analysis Elizabeth Murchison Jon Teague /Adam Butler/ Simon Forbes Remco Loos/ MyrtoKostadima Ensembl/John Collins MyrtoKostadima/ Remco Loos Laura Clarke
NGS Course – Data Flow Rajesh Radhakrishnan RaskoLeinonen Arnaud Oisel Marc Rossello VadimZalunin ENA/SRA submission and retrieval Overview Sequence archives KarimGharbi Data compression DNA Sequencing RNA Sequencing Guy Cochrane Gene regulation Gene annotation Gene expression Resequencing & assembly Genome variation & disease RNA-Seq Ensembl gene build TimotheeCezard ChIP-seq analysis RNA-Seq Transcriptome analysis Elizabeth Murchison Slides and tutorials are available at: https://www.wiki.ed.ac.uk/display/GenePoolExternal/NGS+workshop+16.10.2012+at+EBI Jon Teague /Adam Butler/ Simon Forbes Remco Loos/ MyrtoKostadima Ensembl/John Collins MyrtoKostadima/ Remco Loos Laura Clarke
NGS Course – Data Flow Rajesh Radhakrishnan RaskoLeinonen Arnaud Oisel Marc Rossello VadimZalunin ENA/SRA submission and retrieval Overview Sequence archives KarimGharbi Data compression DNA Sequencing RNA Sequencing Guy Cochrane Gene regulation Gene annotation Gene expression Resequencing & assembly Genome variation & disease RNA-Seq Ensembl gene build TimotheeCezard ChIP-seq analysis RNA-Seq Transcriptome analysis Elizabeth Murchison Jon Teague /Adam Butler/ Simon Forbes Remco Loos/ MyrtoKostadima Ensembl/John Collins MyrtoKostadima/ Remco Loos Laura Clarke
Overview • DNA (Re)sequencing • Sequencing technologies • Sequencing output • Quality control • Mapping • Mapping programs • Sam/Bam format • Mapping improvements • Variant calling • Types of variants • SNPs/indels • VCF format
Overview • DNA (Re)sequencing • Sequencing technologies • Sequencing output • Quality control • Mapping • Mapping programs • Sam/Bam format • Mapping improvements • Variant calling • Types of variants • SNPs/indels • VCF format
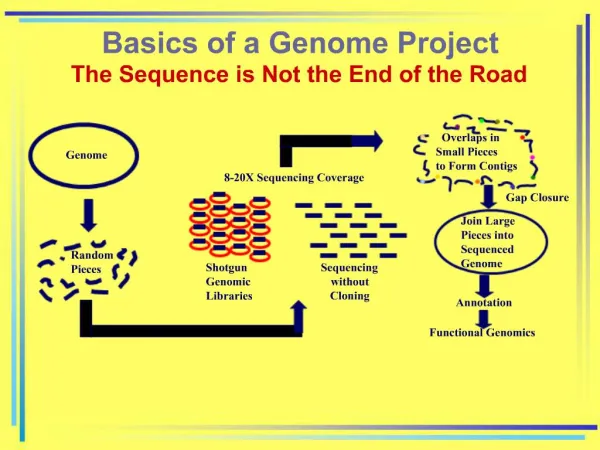
Resequencing genomes Library prep Library prep DNA Extraction Library prep
Sequencing data Sequence data • Precise • Fairly unbiased • Easy to QC GATGGGAAGA GCGGTTCAGC AGGAATGCCG AGACCGATAT CGTATGCCGT Coverage depth data • Can be biased • Hard to know what’s true
Sequencer specific errors Homopolymer run create false indels Specific sequence patterns can create phasing issues
Sequencer specific errors Specific sequence patterns can create phasing issues
Sequencing output (Fastq format) Example fastq record: @ILLUMINA06_0016:6:1:5388:12733#0 GATGGGAAGAGCGGTTCAGCAGGAATGCCGAGACCGATATCGTATGCCGTCTTCTGCTTGAAAAAAAAAAAAAAG + CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDDADACBCCCDADBDDCBCD;BBDBDBBBB%%%%%%%%%
Sequencing output (Fastq format) Example fastq record: @ILLUMINA06_0016:6:1:5388:12733#0 GATGGGAAGAGCGGTTCAGCAGGAATGCCGAGACCGATATCGTATGCCGTCTTCTGCTTGAAAAAAAAAAAAAAG + CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDDADACBCCCDADBDDCBCD;BBDBDBBBB%%%%%%%%%
Sequencing output (Fastq format) Example fastq record: @ILLUMINA06_0016:6:1:5388:12733#0 GATGGGAAGAGCGGTTCAGCAGGAATGCCGAGACCGATATCGTATGCCGTCTTCTGCTTGAAAAAAAAAAAAAAG + CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDDADACBCCCDADBDDCBCD;BBDBDBBBB%%%%%%%%%
Quality control • Questions you should ask (yourself or your sequencing provider): • Sequencing QC: • How much sequencing? • What’s the sequencing quality? • Library QC: • What’s the base profile across the reads? • Is there an unexpected GC bias? • Are there any library preparation contaminants? • Post mapping QC: • What is the fragment length distribution? (for paired end) • Is there an unexpected Duplicate rate?
Example with FastQC http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/
Example with FastQC http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/
Overview • DNA (Re)sequencing • Sequencing technologies • Sequencing output • Quality control • Mapping • Mapping programs • Sam/Bam format • Mapping improvements • Variant calling • Types of variants • SNPs/indels • VCF format
Mapping Reads to a reference genome • Problems: • How to find the best match of short sequence onto a large genome (high sensitivity) • How to not find a match when • for 100,000,000,000 reads in reasonable amount of time. • Solution: • Hashing based algorithms: • BLAST, Eland, MAQ, Shrimps, GSNAP, Stampy • More sensitive when SNPs/Indels • Suffix trie + Burrows Wheeler Transform algorithms: • Bowtie, SOAP BWA • Faster
Different software for different applications Transcriptome to genome Mapping to distant reference Very fast mapping GSNAP Stampy bowtie Tophat Shrimp BWA
Different software for different applications Transcriptome to genome Mapping to distant reference Very fast mapping Genomatics Bwasw Splitseek GSNAP Stampy Bowtie Mr fast Tophat Shrimp Bwa CLC bio Smalt Mrs fast Partek Ssaha2
Different software for different applications Transcriptome to genome Mapping to distant reference Very fast mapping Genomatics Bwasw Splitseek Mapper GSNAP Stampy Bowtie Mr fast Fastq Sam/Bam Tophat Shrimp Bwa CLC bio Smalt Mrs fast Partek Ssaha2
SAM/BAM format • SAM: Sequence Alignment/Map format v1.4 • The SAM Format Specification Working Group (Sept 2011) • http://samtools.sourceforge.net/SAM1.pdf • Standardized format for alignment • Bam: binary equivalent of SAM • Bam can be indexed for fast record retrieval • Manipulate Sam/Bam file using samtools and others • 2 parts: • Header: contains metadata about the sample • Alignment:
SAM/BAM format COLUMNS: 1 QNAME String Query template NAME 2 FLAG Int bitwise FLAG 3 RNAME String Reference sequence NAME 4 POS Int 1-based leftmost mapping POSition 5 MAPQ IntMAPping Quality 6 CIGAR String CIGAR string 7 RNEXT String Ref. name of the mate/next fragment 8 PNEXT Int Position of the mate/next fragment 9 TLEN Int observed Template LENgth 10 SEQ String fragment SEQuence 11 QUAL String ASCII of Phred-scaled base QUALity+33≈
Bitwise flag 83 = 1010011 in binary format
Bitwise flag 83 = 1010011 in binary format http://picard.sourceforge.net/explain-flags.html
CIGAR alignment M alignment match (can be a sequence match or mismatch) I insertion to the reference D deletion from the reference N skipped region from the reference S soft clipping (clipped sequences present in SEQ) H hard clipping (clipped sequences NOT present in SEQ) P padding (silent deletion from padded reference) = sequence match X sequence mismatch Ref: AGGTCCATGGACCTG || ||||X||||||| Query: AG-TCCACGGACCTG 2M1D12M or 2=1D4=1X7= Ref: CTTATGTGATC ||||||||||| Query: CTTATGTGATCCCTG 10M4S
Mapping enhancement • Each read is mapped independently: • Can borrow knowledge from neighbor to improve mapping • Picard Marking Duplicates: A duplicated read pair is when both two or more read pairs have the same coordinates. • Samtools BAQ: Hidden markov model that downweight mismatching based if they are close to indel • GATK Indel realignment: take every reads around potential indel and perform a more sensitive alignment • GATK Base recalibration: look at several contextual information, such as position in the read or dinucleotide composition to identify covariate of sequencing errors
Indel realignment AACAATATCTATGGA/TTTCG/TTTTG
Overview • DNA (Re)sequencing • Sequencing technologies • Sequencing output • Quality control • Mapping • Mapping programs • Sam/Bam format • Mapping improvements • Variant calling • Types of variants • SNPs/indels • VCF format
The whole pipeline Final bam file(s) Alignment Realignment Mark duplicates Base recalibration ? Raw data
The whole pipeline Final bam file(s) Alignment Realignment Mark duplicates Base recalibration ? Raw data Final bam file(s) Structural Variant Calling Pool analysis CNV Calling SNPs/Indels Calling
The whole pipeline Final bam file(s) Alignment Realignment Mark duplicates Base recalibration ? Raw data Final bam file(s) Structural Variant Calling Pool analysis CNV Calling SNPs/Indels Calling
VCF format Variant format designed for 1000 genome project - SNPs - Insertions - Deletions - Duplications - Inversions - Copy number variation http://www.1000genomes.org/wiki/Analysis/Variant%20Call%20Format/vcf-variant-call-format-version-41
VCF format Header: define the optional fields ##INFO=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Raw read depth"> ##FORMAT=<ID=GT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Genotype"> Variants: 8 mandatory columns describing the variant 1 column defining the genotype format 1 column per sample describing the genotype for that SNP for that sample http://www.1000genomes.org/wiki/Analysis/Variant%20Call%20Format/vcf-variant-call-format-version-41
HEADER ##fileformat=VCFv4.1 ##samtoolsVersion=0.1.18 (r982:295) ##INFO=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Raw read depth"> ##INFO=<ID=DP4,Number=4,Type=Integer,Description="# high-quality ref-forward bases, ref-reverse, alt-forward and alt-reverse bases"> ##INFO=<ID=MQ,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Root-mean-square mapping quality of covering reads"> ##INFO=<ID=FQ,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Phred probability of all samples being the same"> ##INFO=<ID=AF1,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Max-likelihood estimate of the first ALT allele frequency (assuming HWE)"> ##INFO=<ID=AC1,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Max-likelihood estimate of the first ALT allele count (no HWE assumption)"> ##INFO=<ID=G3,Number=3,Type=Float,Description="ML estimate of genotype frequencies"> ##INFO=<ID=HWE,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Chi^2 based HWE test P-value based on G3"> ##INFO=<ID=CLR,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Log ratio of genotype likelihoods with and without the constraint"> ##INFO=<ID=UGT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="The most probable unconstrained genotype configuration in the trio"> ##INFO=<ID=CGT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="The most probable constrained genotype configuration in the trio"> ##INFO=<ID=PV4,Number=4,Type=Float,Description="P-values for strand bias, baseQ bias, mapQ bias and tail distance bias"> ##INFO=<ID=INDEL,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="Indicates that the variant is an INDEL."> ##INFO=<ID=PC2,Number=2,Type=Integer,Description="Phred probability of the nonRef allele frequency in group1 samples being larger (,smaller) than in group2."> ##INFO=<ID=PCHI2,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Posterior weighted chi^2 P-value for testing the association between group1 and group2 samples."> ##INFO=<ID=QCHI2,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Phred scaled PCHI2."> ##INFO=<ID=PR,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="# permutations yielding a smaller PCHI2."> ##INFO=<ID=VDB,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Variant Distance Bias"> ##FORMAT=<ID=GT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Genotype"> ##FORMAT=<ID=GQ,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Genotype Quality"> ##FORMAT=<ID=GL,Number=3,Type=Float,Description="Likelihoods for RR,RA,AA genotypes (R=ref,A=alt)"> ##FORMAT=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="# high-quality bases"> ##FORMAT=<ID=SP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Phred-scaled strand bias P-value"> ##FORMAT=<ID=PL,Number=G,Type=Integer,Description="List of Phred-scaled genotype likelihoods"> #CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT germline tumor chr4 27668 . T C 8.65 . DP=2;AF1=1;AC1=4;DP4=0,0,0,1;MQ=60;FQ=-27.4 GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 0/1:0,0,0:0:0:3 1/1:38,3,0:1:0:3 chr4 27669 . G T 4.77 . DP=2;AF1=1;AC1=4;DP4=0,0,0,1;MQ=60;FQ=-27.4 GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 0/1:0,0,0:0:0:3 0/1:33,3,0:1:0:4 chr4 27712 . T C 44 . DP=2;AF1=1;AC1=4;DP4=0,0,1,1;MQ=60;FQ=-30.8 GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 1/1:40,3,0:1:0:8 1/1:37,3,0:1:0:8 chr4 27774 . G A 5.47 . DP=2;AF1=0.5011;AC1=2;DP4=1,0,0,1;MQ=60;FQ=-5.67;PV4=1,1,1,1 GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 0/1:34,0,23:2:0:28 0/0:0,0,0:0:0:3 chr4 36523 . A T 10.4 . DP=1;AF1=1;AC1=4;DP4=0,0,1,0;MQ=60;FQ=-27.4 GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 0/1:0,0,0:0:0:3 1/1:40,3,0:1:0:4 DATA
VCF format SNPs #CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT germline chr4 27668 . T C 8.65 . DP=2;AF1=1;AC1=4;… GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 0/1:0,0,0:0:0:3 chr4 27669 . G T 4.77 . DP=2;AF1=1;AC1=4;… GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 0/1:0,0,0:0:0:3 chr4 27712 . T C 44 . DP=2;AF1=1;AC1=4;… GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 1/1:40,3,0:1:0:8 chr4 27774 . G A 5.47 . DP=2;AF1=0.5011; AC1=2; … GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 0/1:34,0,23:2:0:28 chr4 36523 . A T 10.4 . DP=1;AF1=1;AC1=4;… GT:PL:DP:SP:GQ 0/1:0,0,0:0:0:3 Genotype format SNPs quality SNP Identifier SNPs information Filtering reasons Reference base Position Genotype information Alternate base(s) Chromosome name
Variant Filtering Depth of Coverage: confident het call= 10X-20X SNPs quality depends on the caller: 30-50 Genotype quality: 20 Strand bias Biological interpretation