SOIL PHYSICAL COMPONENTS
190 likes | 362 Vues
This presentation, developed by Dr. Charles Mitchell, Extension Agronomist at Auburn University, delves into the essential physical components of soil, including sand, silt, and clay. We explore soil particle sizes, textures, and the significance of soil structure and cation exchange capacity for plant health. Discover how these components influence water retention and root growth, enabling you to address soil-related issues in gardening effectively. A valuable resource for the Extension Master Gardener Volunteer Training Program and beyond.

SOIL PHYSICAL COMPONENTS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
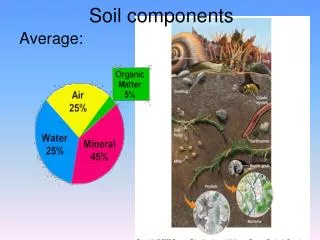
SOIL PHYSICAL COMPONENTS “Getting to the root of the problem” sand Cation exchange air silt roots tillage clay water
0 1mm 2mm 3mm 4mm 5mm SAND 2.0 - 0.5 mm SILT CLAY 0.5 - .002mm <0.002mm Soil Particle Sizes
sandy clay sandy clay loam Soil Texture 100% 0% clay Percent SILT Percent CLAY silty clay loam Clay loam Loam Silt Loam Sandy Loam Loamy Sand 100% 0% Silt Sand 100% 0% Percent SAND
Soil Structure . . . the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates
End of PART 2. “Soil Physical Components” Slide set developed by: Dr. Charles Mitchell Extension Agronomist-Soils & Professor Auburn University for use in the Extension Master Gardener Volunteer Training Program