Tool Spec Sheet
40 likes | 203 Vues
Spectrum Systems. HCC. Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) ORYX Heart Failure Core Measures Scorecard. Tool Spec Sheet. HCC Internal Tool Spec Sheet. Basic Level. [ ____________ ] TOOL DESCRIPTION

Tool Spec Sheet
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Spectrum Systems HCC Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) ORYX Heart Failure Core Measures Scorecard Tool Spec Sheet HCC Internal Tool Spec Sheet Basic Level • [ ____________ ] TOOL DESCRIPTION • Title: Short and tight, of no more than three or four words. Define whether the tool is a Roadmap, Guide, Dashboard, Scorecard, Checklist, Framework, Template, Calculator, or Formula. • Abstract: No more than four lines. The abstract should summarize the tool and its use. • Key Words: List all of the key words that may be pertinent to the core concept that a user might use in a search. • Author: List author organization (HCC or TMIT or other – if other note how it was modified from original source). • Lead Tool Summary Graphic:Use a PPT graphic from HCC graphic library as a lead identifying graphic. Include mini-icons where appropriate. • Spectrum Web Storyboard: Insert instructions for web pres, direction for graphics, animations, text instructions & PN direction to other pages 2 of 2 eg. • Tool Definition: One short paragraph should be provided that defines the Tool. This definition will be presented in a glossary of terms. The tool should be labeled as to whether it is used at all, Basic, Intermediate, Comprehensive, or Very Comprehensive levels. • Background: Provides the why, when, and how, tool was developed and the sources. • Description: Provides the relevance to the healthcare and performance solutions development. Describes how “works” with in with the HCC Spectrum system and related or pertinent Spectrum concepts. Although there is one lead signature graphic, more than one graphic or table may be used in the description. C-T-R’s mentioned in the body of the description will be linked through a framework tree to the definition (suggest pop up window with a close button). Also provide a simple and short example of the tool. The source references should be listed at the end of document. • User Value Views: A “User View” paragraph or set of paragraphs will be provided for Product Development, Business Development, Marketing/Sales, Healthcare Provider, or Healthcare Purchaser. Each will provide a customized view as to how that tool may be used for each user. • References: Use the reference format defined by the NLM Style Guide. The abstract for each referenced article will be posted in the KM system and be viewable with a hyperlink. • Sources: Similar to bibliography, this section should list where certain components of the tool have been found or developed. They may not necessarily be referenced. • Related Concepts: This is a link that leads to a separate page that lists the related concepts that may be of value to the user. • Related Tools: This is a link that leads to a separate page listing related Tools. • Related Resources: This is a link that leads to a separate page listing related Resources. • Video Link: Links to media player of video description of the tool (2-3 minutes) of streaming video. S3 Version 2
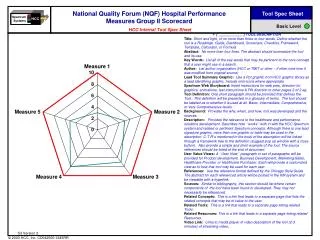
Spectrum Systems HCC Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) ORYX Heart Failure Core Measures Scorecard Tool Description Page 1 of 3 Basic Level • Related Concepts, Tools, and Resources: • Measures-Standards-Practices Grid • Performance M-S-P document • JCAHO Resource • Instructions: • The purpose of this tool is to evaluate the performance of the solution against specific JCAHO Measures-Standards-Practices and determine the opportunity gap. • Step 1: Review the definition of the Measures-Standards-Practices on the following page and determine if the solution has an impact on meeting, supporting, or providing data for the M-S-P. For more details refer to the M-S-P Tool. • Step 2: Click on Radar graph below and update the values using the scale 0-10 (10 being an exact match to fulfilling the measure). Use information as input data for the Index Model to determine specific Procedure volumes targeted by the solution. Notes and Comments: Completed by: Date: Version: Filing Location: S3 Version 2
Completed by: Filing Location: Version: Date: Spectrum Systems HCC Tool Template JCAHO ORYX Heart Failure Core Measures Scorecard Page 2 of 3 Basic Level S3 Version 2
Completed by: Filing Location: Version: Date: Spectrum Systems HCC Tool Template JCAHO ORYX Heart Failure Core Measures Scorecard Page 3 of 3 Basic Level • ORYX is the name given to an initiative that started in 1987, when JCAHO’s Agenda for Change outlined its plan to modernize the accreditation process. The initiative first got off its feet in 1995, when JCAHO began evaluating proposed measures and measurement systems, ultimately approving 200 measurement systems and 8,000 measures giving member organizations a remarkable amount freedom and flexibility. ORYX went operational in March 1999, with performance measurement standards that aggressively targeted five core, high-risk areas. • Heart failure is a condition in which the heart, due to a severe reduction in efficiency, is no longer capable of pumping a sufficient amount of blood to the body’s other organs. This is usually caused by narrowed arteries, past heart attacks, or high blood pressure, and can also occur from congenital heart defects or diseases or infections of the valves or muscle tissue. With any of these problems, blood flow out of the heart will slow, causing back-up in the veins, and eventually swelling of the organ tissues themselves. This occurs most often in the legs (due to gravity) or in the lungs (due to the short distance traveled), the latter producing the most recognizable symptom, shortness of breath. • Treatments include rest, diet, and various drugs, including ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and diuretics to correct the kidneys’ diminished ability to eliminate sodium and water from the bloodstream. • Definitions of the MSP: • Discharge Instructions: Non-compliance with physician instructions following discharge from a hospital is one of the leading causes of re-hospitalization for heart failure. It is therefore the responsibility of the physicians to make the instructions as clear and easy to follow as possible. This measure assesses the percentage of heart failure patients who have been sent home with written instructions or educational material addressing activity level, diet, discharge medications, follow-up appointment, weight monitoring, and what to do if symptoms worsen. • LVF Assessment: Analysis of the Left Ventricular Function will assess the percentage of blood that leaves the heart with each beat. Areas of the heart that have had an injury, represent scar tissue, and have impaired contraction will reduce that percentage. This measure assesses the percentage of heart failure patients who received left ventricular function (LVF) assessment before arrival, during hospitalization, or planned for after discharge. • ACE Inhibitors for Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVSD): LVSD occurs when the contractile function of the left ventricle falls to below 40% of the standard performance rate. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors are a family of medicines that block the formation of angiotensin II, thereby reducing blood pressure. ACE Inhibitors prescribed to heart failure patients with LVSD have shown to significantly reduce recovery time, mortality rates, and re-hospitalization. • Adult smoking cessation advice/counseling: Not only does smoking severely increase the risks of suffering heart failure, but it doubles the mortality rate. The use of nicotine triggers coronary spasm and reduces effects of beta blockers and other treatments. Patients who receive even brief smoking-cessation advice from their physicians are more likely to quit, promoting recovery and preventing further incidences. S3 Version 2