Global Warming
170 likes | 296 Vues
This overview highlights significant findings on global warming and climate change as of 2007. The data indicates that recent warming trends are largely attributed to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, primarily CO2 and CH4. The US Supreme Court's ruling classified CO2 as a pollutant, reinforcing the need for mitigation. Recent observations show profound impacts on ecosystems and increased drought frequency. Projections suggest accelerated warming, particularly in northern latitudes, emphasizing the urgent need for immediate and extensive climate action to avert severe environmental consequences.

Global Warming
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Global Warming Inez Fung University of California, Berkeley April 2007
Climate Change: Recent News • Feb 7 2007: United Nations Env Programme - Intergovt Panel on Climate Change - observed warming since the 20thC is very likely due to anthropogenic greenhouse gases • April 2 2007: US Supreme Court: anthropogenic CO2 is a pollutant • April 7 2007: UNEP IPCC WG 2 - warming has had discernible influence on physical and biological systems
Changing Composition of the Atmosphere Analysis of ancient air bubbles trapped in ice Direct measurements of atm composition in the past centuries Increases since 1800 due to human activities
CO2 CH4 T Now 400,000 yr
At equilibrium:High CO2 --> warm; Low CO2 --> cold J. Hansen
Warmest 12 years: 1998,2005,2003,2002,2004,2006, 2001,1997,1995,1999,1990,2000 50 0.1280.026 100 0.0740.018 Global mean temperatures are rising faster with time Period Rate Years /decade IPCC AR4
Drought is increasing most places Mainly decrease in rain over land in tropics and subtropics, but enhanced by increased atmospheric demand with warming The most important spatial pattern (top) of the monthly Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI) for 1900 to 2002. The time series (below) accounts for most of the trend in PDSI. IPCC AR4
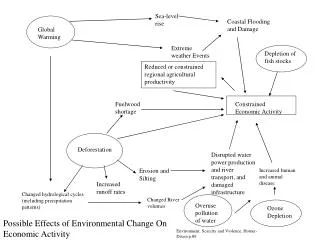
Evaporation from ocean, Increase water vapor in atm Enhance greenhouse effect Increase cloud cover; Decrease absorption of solar energy Decrease snow cover; Decrease reflectivity of surface Increase absorption of solar energy Climate Feedbacks Warming
Observations Attribution • are observed changes consistent with • expected responses to forcings • inconsistent with alternative explanations Climate model: All forcing Climate model: Solar+volcanic only IPCC AR4
9oF 7oF 3oF Projections of Climate Change IPCC AR4
Projections of Climate Change 2020-2029 2090-2099 greatest over land & at most high N latitudes and least over the South. Ocean & parts of the N Atlantic Ocean IPCC AR4
Warming is faster than model projections: Recent rapid melting glaciers on Greenland Jay Zwally
2000 2020 Stern Review 2006
Strong action is needed urgently Stern Review 2006