Understanding Ecosystem Interactions: Roles and Relationships of Organisms
370 likes | 491 Vues
This unit explores the fundamental components of ecosystems, including the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers. Students will learn how to recognize different types of consumers (carnivores, omnivores, and herbivores) and understand the effects of population changes on ecosystem balance. Key concepts include the food chain, food web, and energy flow, as well as the significance of symbiosis, population dynamics, and environmental factors like pollution and extinction. Engaging activities and assessments will deepen understanding of these critical ecological relationships.

Understanding Ecosystem Interactions: Roles and Relationships of Organisms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Our goals for this unit • I will be able to recognize consumers, producers, and decomposers. • I will be able to recognize how changes in populations effect the balance of an ecosystem. • I will be able to recognize carnivores, omnivores, and herbivores. • I will be able to recognize different types of ecosystems and the organisms living in them. • I will be able to analyze both positive and negative effects on ecosystems. • I will be able to explain how a food chain and food web interact. • I will be able to order animals in a food web/food chain.
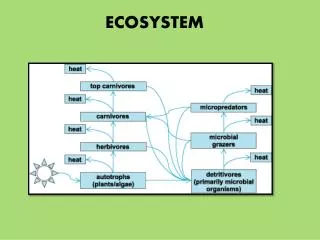
Ecosystem • Short for “ecological system” • Includes all of the living and nonliving organisms existing together in a particular area • Complex set of relationships among the living resources, habitats, and residents of an area; includes plants, trees, animals, fish, birds, micro-organisms, water, soil, and people
Niche • The role of an organism in its habitat
Habitat • The natural environment where an organism lives
Symbiosis • A close, long lasting relationship between two species
Population • All the members of the same type of organism living in the same ecosystem
Predator • An animal that hunts and eats other animals
Prey • An animal that is hunted and eaten by a predator
Extinction • The dying out of all the members of a species
Endangered Species • A species that is close to extinction
Pollution • The addition of harmful things to the environment
Threatened Species • A species that is close to becoming endangered
Food Chain • The description of how energy in an ecosystem flows from one organism to another
Food Web • The description of all the food chains in an ecosystem
Producer • An organism that uses the Sun’s energy to make its own food
Consumer • An organism that eats other organisms
Different types of consumers • Carnivore- An animal that eats other animals • Herbivore- An animal that eats only plants • Omnivore- An animal that eats both plants and animals
LEVELs OF cONSUMERS • Primary consumer- an animal that gets all its energy from plants (herbivore) • Secondary consumer- an animal that eats primary consumers (carnivore) • Tertiary consumer- an animal usually at or near the top of the food chain; eat other consumers (carnivores or omnivores)
Decomposer • An organism that breaks down dead plants and animals into simpler materials that enrich the soil
Energy Pyramid • Shows how energy moves to each level of an ecosystem
Test Prep • Which would have the same effect on a zebra population as increasing the number of lions in the habitat? • The grass-eating insects die from disease. • No fires occur during the dry season. • Antelopes and wildebeests move into the area. • Trees are uprooted during a summer storm.
Test Prep • A cat eats a mouse. Which is the cat? • Parasite • Population • Predator • Prey
Test Prep • A tick is an animal that takes blood from its host. Which type of symbiosis does this describe? • Commensalism • Mutualism • Niche • Parasitism
Test Prep • Two species of birds share an island and depend on the same food source. Which would likely happen if food became scarce? • The birds would all fly away. • Both birds would become extinct. • The island’s bird population would decrease. • The smallest bird species would become extinct.
Test prep • Which of these is a predator/prey relationship? • A mouse eats a seed. • A plant gets energy from the Sun. • A spider eats a cricket. • An owl uses a cactus for a home.
Test prep • Which is a role of lions in an ecosystem? • Lions help keep the population of trees under control. • Lions help keep the population of zebras under control. • Lions help keep the population of wolves under control. • Lions help keep the population of grasses under control.
Test Prep • A town used pesticides to control mosquitoes in the • area. Scientists later observed that the population of • one type of bat had decreased. Which is the BEST • conclusion you can draw from this information? • People overhunted the bats. • This type of bat ate mosquitoes. • The bats’ habitat was destroyed. • The bats died from disease spread by the mosquitoes.
Test Prep • The zebra mussel was introduced into a lake ecosystem. Within a few years, the zebra mussel population soared, and it showed no sign of declining. Which conclusion can you draw? • The mussels will soon become extinct. • The mussels are not adapted to freshwater. • The mussels play a vital role in the lake’s ecosystem. • The mussels have no natural predators in the lake.
Test Prep • In the last several years, the number of rabbits in a • Mississippi forest has remained the same. Which of the • following would MOST LIKELY cause the number of rabbits • to decrease? • Plant more tress in a forest. • Increase the size of the rabbits’ habitat. • Increase the number of decomposers in the habitat. • Introduce carnivores, such as hawks and bobcats, into the habitat.