Permanent Molars
251 likes | 1.57k Vues
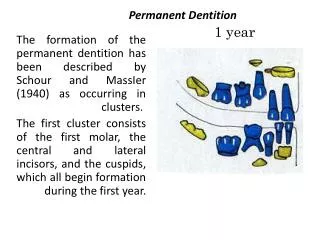
Permanent Molars. An Overview. General Descriptions. Largest, most posterior teeth Non-succedaneous Eruption pattern: 1st and last permanent teeth to erupt. Arch Positions. 6th, 7th, and 8th in each arch First molars: “6-year” molars Second molars: “12-year” molars

Permanent Molars
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Permanent Molars An Overview
General Descriptions • Largest, most posterior teeth • Non-succedaneous • Eruption pattern: 1st and last permanent teeth to erupt
Arch Positions • 6th, 7th, and 8th in each arch • First molars: “6-year” molars • Second molars: “12-year” molars • Third molars: “wisdom teeth”
Function • Mainly grinding • 1st molars are “cornerstones of occlusion” • Maintenance of “vertical dimension of occlusion”
General Characteristics • Crowns generally largest and most complex of all teeth • At least 3 cusps, typically 4 or 5 • At least 2 buccal cusps • Normally multirooted
Introduction • Larger M-D and F-L to other maxillary teeth except: shorter O-C • O-C dimension is less than M-D and F-L (FL>MD>OC) • Largest to smallest: 1st, 2nd, 3rd molars
General Characteristics of Maxillary Molars: • Crowns wider F-L than M-D* • Usually 4 cusps: ML, MB, DB, DL (largest to smallest) 2 3 1 4
Maxillary molars… • Buccal cusps closer to same size; lingual cusps differ in size • Presence of oblique ridge and distolingual groove*
Maxillary molars… • Crowns are rhomboidal or heart-shape (occlusal view) • One buccal pit and one lingual pit • Three occlusal pits: mesial, central, distal
Maxillary molars… • Crowns are trapezoidal from facial, lingual, proximal views • Facial HOC at cervical third • Lingual HOC at middle third • Usually 3 root branches: L, MB, DB (largest to smallest)
How To Tell Right From Left: • Distolingual groove/oblique ridge • MB root broader than DB root • Buccal ridge prominence towards mesial
Introduction • General size diminishes from 1st to 3rd molars • Shorter O-C than premolars and anteriors
General Characteristics of Mandibular Molars • Crowns wider M-D than F-L • Crowns rectangular (occlusal view) • Crowns rhomboidal from proximal view • Crowns trapezoidal from facial or lingual views
Mandibular molars… • Usually 4 - 5 cusps; both lingual cusps nearly same size • MB, ML, DL, DB, D (largest to smallest cusps) - mandibular 1st molar • Three occlusal pits: mesial, central, distal • Two buccal pits - 1st molar • One buccal pit - 2nd molar • No lingual pit 4 1 5 3 2
Mandibular molars… • Presence of two root branches (M & D), but usually three pulp canals: MB, ML, D • Facial HOC at cervical third • Lingual HOC at middle third
How To Tell Right From Left: Mesial root broader than distal root Distal cusp of 1st molar MB “bulge” of crown with 2nd and 3rd molars