Ionic and Covalent Compounds
200 likes | 572 Vues
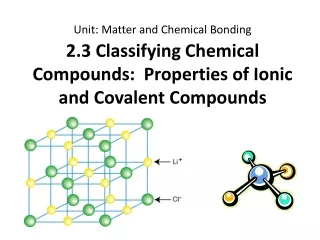
Ionic and Covalent Compounds. IONIC. Ionic Compounds are compounds where two or more ions are next to each other held by electrical attraction Do not consist of molecules Formed by the complete transfer of electrons from a metal Positive charged ions are called cations

Ionic and Covalent Compounds
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ionic and Covalent Compounds
IONIC • Ionic Compounds are compounds where two or more ions are next to each other held by electrical attraction • Do not consist of molecules • Formed by the complete transfer of electrons from a metal • Positive charged ions are called cations • Negative charged ions are called anions • Ionic Compounds form large crystals that you can see. Ex: Table Salt • Properties • High melting & boiling points • To melt, ions can not be in fixed locations OMPOUNDS
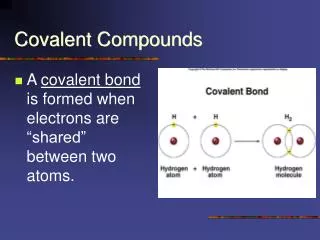
Covalent Compounds • Have atoms that are bonded and shear electrons from one to another • Covalent Compounds are formed when 2 non-metals bond to each other • Made up of molecules, gases, solids, and liquids • Usually do not conduct electricity as a solid or when molten or in solution • Usually does not dissolve in water
Similarities and Differences Covalent • Gases, liquids, or solids( made of molecules) • Low melting & boiling points • Poor electrical conductors in all phases • Many soluble in non polar liquids but not in H2O Ionic • Crystalline Solids (made of ions) • High melting & boiling points • Conducts electricity when melted • Many soluble in H2O but not in non polar liquids.
Forming Covalent Bonds • Bonds formed between two non metals that have similar electronegativities. Neither atom is “strong” enough to attract electrons from each other. For stability, they share electrons from outer molecular orbits.
Naming and Writing Formulas • Ionic • Write symbol and charges for element • Find the least common multiple of the charges • List Cations first, and then Anions Ex: Barium Fluoride Barium= Ba Fluoride= F Charge = 2+ Charge= 1- BaF2 • Covalent • Name the element (s) • If more then one atom of the less- electronegative element a prefix is needed. • Prefix that shows the # of atoms and name of more electronegative atom (+ide)
~Ionic Compounds- Barium Fluoride & Potassium Oxide~ Name: Barium/ Fluoride Formula: BaF2 Charges: Ba=2+ F=1- How they form- The metal cation (Barium) forms with the non-metal (Fluoride) FUN FACTS: Used for welding rod coatings, optical windows, lenses, enamel, and prisms.
Name: Potassium Oxide Formula: K2O Charges: K= 2+ O=1- How they form: Potassium oxide is produced from the reaction of oxygen and potassium *Facts* • Used in some fertilizers and cements. 2. Used in first aid and fire fighting.
~Covalent Compounds- Silicon Dioxide & Carbon Monoxide ~ 2. Most abundant mineral in the earth’s crust. 3. used in the extraction of DNA and RNA. Ex: quartz • Name: Silicon Dioxide • Formula: SiO2 • Valence electrons: Silicon=4 Oxygen=6 • How they bond: the Dioxide bonds with the silicon and the silicon needs 4 more pairs for silicon to be satisfied (8 valence electrons) Facts • Most commonly found in nature as sand or quartz as well as in the cell walls of diatoms.
Name: Carbon Monoxide • Formula: • Valence Electrons: • How they bond: carbon forms with oxygen making them bond to form carbon monoxide. • Facts • Major industrial gas • Carbon monoxide, though thought of as a pollutant today, has always been present in the atmosphere. It occurs dissolved in molten volcanic rock at high pressures in the earth’s mantle.