Cumulative Infiltration and Rainfall Excess Computation with Fortran
110 likes | 265 Vues
This Fortran-based implementation includes two core functions: a Newton-Raphson method for calculating incremental cumulative infiltration and a Green-Ampt method for real-time rainfall excess under steady conditions. The Newton's method ensures convergence based on input parameters like real soil properties (phi, dtheta, K, dt) and provides sophisticated checks for function stability. The interactive Green-Ampt subroutine evaluates infiltration across a 2-D spatial domain, adapting to rainfall intensity, soil characteristics, and adjacent cell inflows. This robust tool is suitable for hydrological modeling tasks.

Cumulative Infiltration and Rainfall Excess Computation with Fortran
E N D
Presentation Transcript
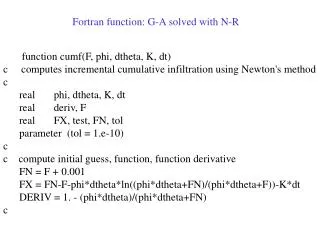
Fortran function: G-A solved with N-R function cumf(F, phi, dtheta, K, dt) c computes incremental cumulative infiltration using Newton's method c real phi, dtheta, K, dt real deriv, F real FX, test, FN, tol parameter (tol = 1.e-10) c c compute initial guess, function, function derivative FN = F + 0.001 FX = FN-F-phi*dtheta*ln((phi*dtheta+FN)/(phi*dtheta+F))-K*dt DERIV = 1. - (phi*dtheta)/(phi*dtheta+FN) c
Do 100 I=1,20 FN=FN-FX/DERIV FX = FN-F-phi*dtheta*log((phi*dtheta+FN)/(phi*dtheta+F))-Ks*dt DERIV = 1. - (phi*dtheta)/(phi*dtheta+FN) c Convergence test: if (abs(FN) .gt. 1.) then test=abs(FX/FN) else test=abs(FX) end if if (test .lt. tol) then cumf = FN return endif 100 continue if (i.eq.21) print *, 'Newtons Method Failed in cumf.for' return end
Fortran function: 2-D Interactive G-A subroutine rainex(F,h,p,q,re,phi,dtheta,Ks,r,dt,dx,dy,minh,minp, & minq,Nx,Ny,mxszx,mxszy,ponded) c c computes infiltration/excess using the Green-Ampt method and c allows for fully "interactive" infiltration under steady rain c rainfall excess is analagous to lateral inflow c integer Nx, Ny, mxszx, mxszy real p(0:mxszx,0:mxszy), re(0:mxszx,0:mxszy) real phi(0:mxszx,0:mxszy), minq real dtheta(0:mxszx,0:mxszy), Ks(0:mxszx,0:mxszy) real q(0:mxszx,0:mxszy), h(0:mxszx,0:mxszy) real r, minp, dt, F(0:mxszx,0:mxszy), dx, dy real minh, avef, fc, oldF, tdt, tempF, tempfc, avail logical ponded(0:mxszx,0:mxszy)
c loop over spatial domain do 10 k=0,Ny do 11 j=0,Nx c c *** if cell(j,k) is not ponded *** if (.not.ponded(j,k)) then c c compute potential infiltration rate fc = Ks(j,k)*(phi(j,k)*dtheta(j,k)/F(j,k)+1.)
c compute rate available to infiltrate c available = rain rate + flow rate from adjacent cells avail = r if (k.eq.0) then if (j.eq.0) then if (p(j+1,k).lt.0.0) avail = avail - p(j+1,k)/dx if (q(j,k+1).lt.0.0) avail = avail - q(j,k+1)/dy elseif (j.eq.Nx) then if (p(j-1,k).gt.minp) avail = avail + p(j-1,k)/dx if (q(j,k+1).lt.0.0) avail = avail - q(j,k+1)/dy else if (p(j-1,k).gt.minp) avail = avail + p(j-1,k)/dx if (p(j+1,k).lt.0.0) avail = avail - p(j+1,k)/dx if (q(j,k+1).lt.0.0) avail = avail - q(j,k+1)/dy endif ...
c if potential rate is greater than available rate, may remain unponded if (fc.ge.avail) then oldF = F(j,k) tempF = F(j,k) + avail*dt tempfc = Ks(j,k)*(phi(j,k)*dtheta(j,k)/tempF+1.) c allow for ponding to occur during time interval if (tempfc.ge.avail) then F(j,k) = tempF avef = avail re(j,k) = r - avef else ponded(j,k) = .true. tempF = Ks(j,k)*phi(j,k)*dtheta(j,k)/(avail-Ks(j,k)) tdt = dt-(tempF-F(j,k))/avail F(j,k)= cumF(tempF,phi(j,k),dtheta(j,k),Ks(j,k),tdt) avef = (F(j,k) - oldF)/dt re(j,k) = r - avef endif
c if potential rate is less than available, now ponded elseif (fc.lt.avail) then ponded(j,k) = .true. oldF = F(j,k) F(j,k) = cumF(F(j,k),phi(j,k),dtheta(j,k),Ks(j,k),dt) avef = (F(j,k) - oldF)/dt re(j,k) = r - avef c endif
c *** if cell(j,k) is ponded *** else c c compute potential infiltration rate fc=Ks(j,k)*(phi(j,k)*dtheta(j,k)/F(j,k)+1.) c c compute available rate c available rate = rain rate + depth on cell + flow from adjacent cells avail = r if (h(j,k).gt.minh) avail = avail + h(j,k)/dt
c if potential rate less than available c actual = potential, remains ponded if (fc.lt.avail) then oldF = F(j,k) F(j,k) = cumF(F(j,k),phi(j,k),dtheta(j,k),Ks(j,k),dt) avef = (F(j,k) - oldF)/dt re(j,k) = r - avef
c if potential rate greater than available c actual rate = available, possible unponding here elseif (fc.ge.avail) then c increase available to account for flow from adjacent cells if (k.eq.0) then if (j.eq.0) then if (p(j+1,k).lt.0.0) avail = avail - p(j+1,k)/dx if (q(j,k+1).lt.0.0) avail = avail - q(j,k+1)/dy elseif (j.eq.Nx) then if (p(j-1,k).gt.minp) avail = avail + p(j-1,k)/dx if (q(j,k+1).lt.0.0) avail = avail - q(j,k+1)/dy else if (p(j-1,k).gt.minp) avail = avail + p(j-1,k)/dx if (p(j+1,k).lt.0.0) avail = avail - p(j+1,k)/dx if (q(j,k+1).lt.0.0) avail = avail - q(j,k+1)/dy endif ...
if (fc.lt.avail) then oldF = F(j,k) F(j,k) = cumF(F(j,k),phi(j,k),dtheta(j,k),Ks(j,k),dt) avef = (F(j,k) - oldF)/dt re(j,k) = r - avef elseif (fc.ge.avail) then ponded(j,k) = .false. oldF = F(j,k) F(j,k) = F(j,k) + avail*dt avef = avail re(j,k) = r - avef endif