The Nervous System
570 likes | 707 Vues
This comprehensive overview of the nervous system highlights its key structures and functions, including the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The role of neurons, synapses, and neuroglia is explored, detailing their functions in transmitting signals and maintaining homeostasis. We discuss reflex arcs, the organization of the spinal cord, and the importance of various types of neurotransmitters in communication within the nervous system. Understanding these concepts is essential for grasping how the nervous system orchestrates bodily responses and maintains equilibrium.

The Nervous System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Nervous System Ch. 12-17
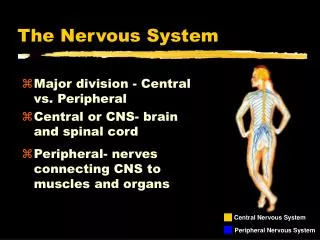
The Nervous System Introduction • Composed of • Brain • Spinal Cord • Nerves • 2 Major Subdivisions • CNS (Central Nervous System) • Brain, Spinal Cord • PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) • Cranial and Spinal Nerves • 2 Major Subdivisions • Afferent incoming pathways • Efferent Outgoing pathways
Neurons • Remember neuron structure: • The Cell Body or Soma • Contains a nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm along with all other organelles found within a cell • The Dendrites • Extensions from Cell Body/Soma • Receives information • The Axon • Single, long extension from Cell Body/Soma • Branch out into telodendria and end at synaptic/axon terminals
The Synapse • Each synaptic/axon terminal is part of a synapse • Site where the neuron communicates with another cell • Presynaptic Cell: sends the message (usually a neuron) • Postsynaptic Cell: receives the message (any cell type) • After a series of electrical signals is transmitted through the neuron, the axon/synaptic terminals release chemicals or neurotransmitters to the dendrite of another cell to continue the message
Synaptic Cleft Synapse
Neuron Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r71RoIkftd4
Neuroglia • Higher quantity and variation in CNS than PNS • Central Nervous System • Ependymal Cells • Astrocytes • Microglia • Oligodendrocytes • Peripheral Nervous System • Schwann Cells • Satellite Cells
CNS Neuroglia Ependymal Cells Microglia Removes cell debris, wastes, and pathogens by phagocytosis • Line ventricles in the brain and spinal cord • Aid in producing, circulating and monitoring of cerebrospinal fluid
CNS Neuroglia Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes Myelinate axons Provide structural framework • Provide structural support • Regulate ion, nutrient, and dissolved gas concentrations • Absorb and recycle neurotransmitters • Form scar tissue after injury
PNS Neuroglia Schwann Cells Satellite Cells Surround neuron cell bodies Regulate gas, nutrient, and neurontransmitter levels • Surround all axons • Responsible for myelination • Participate in repair process after injury
Synaptic Activity • Messages move from 1 location to another in the form of action potentials along neurons • Also known as nerve impulses • Messages move across the synapse • Can be electrical • Can be chemical (use of neurotransmitter)
Electrical Synapses • Presynaptic and postsynaptic cell membranes are locked together • Local electrical currents and directly transferred from cell to cell = • very rapid electrical impulse • Efficient action potential transfer from cell to cell
Chemical Synapses • Presynaptic and postsynaptic cell membranes are NOT locked together • Message not guaranteed to be transferred to the next cell dependent on the amount of neurotransmitters released • Different neurotransmitters: • Acetocholyne: found at neuromuscular junction • Norepinephrine: excitatory effect, adrenaline • Dopamine: Parkinson’s disease (rigidity of muscles) • Serotonin: attention, emotion, responsible for depression • GABA: reduce anxiety
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Chapter 13
Spinal Cord Anatomy • Posterior/Anterior/Lateral Horn of Gray matter • Anterior Median Fissure • Posterior Median Sulcus • Spinal Nerve (Posterior/Anterior Roots) • Spinal Ganglion
Spinal Cord Anatomy • Adult – 18 inches in length • Only reaches down to L1-L2 • Spinal Meninges: specialized membranes that surround the spinal cord • Dura Mater • Arachnoid • Pia Mater • Bacterial or vial infections of the Meninges Meningitis
PiaMater Meninges • Meshwork of connective tissue • Dense area of vessels Dura Mater Arachnoid Filled with cerebrospinal fluid (SPF)—shock absorber Spinal tap • Tough, fibrous outermost layer • Collagen fibers • Covered with blood vessels and adipose tissue • Epidural Space
Nerve Plexuses • Complex interwoven network of nerves Plexus. • Cervical Plexus • C1-C5 (muscles of neck, thoracic cavity) • Brachial Plexus • C5-T1 (muscles of pectoral girdle and upper limb) • Lumbar Plexus • T12-L4 • Sacral Plexus • L4-S4
Refluxes Chapter 13
Reflexes • Rapid automatic responses to a specific stimuli made by a receptor • Preserve homeostasis • Rapid adjustments • The Reflex Arc: wiring of a single reflex • Beings at the receptor • Ends at peripheral effector (ex: muscle fiber)
Reflexes • Sensory Receptors • Proprioreceptors: provide info about body position and muscle control • Vestibular Receptors: provide a sense of equilibrium • Cutaneous Receptors: touch, pressure, heat and cold • Photoreceptors: respond to light • Chemoreceptors: respond to taste • Nocioreceptors: pain receptors
Reflexes • Arrival of a stimulus and activation of receptor (pain) • Activation of a Sensory Neuron (action potential along axons of neurons spinal cord) • Information Processing (neurotransmitter released and sensation related to brain) • Activation of Motor Neuron (axons carry action potential back towards the origin of pain) • Response of Peripheral Effector (release of neurotransmitter to skeletal muscle fiber contraction pulls hand away from pain) • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wLrhYzdbbpE
Reflexes • Receptor Density • More dense the receptors = more “sensitive” the area • Upon stimulation… • Phasic: receptors respond with an initial burst of action potentials and rapidly decrease, even though stimulus continues • Tonic: receptors firing at a constant rate as long as the stimulus is applied • Lab on reflexes
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Chapter 14
Human Brain • Contains 98% of neural tissue • Weighs about 3 lbs • Covered by a neural cortex (superficial layer of gray matter • Main Areas • Cerebrum • Cerebellum • Diencephalon • Brain Stem
Cerebrum • Largest portion of the brain • 2 hemispheres • Controls thoughts, sensations, intellect, memory, and complex movements • Lobes (correspond with cranial bones) • Frontal • Parietal • Occipital • Temporal
Cerebrum • Landmarks • Longitudinal fissure (separates the 2 hemispheres) • Central Sulcus (separates the frontal from parietal lobes) • Lateral Sulcus (separates the frontal from temporal) • Parieto-occipital sulcus (separates the parietal from the occipital) • White Matter • Dense region of axons
Cerebrum • Motor and Sensory Areas • Frontal Lobe = Voluntary control of skeletal muscles • Parietal Lobe = conscious perception of touch, pressure, vibration, pain, temperature, and taste • Occipital Lobe = conscious perception of visual stimuli • Temporal Lobe = conscious perception of auditory and olfactory stimuli, speech • All Lobes = Integration and processing of sensory data and motor activities
Cerebellum • 2nd Largest portion of the brain • 2 hemispheres • 2 Primary Functions • Adjusting Postural muscles of the body • Programming and fine-tuning movements
Other Major Regions of the Brain • Diencephalon: • Thalamus: relay and processing centers for sensory information • Hypothalamus: emotions, autonomic function, hormone production, body temp regulation
Other Major Regions of the Brain • Brain Stem :link between cerebrum and brain stem • Mesencephalon: aka “midbrain”; visual and auditory information • Pons: sleep & respiration • Medulla Oblongata: regulate heart rate, blood pressure, digestion
Ventricles of the Brain • Chambers filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) • Lateral Ventricles (2 in each hemisphere of cerebrum) • Third Ventricle • Interventricular Foramen (connection between the lateral ventricles and third ventricle) • Cerebral Aqueduct • (connection between the third ventricle and fourth ventricle) • Fourth Ventricle • Narrows and opens into the spinal cord
Protection and Support • Protected by • Bones of cranium: mechanical protection (car) • Cranial Meninges: anchor (seat belt) • Dura Mater: outer layer • Arachnoid: middle layer • Pia Mater: surface of brain • Cerebrospinal Fluid: cushions against shocks/jolts (air bag)
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) • Function: • Cushion • Support • Transport nutrients/chemical messengers/waste products • Formation: • Choroid plexus (in all ventricles): specialized cells that produce CSF
Blood Supply to the Brain • Brain requires a tremendous amount of blood • Receives 15-20% of blood pumped by heart • Interruption unconsciousness/irreversible brain damage • Dependent on constant supply of oxygen & glucose • Receives blood through arteries
Hydrocephalus • Condition with infants • Prior to fusion of cranial bones • Excess CSF (due to blockage or constriction of the meninges)causes the skull to enlarge • Infants suffer some degree of mental retardation
Cranial Nerves • Part of the PNS • Connected to the brain and branch out • 12 of them • Attaches the brain near a sensory or motor neuron • 2 of each
Cranial Nerves • Olfactory Nerves smell • Optic Nerves Vision • Oculomotor Nerves Eye Movements • Trochlear Nerves Eye movements • Trigeminal Nerves Sensory/Motor to face • Abducens Nerves Motor eye movements • Facial Nerves Sensory/Motor to face • Vestibulocochlear Nerves balance/equilibrium and hearing • Glossopharyngeal Nerves Sensory/Motor to head and neck • Vagus Nerves Sensory/Motor to thorax and abdomen • Accessory Nerves Motor to muscles of neck and upper back • Hypoglossal Nerves Motor for tongue movements
“Oh, once one takes the anatomy final, very good vacations are heavenly”
Conscious/Unconscious • Conscious = state of awareness of external stimuli • Unconscious = number of conditions, deep, unresponsive state drifting into sleep
Levels of Sleep • 2 levels, patterns of brain activity • Slow wave sleep • Deep sleep/non-REM sleep • Entire body relaxed • Cerebral cortex activity at minimum • Heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, energy utilization decline by 30% • Rapid Eye Movement (REM sleep) • Active dreaming • Changes in blood pressure/respiratory rate • Muscle tone decreases • Neurons controlling eye muscles stop regulation = eyes move rapidly as dream events unfold
Sleeping Cycles • REM and Deep sleep alternate throughout the night • Starts with Deep sleep = 1.5 hours • REM last on average 5 minutes • Determined by an EEG • Electroencephalogram: graphic record of the electrical activities of the brain
Alzheimer’s Disease • Loss of cerebral functions • Symptoms appear around 50-60 years old • Can affect younger individuals but is rare • Currently affects 2 million ppl in USA • 100,000 deaths each year • Chromosome 14, 19, and 21 • Majority of Downs Syndrome develop it (21)