Tree of Life
480 likes | 867 Vues
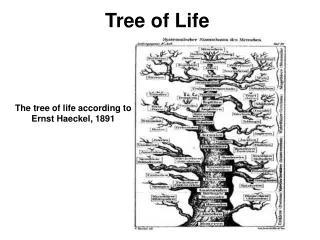
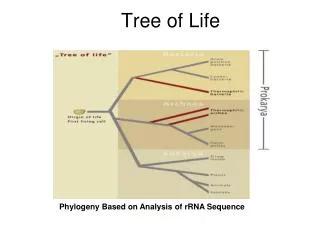
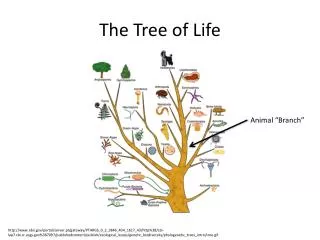
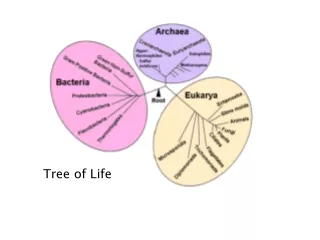
Tree of Life. old view – humans are best. modern view – all life equal. Modern Taxonomy. Differences in an RNA subunit indicate 3 major taxa of life on Earth. All Life on Earth. RNA subunit. Domains. Archaea. Bacteria. Eukarya. (ancient bacteria). (true bacteria). (eukaryotes).

Tree of Life
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tree of Life old view – humans are best modern view – all life equal
Modern Taxonomy Differences in an RNA subunit indicate 3 major taxa of life on Earth. All Life on Earth RNA subunit Domains Archaea Bacteria Eukarya (ancient bacteria) (true bacteria) (eukaryotes)
Domain Archaea Domain Archaea has 1 Kingdom Archaea Archaebacteria
Domain Archaea KingdomArchaebacteria Characteristics prokaryotic unicellular autotrophic or heterotrophic cell wall no peptidoglycan lives in extreme environments
Domain Archaea KingdomArchaebacteria Prokaryotic – no membrane bound organelles
Domain Archaea KingdomArchaebacteria Unicellular – one cell
Domain Archaea KingdomArchaebacteria autotrophic or heterotrophic autotrophic (make their own food) heterotrophic
Domain Archaea KingdomArchaebacteria Cell Wall – structure around the cell membrane for support
Domain Archaea KingdomArchaebacteria No Peptidoglycan – other bacteria have it in the cell wall Archaebacteria other bacteria
Domain Archaea KingdomArchaebacteria Archaebacteria live in extreme environments. some can live in a geyser (hot springs) some can live in a volcanic vent
Domain Archaea KingdomArchaebacteria Examples methanogen
Domain Bacteria Domain Bacteria has 1 Kingdom Bacteria Eubacteria (true bacteria)
Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Characteristics prokaryotic unicellular autotrophic or heterotrophic cell wall peptidoglycan common bacteria that live around us
Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Prokaryotic – no membrane bound organelles
Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Unicellular – one cell
Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria autotrophic or heterotrophic autotrophic heterotrophic
Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Cell Wall – structure around the cell membrane for support
Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Peptidoglycan found in the cell wall Archaebacteria Eubacteria
Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria They are the common bacteria – many cause disease. Lyme Disease E. coli – food poisoning Legionnaires Disease Pneumonia bacteria bacterium with flagella
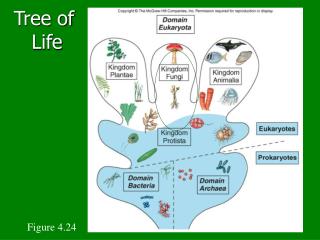
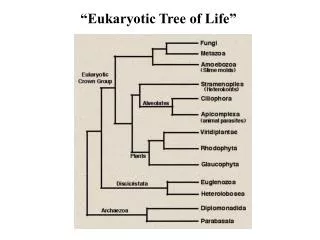
Domain Eukarya Domain Eukarya has 4 Kingdoms Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista Characteristics eukaryotic unicellular (usually) some plant-like - photosynthetic some animal-like - heterotrophic some fungus-like – decomposers some have cell walls with cellulose
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista eukaryotic – membrane bound organelles
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista Unicellular – one cell
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista some are plant-like - photosynthetic Two species of algae (protists).
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista some are animal-like - heterotrophic
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista some are fungus-like - decomposers
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista Other Examples Volvox (green algae) Diatoms Paramecium
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi Characteristics eukaryotic multicellular (usually) heterotrophic (decomposers) cell walls with chitin
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi eukaryotic – membrane bound organelles
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi multicellular – many cells (billions/trillions)
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi heterotrophic - decomposers
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi cell walls with chitin
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi Examples athletes foot bracket fungus morel – edible bread molds yeast mushroom – poisonous
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae Characteristics eukaryotic multicellular photosynthetic cell walls with cellulose
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae eukaryotic – membrane bound organelles
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae multicellular – many cells (billions/trillions)
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae photosynthetic – can make its own food
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae cell walls contain cellulose cellulose formula cellulose fibers
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae Examples flowering trees conifers (cones) flowers moss fern
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Characteristics eukaryotic multicellular heterotrophs (consumers) no cell walls mobile (motile)
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia eukaryotic – membrane bound organelles
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia multicellular – many cells (billions/trillions) muscle cells
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia heterotrophs - consumers
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia no cell walls
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia motile – at least part of their lives
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Examples