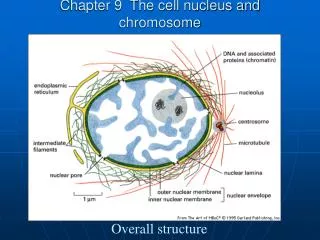
Chapter 6: Chromosome Mutations
140 likes | 441 Vues
Chapter 6: Chromosome Mutations. *Chromosome mutations/aberrations. Variation in chromosome number: *aneuploidy *euploidy *polyploidy. Nondisjunction. Homologous chromosomes: during anaphase I. Sister chromatids: during anaphase II. Monosomy.

Chapter 6: Chromosome Mutations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 6: Chromosome Mutations *Chromosome mutations/aberrations Variation in chromosome number: *aneuploidy *euploidy *polyploidy
Nondisjunction Homologous chromosomes: during anaphase I Sister chromatids: during anaphase II
Monosomy *Condition in which one member of a chromosome pair is missing (2n-1) In Drosophila: Haplo-IV are monosomic for chromosome 4 *develop more slowly, reduced size, impaired viability In Plants: Maize, tobacco, evening primrose, Jimson weed *Segmental deletions *Cri-du-chat (46,5p-)
Trisomy *Condition in which one chromosome is present in three copies (2n+1) In Plants: Jimson weed, rice In Drosophila and humans: Has severe effects, usually lethal Exceptions: Patau syndrome, 47,13+ Edwards syndrome, 47,18+
Polyploidy 1) Addition of one or more sets of chromosomes (replication) 2) Combination of chromosome sets from different species
Arise in several ways: *failure of all chromosomes to segregate during meiosis *two sperm may fertilize an ovum *experimentation Polyploidy Autopolyploidy The benefits of autopolyploid breeding: increased size of plant organs- roots, leaves, flowers fruits, seeds
Polyploidy Allopolyploidy
Variations in Chromosome Structure Deletions
Crossover: A A A A A A A B B B B B B B C C C C C C C D D D D D D D A B C D A B C D A B C D A B C D A B C D Variations in Chromosome Structure Duplications Due to unequal crossing over:
Variations in Chromosome Structure Inversions *Paracentric *Pericentric
Variations in Chromosome Structure Translocation
Variations in Chromosome Structure Translocation – unbalanced gametes are produced