-Types of Solutions -Facilitated Diffusion -Active Transport
340 likes | 579 Vues
-Types of Solutions -Facilitated Diffusion -Active Transport. Bellwork. What is diffusion? What is osmosis? Draw a picture of the same concentration of solutes inside a cell as outside a cell. Draw a hyper person. Have data out and ready to hand in. Dialysis Tubing.

-Types of Solutions -Facilitated Diffusion -Active Transport
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Bellwork • What is diffusion? • What is osmosis? • Draw a picture of the same concentration of solutes inside a cell as outside a cell. • Draw a hyper person. Have data out and ready to hand in
Dialysis Tubing • Is also IMPERMEABLE to sucrose… • Which is good, because I made a bunch of sucrose solutions of different concentrations, and I can’t remember which is which.
Dialysis Lab – Your Job • Objective: To determine which of the unknown solutions is High, Medium and Low concentration. • Purpose: To observe the process of osmosis first hand and to use this process to understand how dialysis works.
Materials • 3 Unknown colored solutions (High, Med and Low Concentration) • Water (150 mL) • 3 beakers* • 3 pieces of dialysis tubing* • 3 pipettes • Scissors • Scale • Paper towel • PROCEDURES: Watch demo, and write down procedures
Lab Title: Osmosis Lab (+ catchy title) • Problem/Question: Does ______________ of _________ in the bag affect the final ________ of the bag in ___ after in soaks in water. • Hypoth: • if _________________ (color solution) has (highest/lowest solute concentration) relative to the • Then _________________ • As measured by __________
Data table: Mass of dialysis tubes in grams Diagram: Draw all 3 set ups at the start of the experiment and 15 minutes later. -Include particulate drawings showing H20, and sucrose molecules. -Label the solute and the solvent. -Use arrows to show the flow of water
Materials: • Procedures: • Data Table: • Qual. Observations • Graph: line/bar • Conclusion
Know Your Prefixes!!! • Iso – same • Hypo – Low • Hyper – High • Tonic – Liquid/Solution
Hypertonic • Hyper= more/too much • Higher concentration solution outside the cell
Isotonic • Iso= same • Same concentration outside the cell as inside
Hypotonic • Hypo= less/too little • Lower concentration solution outside the cell
Passive Transport • Oxygen and Carbon dioxide enter and leave the cell through simple diffusion
Passive Transport • Small unpolarized (not ions) molecules can pass through the cell membrane without a protein channel.
Slate Practice • Lets revisit our salt water example • According to simple diffusion, draw what will happen here.
Slate Practice • The solute will spread out until it is evenly dispersed.
How does this work in cells? • Draw what happens to a cell with lots of solute in it, dropped in a beaker of pure H2O? Remember that the cell membrane is permeable to water but not solutes.
How does this work in cells? • Water follows solute into the cell… and the cell swells up.
How does this work in cells? • If it swells up too much, the cell can burst if the membrane gets pulled apart.
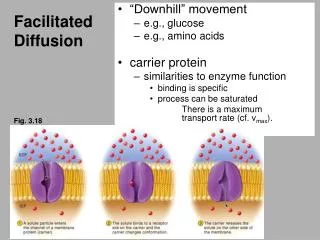
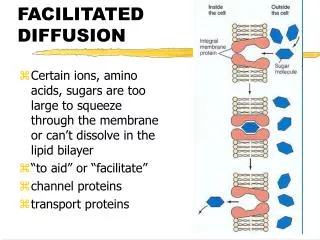
FACILITATED DIFFUSION • (another easy way – NO energy required!) • molecules Glucose, sodium ions and chloride ionsneed help (facilitated) getting across membrane • Carrier proteins help
Active Transport • Energy (ATP) required for movement. • Solutes are movedAGAINST the concentration gradient. (from low to high conc.)
Notes Check • Look back at your notes for Passive and Active Transport. • List two differences between passive transport and active transport. • Name one thing they have in common!
Active vs. Passive Transport • Differences • Active Uses ATP- This is the energy source for the cell. • Active goes against the gradient • Similar • Both have carrier proteins • Both move molecules that cannot go through the membrane on their own
How do cells move really large molecules in and out of the cell? • Endocytosis- cell takes in substances • Exocytosis- cell releases substances (out) • ACTIVE TRANSPORT – requires ATP (energy)
Endocytosis • A portion of the cell membrane surrounds the desired molecule outside the cell. • The cell membrane rejoins pinching off a sac-like organelle called a vesicle. • There are 2 types of endocytosis: phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
Exocytosis • The reverse of endocytosis • Wastes and cell products are packaged by the golgi body in sacs called vesicles. • These vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and the materials are secreted out of the cell.
Cellular Transport Requires ______
Cellular Transport Transport ATP Requires ______ Moves with gradient Moves against gradient PASSIVE ACTIVE Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion Proteins and ATP Endocytosis Exocytosis Osmosis Glucose transport Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide Na+/K+ Pump Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic Passive Transport: Diffusion: Osmosis: Hypertonic solution: Hypotonic solution: Isotonic solution: Active Transport: Na+/K+ Pump: Facilitated diffusion: Glucose transport:
Your Crazy Study Page For Mon’ Test Solution: Solute-particle Solvent-liquid Don’t forget: Draw a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and carbohydrates (& their functions) Passive vs. Active Diffusion Osmosis ENDO EXO
Closure 1. What is the difference between active and passive transport? 2. LIST 2 kinds of passive transport. 3. With a concentration gradient, molecules move from areas of ____ concentration to areas of ____ conc. 4. During osmosis, if there is more salt inside the cell than outside, which way would water move?














![No energy is used [High] [Low] (it’s the natural flow)](https://cdn1.slideserve.com/2802328/no-energy-is-used-high-low-it-s-the-natural-flow-this-means-it-goes-down-a-concentration-gradient-dt.jpg)