Conversion Factors and Unit Cancellation in Math Practice
490 likes | 514 Vues
Learn about conversion factors and unit cancellation in math with examples covering metric and non-metric units. Practice solving problems using the factor label method.

Conversion Factors and Unit Cancellation in Math Practice
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A physical quantity must include: Number + Unit
Calculation Corner: Unit Conversion 1 foot = 12 inches
Calculation Corner: Unit Conversion 1 foot = 12 inches 1 foot = 1 12 inches
Calculation Corner: Unit Conversion 1 foot = 12 inches 1 foot = 1 12 inches 12 inches = 1 1 foot
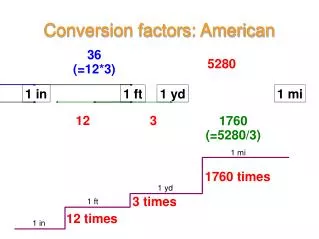
Calculation Corner: Unit Conversion 1 foot 12 inches 12 inches 1 foot “Conversion factors”
Calculation Corner: Unit Conversion 1 foot 12 inches 12 inches 1 foot “Conversion factors” 12 inches ( ) ( ) = 36 inches 3 feet 1 foot
Dimensional Analysis • A mathematical way to convert one unit to another. This works for metric units and non-metric (English) units. • This works by taking the unit you are given and multiplying it by a conversion factor. CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
Example 1: Convert 3m to cm For meters to cancel out, meters in the conversion factor must be on the opposite side of the fraction (fence). 3m Given Conversion Factor Multiply every number on top of the fence and divide by the bottom. 100 cm 1m CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
Example 2: Convert 1516 g to kg 1516 g conversion factor 1 kg 1000 g CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
Whiteboard Problem 1 • Convert 1200 cm to m. CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
Example 4: Convert 7200mm to km 7200 mm = .0072 km 1 km 1 cm 10 mm 100,000 cm CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
Non-Metric (English) Unit Conversions • Common Conversion Factors • 5280 ft = 1 mile • 12 in = 1 ft • 1 mile = 1600 m • 1 in = 2.54 cm • 3 ft = 1 yard English to Metric conversion factors CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
Example 4: Convert 2 miles to ft 2 mi 5280 ft 1 mi CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
Whiteboard Problem 4 • Convert 5 ft to cm CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
Example 5: Convert 5 ft to cm 5 ft 2.54 cm 12 in 1 in 1 ft CLE.3231.Math.1 Graph relationships and functions between manipulated (independent) variables and responding (dependent) variables.CLE.3231.Math.2 Solve for variables in an algebraic formula.
______ 100 cm 100 cm 1 m ______ 1 m 1 m 100 cm ______ 132 cm ( ) equality: 1 m = 100 cm (or 0.01 m = 1 cm) How many cm are in 1.32 meters? applicable conversion factors: or X cm = 1.32 m = We use the idea of unit cancellation to decide upon which one of the two conversion factors we choose.
0.0872 m 100 cm ______ 1 m ______ 1 m 100 cm ______ ( ) 1 m 100 cm equality: 1 m = 100 cm How many meters is 8.72 cm? applicable conversion factors: or X m = 8.72 cm = Again, the units must cancel.
1 ft ______ 1 ft 12 in 12 in ( ) ______ 12 in ____ 1 ft 3.28 ft equality: 1 ft = 12 in How many feet is 39.37 inches? applicable conversion factors: or X ft = 39.37 in = Again, the units must cancel.
1 km 1,000 m ( ) ______ ( ) ____ 1 m 10 dm 1.5 km How many kilometers is 15,000 decimeters? X km = 15,000 dm =
( ) _____ 60 min 1 h 378,432 s ( ) ( ) ____ 60 s 3.78 x 105 s ____ 24 h 1 min 1 d How many seconds is 4.38 days? X s = 4.38 d = If we are accounting for significant figures, we would change this to…
The steps to follow Now we are ready to solve problems using the factor label method. The steps involved are: • Write down the desired quantity/units • Equate the desired quantity to given quantity • Determine what conversion factors you can use (both universal and question specific) • Multiply given quantity by the appropriate conversion factors to eliminate units you don’t want and leave units you do want • Complete the math
Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km First write down the desired quantity
Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47 mi Next, equate desired quantity to the given quantity
Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47 mi Now we have to choose a conversion factor
1 km 0.621 mi 0.621 mi 1 km Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47 mi What conversion factors are possible?
1 km 0.621 mi 0.621 mi 1 km Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47 mi Pick the one that will allow you to cancel out miles
1 km 0.621 mi 0.621 mi 1 km Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47mi Pick the one that will allow you to cancel out miles
1 km 0.621 mi 0.621 mi 1 km Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47mi Multiply given quantity by chosen conversion factor
x 1 km 0.621mi Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47mi Multiply given quantity by chosen conversion factor
x 1 km 0.621mi Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47mi Cross out common factors
x 1 km 0.621 Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47 Cross out common factors
x 1 km 0.621 Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47 Are the units now correct?
x 1 km 0.621 Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47 Yes. Both sides have km as units.
x 1km 0.621 Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) # km = 47 Yes. Both sides have km as units. #km
x 1 km 0.621 Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) = 75.7 km # km = 47 Now finish the math.
x 1 km 0.621 Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0.621 miles) = 75.7 km # km = 47 The final answer is 75.7 km
Summary The previous problem was not that hard In other words, you probably could have done it faster using a different method However, for harder problems the factor label method is easiest
L W Example Problem Measured dimensions of a rectangle: length (L) = 9.70 cm width (W) = 4.25 cm Find area of rectangle. A = L . W = (9.70 cm)(4.25 cm) = 41.2 cm 2 . cm
( ( ( ( ) ) ) ) ______ ______ ______ ______ 1 m 1 m 1 m 1 m 100 cm 100 cm 100 cm 100 cm 2 X m2 = 41.2 cm2 = 0.412 m2 WRONG! Convert 41.2 cm2 to m2. = 0.412 cm.m Recall that… 41.2 cm2 = 41.2 cm.cm X m2 = 41.2 cm.cm = 0.00412 m2 X m2 = 41.2 cm2 = 0.00412 m2
10 mm 10 mm 10 mm 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm ( ( ( ) ) ) _____ _____ _____ 2 Convert 41.2 cm2 to mm2. Recall that… 41.2 cm2 = 41.2 cm.cm X mm2 = 41.2 cm.cm = 4,120 mm2 X mm2 = 41.2 cm2 = 4,120 mm2
Length = 15.2 cm Width = 3.7 cm Height = 8.6 cm Measured dimensions of a rectangular solid: H W Find volume of solid. L V = L . W . H = (15.2 cm)(3.7 cm)(8.6 cm) = 480 cm 3
( ( ( ( ) ) ) ) 1 m 1 m 1 m 1 m _____ _____ _____ _____ 100 cm 100 cm 100 cm 100 cm ( ) 3 1 m _________ 3 1000000 cm cm.cm.cm 2 3 X m3 = 480 cm Convert to m3. = or 3 X m3 = 480 cm3 = 0.000480 m3 or 4.80 x 10-4 m3 X m3 = 480 cm3 =
Convert to m3... Measured dimensions of a rectangular solid: Length = 15.2 cm Width = 3.7 cm Height = 8.6 cm 0.152 m 0.037 m 0.086 m H W Find volume of solid. L V = L . W . H = (0.152 m)(0.037 m)(0.086 m) m = 0.000480 3
By what factor do mm and cm differ? 10 By what factor do mm2 and cm2 differ? 100 By what factor do mm3 and cm3 differ? 1,000 1 cm = 10 mm 1 cm2 = 100 mm2 (1 cm)2 = (10 mm)2 1 cm3 = 1000 mm3 (1 cm)3 = (10 mm)3