Global Warming
100 likes | 243 Vues
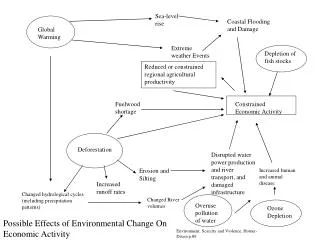
Global warming is primarily caused by the greenhouse effect, where gases like CO2, CH4, and N2O trap heat from the sun. Since the Industrial Revolution, levels of these gases have significantly increased, leading to climate change, which has manifested in rising global temperatures, melting ice, and rising sea levels. Average surface temperatures have risen by 0.5-1.0% since the late 19th century, with the 20th century witnessing the warmest years on record. Future predictions indicate significant temperature increases, higher precipitation, and coastal flooding among various environmental impacts.

Global Warming
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Global Warming by Alex Kiss
Natural Warmth • The Earth’s surface is heated primarily by sunlight • It radiates long wavelength photons of Infrared (IR) • Certain “greenhouse” gases trap some escaping radiation, exciting them to vibrate and rotate, effectively heating the air. Examples: CO2, CH4, N2O, O3, H2O
Consequences • Without this natural “greenhouse effect” acting as a blanket, temperatures near the surface would be around -18°C (0°F) • Instead the average is 15°C (59°F), which is warm enough to assure a liquid ocean and conditions suitable for life
Pollution • Since the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric concentrations of naturally occurring greenhouse gases: • Carbon dioxide has increased by 30% • Methane has more than doubled • Nitrous oxide has risen by more than 15% • Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), are unnatural and highly effective greenhouse gases generated in a variety of industrial processes.
Where Do They Come From? • Combustion of fossil fuels to run cars and trucks, heat homes and businesses, and power factories contributes to: • 98% of U.S. carbon dioxide emissions • 24% of methane emissions • 18% of nitrous oxide emissions • Methane is emitted during the production and transport of coal, natural gas, and oil, from the decomposition of organic wastes in landfills, and from the raising of livestock. • Nitrous oxide is emitted during industrial and agricultural activities as well as the combustion of solid wastes and fossil fuels.
Climate Change • Average global surface temperature has increased 0.5-1.0% since the end of the 19th century. • The 20th century’s 10 warmest years occurred in the last 15 years of the century, 1998 being the warmest. • Snow cover in the northern hemisphere and floating ice in the Arctic Ocean have decreased. • Globally, sea level has risen 4-8 inches over the last century
Future Predictions • Increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases are likely to accelerate the rate of climate change. • Scientists believe average global surface temperatures could rise by 2.2-10°F in the next century. • Evaporation will increase in the next century, increasing average global precipitation. Also, Intense rainstorms are likely to become more frequent. • Sea level is likely to rise two feet along most of the U.S coast.