Migration Patterns
140 likes | 691 Vues
Migration Patterns. AP Human Geography. Review. International vs. Internal migration Inter-regional vs. Intra-regional migration. Net Migration. Net out-migration. Net in-migration. Places where more people migrate from (LDC’s) Asia, Africa, Latin America.

Migration Patterns
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Migration Patterns AP Human Geography
Review • International vs. Internal migration • Inter-regional vs. Intra-regional migration
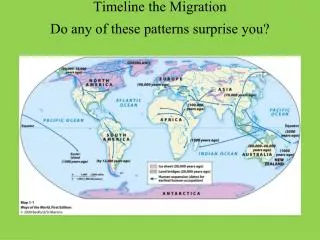
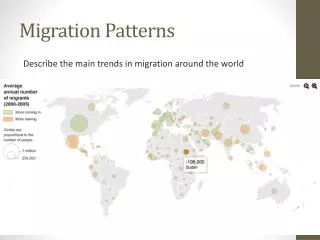
Net Migration Net out-migration Net in-migration • Places where more people migrate from (LDC’s) • Asia, Africa, Latin America • Places that more people migrate to (MDC’s) • N. America, Europe, Oceania
Historical Immigration to the U.S. • Era #1: Colonial Period (1600’s-1840) • Who: European settlers (English), African slaves • Era #2: Mid 1800’s (19th century) to early 1900’s. • Who: Europeans, specifically Germans, Italians, Irish, English, Eastern Europeans • Era #3: Post WWII (1950’s- present) • Who: Latin Americans (Mexico), Asians (China, India) • Reasons remain the same over time… • Poor conditions at home (push) • Economic opportunity in U.S. (pull)
Other issues • Unauthorized/ undocumented/ “illegal” immigration • 12 million + in the U.S. • 59% from Mexico • Controversy • May work jobs most refuse • Path to citizenship • Build a wall?
Chain Migration • Migration of people to a specific location because other family members/ friends/ nationals have previously migrated • May result in enclaves in urban areas • Polish in Chicago • Cubans in Miami • Puerto Ricans in NYC • Chinese in San Francisco
Inter-regional Migration in the U.S. • East coast to interior (early 1800’s) • Improved transportation • Cheap land • East coast to California (1840’s) • Gold • Settlement of the Great Plains (1850’s) • Advances in agriculture • Railroads • South (1980’s- present) • Jobs • Climate (Sunbelt)
Intra-regional migration • Rural to Urban (urbanization) • Has already occurred in MDC’s • Rapidly occurring in LDC’s • Jobs (shift from AG to IND, SERVICE) • Urban to Suburban • Occurring in MDC’s • Lifestyle choice (space, school, safety) • Urban to Rural • Counter urbanization • Lifestyle (peaceful, relaxed) • Technology makes world smaller • MDC’s -> Urban to Suburban • LDC’s -> Rural to Urban