Warm UP!
690 likes | 880 Vues
Warm UP! . Take an index card from the front bookcase. Tell me one challenge you had with the test. Tell me what might have helped you be better prepared for the test. What is the difference?. Between this question and. This one?. Which one of these is a characteristic of behaviorism?

Warm UP!
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Warm UP! • Take an index card from the front bookcase. • Tell me one challenge you had with the test. • Tell me what might have helped you be better prepared for the test.
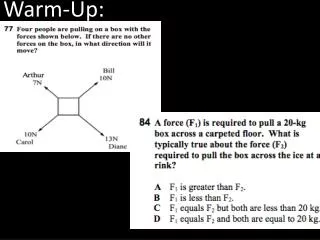
What is the difference? Between this question and This one? Which one of these is a characteristic of behaviorism? Punishments Evolution Medicinal treatments The unconscious mind • The quotation below is consistent with the views of which of the following schools of psychology? • “Give me a dozen healthy infants, well formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I’ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to be any type of specialist I might select- doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief and yes, even beggar-man and theif….” • Existentialism • Structuralism • Humanism • Gestalt • Behaviorism
Lets look at the test • Look over your test. • Pick two questions you would like to look at more closely. • Remediation- Tell me… What you needed to know to answer it and the page # in the book where you can find that info.
Psychological Research Methods Excavating Human Behaviors Stolen from www.appsychology.com Made my Mr. Kaplan, majorly altered by Mr. C
Research Methods Questions What is a theory? A hypothesis? • What are 3 measurements of central tendency? • What is standard deviation? • What are types of descriptive research? • What is correlational research? 22 note • What is a correlation coefficient? cards • What is experimental research? • What is an operational definition? • What are confounding (extraneous) variables? • What is validity? Reliability? • What is the placebo effect? • What is independent variable? Dependent variable? • What is a double-blind study? • What is bias? Hindsight bias? Experimenter bias? • What is random sampling? • What is a correlation coefficient? • Experimental group? Control group? • What is a case study? • What is a longitudinal study? Cross-sectional study? • What is an Institutional Review Board? • What are the APA’s ethical guidelines for animal research? • What are the APA’s ethical guidelines for human research?
Why do we need science? Science is usually the best thing we have. Without science, we’d still be drilling holes in people’s heads to get the demons out. We’d hold on to our beliefs even if they were wrong.
What is Experimental Research? • Explores cause and effect relationships. • Has control and experimental groups • Laboratory experiments are good at controlling variables. Eating too many bananas causes Constipation
Experimental Vocabulary (separate line for each) • Independent Variable: factor that is manipulated (the medicine) (What you are doing to the subject) • Dependent Variable: factor that is measured (anxiety) • Extraneous or Confounding Variables: factors that affect DV, that are not IV. (factors that screw up the experiment!) (other meds?, other sources of stress) • Experimental Group: Group exposed to IV (those who get the pill) • Control Group: Group not exposed to IV (Those who get the sugar pill) • Placebo: inert substance that is in place of IV in Control Group (The sugar pill)
Steps in Designing an Experiment • Hypothesis • Pick Population: Random Selection then Random Assignment. • Operationalize the Variables • Identify Independent and Dependent Variables. • Look for Extraneous Variables • Type of Experiment: Blind, Double Blind etc.. • Gather Data • Analyze Results • repeat
Let’s do an experiment. • Hypothesis: The red pill will reduce anxiety. • We operationalize the definition of anxiety to mean those whose doctors claim they suffer from anxiety. • We find 100 people who fit the operationalized definition
We randomly assign half the men to the experimental group and half the men to the control group. (Same with women). • I, the researcher, do not know which group will receive the medication and which will receive the placebo. That means this is a double-blind experiment. This will reduce experimenter bias.
The experimental group will receive the actual medication. The medication is called the independent variable. • The control group will receive a sugar pill (the placebo). • The research team will ask all participants to measure their level of anxiety on a scale from 1 to 10. Anxiety is the dependent variable (what is measured).
The control group will usually report a decrease in anxiety even though they received no medicine. This is called the placebo effect.
Now that the experiment phase is done, you must consider the confounding variables. This is the stuff that will screw up your experiment. Ex: what if the control group had a mean age much less than the experimental group? What if the 2 groups had a different percentage of women?
Our original hypothesis was: the red pill will reduce anxiety by 40%. • Results: The experimental group reported a mean of 10% reduction in anxiety versus a 5% reduction for the control group. • Theory: After several replications, the medicine has no significant effect on anxiety.
Reliability and validity? • A finding is reliable if it can be replicated. If subsequent studies show that the red pill reduces anxiety then the findings are reliable, thus supporting the hypothesis. • A study is valid if it measures what it is supposed to measure. If our experiment measured hypertension instead of anxiety, then the test in invalid, even if it is reliable.
Is the TAKS valid and reliable? • If a similar TAKS test given to a group of 8th graders produces the same scores, then it’s reliable. • If students fail the 8th grade math TAKS because the wording is on the 10th grade level, then people might question the validity. A valid math test tests math, not reading level. Hmmmmm.
Warm up • Take out your test corrections and be ready to turn it in. • Take out your notes. We will be adding to them.
2. “Students will be able to read a statement printed in the Comic Sans font faster than the same statement written in the Lucida Calligraphy font.” The previous statement is a(n) a) hypothesis b) theory c) replication d) operational definition
3. A theory is a) a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables b) a system of interrelated ideas used to explain a set of observations c) a statement of research results that have been proven to be correct d) a preliminary proposal that has yet to be tested
Descriptive Research What is going on in this picture? We cannot say exactly, but we can describe what we see. • Any research that observes and records. • Does not talk about relationships, it just describes. Thus we have…..
Types of Descriptive Research • The Case Study • The Survey • Naturalistic Observation • Cross-sectional study
The Case Study • Where one person (or situation) is observed in depth. What are the strengths and weaknesses of using a tragedy like the Columbine School Shootings as a case study?
Longitudinal studies • A subject is studied for a long long long time. • Twins separated at birth are surveyed at ages 5, 10, 15, 20, 30 years.
Cross-sectional study • Different groups of people are compared and contrasted. • Blacks vs whites on attitudes towards psychotherapy • Poor vs. middle-class on extrovertedness
The Survey Method • Used in both descriptional and correlational research. • Use Interview, mail, phone, internet etc… • The Good- cheap, anonymous, diverse population, and easy to get random sampling (a sampling that represents your population you want to study).
Random Sampling sample census
Why do we sample? • One reason is the False Consensus Effect: the tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors.
Survey Method: The Bad • Low Response Rate • People Lie or just misinterpret themselves. • Wording Effects • Social desirability bias. How accurate would a survey be about the frequency of diarrhea? Homosexuality? Infidelity?
Naturalistic Observation • Observing and recording behavior in natural environment. • No control- just an observer. What are the benefits and detriments of Naturalistic Observation?
Correlational Research • Detects how well one variable predicts, not causes another variable. • Does NOT say that one variable causes another. There is a positive correlation between ice cream and murder rates. Does that mean that ice cream causes murder?
Correlation • Studies show that there is a strong correlation between how many books are present in a child’s home and college completion rate. • Do the books cause a person to complete college?
Low Self-esteem Depression Depression Low Self-esteem Low Self-esteem Depression Distressing events or biological predisposition Correlation and Causation • Three possible cause-effect relations
Measured using a correlation coefficient. • A statistical measure of the extent to which two factors relate to one another
Which correlation coefficient has the strongest relationship? The weakest? • A. .79 • B. -.88 • C. .09 • D. 3.6 • E. -.05 B has the strongest. E has the weakest D. is invalid
Analyze Results • Use measures of central tendency (mean, median and mode). • Use measures of variation (range and standard deviation).
What is bias? • Attitudes and beliefs that can skew results.
Hindsight Bias • The tendency to believe, after learning the outcome, that you knew it all along. Many believe that Obama was better for the country. Would we feel different if McCain won?
Experimenter bias • The people running the experiment think they know the truth already. • Ex: The tobacco industry funds an experiment. The results: cigarette smoke has a neutral effect on asthma. • Ex: A doctor wants to cure AIDS, so she unconsciously biases the experiment by giving the sickest patients the placebo.
2 types of statistics • Descriptive statistics are used to reveal patterns through the analysis of numeric data (describe what is there) (Ex: 25% of Republicans pray before sex.) • Inferential statistics make an inference about the population from a sample. Ex: predicting how people will vote based on polling a 1000 people.
What is an institutional review board? • All academic research must be approved by an institutional review board at a local university. They review it for ethics and procedural errors.
Ethical guidelines for animal research? • 1. must have clear scientific purpose • 2. humane care for animals • 3. animals must be trapped or bought legally • 4. suffering must be minimized.
Guidelines for human research? • Coercion – Participation must be voluntary • Informed consent – They must know that they are involved in research and give their consent. If they are deceived, what they DID consent to must be similar to actual study. Minimize trauma. • Anonymity/confidentiality/privacy • Risk – mental and physical safety • Debriefing procedure – afterward, participants must be told of purpose of study - need ability to contact researcher about results.
Correlation O Ring failure • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j4JOjcDFtBE • http://www.apa.org/education/k12/challenger.aspx
M&M Experiment • According to the Mars company, each package of Milk Chocolate M&M’s should contain 24% blue, 14% brown, 16% green, 20% orange, 13% red, and 14% yellow M&M’s. • Lets test it!!
Chapter 2 Quiz The Research Enterprise in Psychology