Understanding Acids, Bases, and the pH Scale: Properties and Applications
70 likes | 200 Vues
Acids and bases are essential concepts in chemistry, classified by their pH levels. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, measuring acidity or basicity. Acids, with pH 0-6.9, have hydrogen ions (H+) and exhibit sour taste, react with metals, and turn indicators red. Examples include lemon juice and milk. Bases, with pH 7.1-14, contain hydroxide ions (OH-) and are bitter, slippery, and turn indicators blue, like bleach and antacids. Neutral substances have a pH of 7, while buffers help neutralize strong acids or bases, producing salts in the process.

Understanding Acids, Bases, and the pH Scale: Properties and Applications
E N D
Presentation Transcript
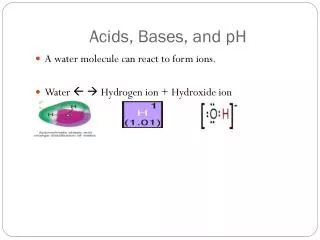
Ch. 8 Acids, Bases, and pH
pH Scale • Used to measure how acidic or basic a substance is • Ranges from 0-14
Acids • Have H+ (hydrion) ions • pH: 0-6.9 • Properties • Sour taste • React with metals • Turn indicator RED • Ex: lemon juice, milk
Bases • Have OH- (hydroxide) ions • pH: 7.1-14 • Properties • Bitter taste • Have a slippery feel (like when you get bleach or cleaners on your hands) • Turns indicator BLUE • Ex: bleach, antacid
Neutral • pH: 7 • Ex: PURE water (tap water, bottled water, etc. are not PURE because there are minerals added to them)
Buffers • A weak base or acid used to NEUTRALIZE a strong acid or base • Weak base neutralizes a strong acid • Weak acid neutralizes a strong base • Salts are produced when neutralization occurs • Ex: HCl + NaOHNaCl + H2O • Ex: using an antacid for heartburn • Heartburn – caused by stomach acid (STRONG ACID) entering the esophagus • Antacid – products like Tums and Rolaids (WEAK BASE)