Demand Analysis
190 likes | 396 Vues
Demand Analysis. Demand Elasticity Supply Equilibrium. Behind the Demand Curve: Theory of Consumer Choice. Balance preferences and spending power Weigh willingness to buy against ability to buy Match desire to buy and ability to buy. Utility Theory.

Demand Analysis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Demand Analysis • Demand • Elasticity • Supply • Equilibrium
Behind the Demand Curve: Theory of Consumer Choice • Balance preferences and spending power • Weigh willingness to buy against ability to buy • Match desire to buy and ability to buy
Utility Theory • Goal of maximizing utility s.t. an income constraint • U = U(X, Y) • s.t. M = pxX + PyY • Consumers can rank preferences • Consumers have income to spend • There are goods to buy
Consumer Equilibrium • Maximize utility s.t. income constraint • Given limited budget and positive prices, reach highest level of utility • Income and substitution effects • Equilibrium implies: MUx/MUy = px/py
Consumer Choice Using Lagrangians • Deriving the decision rule with mathematics
Basis for Demand • Direct demand • Derived demand
The Demand Function • Determinants of demand • Qd = Qd (Po|T, C, I, Pn, R, E )
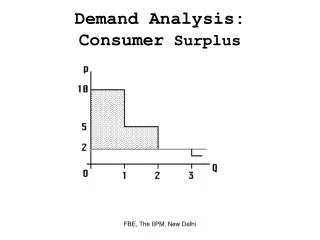
The Demand Curve • The amount of a good consumers are willing to buy at various prices • The maximum price consumers are willing to pay for a given amount of a good
The Concept of Elasticity • Defined • Formula • Point v. arc elasticity • The relationship between elasticity and slope
Nature of Elasticity • Perfectly elastic • Elastic • Unit elastic • Inelastic • Perfectly Inelastic
Issues in Elasticity • Elasticity-revenue relationship • Optimal pricing • Straight-line demand curves • MR = P(1 + 1/e)
Determinants of Price Elasticity • Substitutability • Complementary goods • Relative importance in budget • Time
Income Elasticity of Demand • Superior goods • Normal goods • Inferior goods • Giffen goods
Cross Elasticity of Demand • Substitutes • Complements
Basis for Supply • Supply decisions based on cost of production
Market Supply • Determinants of supply • Qs = Qs (Po|Pr, K, M)
The Supply Curve • The amount of a good suppliers are willing to provide at various prices • The minimum price suppliers are willing to accept to make a given amount of a good available
Market Equilibrium • Superimpose demand and supply • If Qs = Qd, no tendency to change
Applications • Excise tax • Quotas and tariffs • Agricultural policy